Principle 2
advertisement
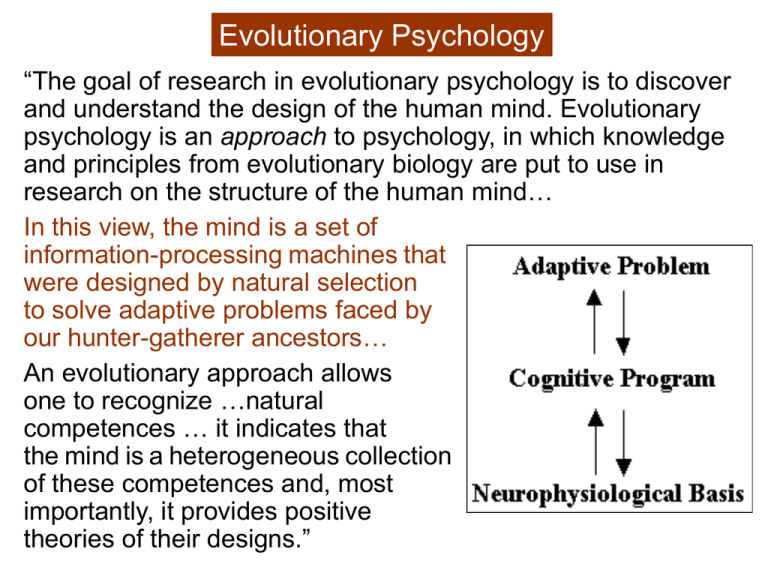
Evolutionary Psychology “The goal of research in evolutionary psychology is to discover and understand the design of the human mind. Evolutionary psychology is an approach to psychology, in which knowledge and principles from evolutionary biology are put to use in research on the structure of the human mind… In this view, the mind is a set of information-processing machines that were designed by natural selection to solve adaptive problems faced by our hunter-gatherer ancestors… An evolutionary approach allows one to recognize …natural competences … it indicates that the mind is a heterogeneous collection of these competences and, most importantly, it provides positive theories of their designs.” The Standard Social Science Model (SSSM) “Both before and after Darwin, a common view among philosophers and scientists has been that the human mind resembles a blank slate, virtually free of content until written on by the hand of experience … Over the years, the technological metaphor used to describe the structure of the human mind has been consistently updated, from blank slate to switchboard to general purpose computer, but the central tenet … has remained the same … [and] has become the reigning orthodoxy in mainstream anthropology, sociology, and most areas of psychology… According to this orthodoxy: all of the specific content of the human mind originally derives from the "outside" – from the environment and the social world – and the evolved architecture of the mind consists solely or predominantly of a small number of general purpose mechanisms that are content-independent, and which sail under names such as … 'learning,' 'intelligence,' 'imitation,‘ culture‘… SSSM versus EP SSSM: Same general-purpose mechanisms govern all psychological tasks (except basic perception, language), e.g., how one • learns to recognize emotional expressions • thinks about incest • acquires ideas and attitudes about friends and reciprocity Mechanisms of reasoning, learning, and memory operate uniformly – they are content-independent or domain-general. EP: All normal human minds reliably develop a collection of domain-specific reasoning and regulatory circuits. “These circuits organize the way we interpret our experiences, inject certain recurrent concepts and motivations into our mental life, and provide universal frames of meaning that allow us to understand the actions and intentions of others”. Five Principles Principle 1: The brain is a physical system. It functions as a computer. Its circuits are designed to generate behavior that is appropriate to your environmental circumstances. Principle 2: Our neural circuits were designed by natural selection to solve problems that our ancestors faced during our species' evolutionary history. “The reason we have one set of circuits rather than another is that the circuits that we have were better at solving problems that our ancestors faced during our species' evolutionary history than alternative circuits were”. For example, just as natural selection has shaped dung flies to approach dung, it has shaped us to avoid it. Five Principles Principle 2: Our neural circuits were designed by natural selection to solve problems that our ancestors faced during our species' evolutionary history. Designed to solve adaptive problems, i.e., problems • that cropped up again and again during the evolutionary history of a species • whose solution affected the reproduction of individual organisms “Obviously, we are able to solve problems that no huntergatherer ever had to solve – we can learn math, drive cars, use computers. Our ability to solve other kinds of problems is a side-effect or by-product of circuits that were designed to solve adaptive problems. For example, the fact that we can surf and skateboard are mere by-products of adaptations designed for balancing while walking on two legs”. Five Principles Principle 3: Consciousness is just the tip of the iceberg; most of what goes on in your mind is hidden from you. As a result, your conscious experience can mislead you into thinking that our circuitry is simpler that it really is. Most problems that you experience as easy to solve are very difficult to solve – they require very complicated neural circuitry. Principle 4: Different neural circuits are specialized for solving different adaptive problems. “A basic engineering principle is that the same machine is rarely capable of solving two different problems equally well. We have both screw drivers and saws because each solves a particular problem better than the other”. Five Principles Principle 5: Our modern skulls house a stone age mind. “Natural selection, the process that designed our brain, takes a long time to design a circuit of any complexity. The time it takes to build circuits that are suited to a given environment is so slow it is hard to even imagine – it's like a stone being sculpted by wind-blown sand. Even relatively simple changes can take tens of thousands of years. “ Actually evidence is accumulating in many areas that selection can occur quickly, at least sometimes. The Environment of Evolutionary Adaptedness (EEA): Hunter-gatherer (foraging) societies of the African savanna. Five Principles Principle 4: Different neural circuits are specialized for solving different adaptive problems. Five Principles T & C: Brains do not use the propositional calculus (or any other general algorithm) to solve (many) problems. Reasoning instincts: An example Wason Selection Task: Subject is asked to look for violations of a conditional rule of the form If P then Q. Rule: "If a Cambridge resident goes into Boston, then that person takes the subway.” Boston Arlington subway cab Each card represents one person. One side of a card tells where a person went, and the other side of the card tells how that person got there. Indicate only those card(s) you definitely need to turn over to see if any of these people violate this rule. Boston & cab cards – only ~25% of subjects get this right! Reasoning instincts: An example Wason Selection Task: Subject is asked to look for violations of a conditional rule of the form If P then Q. People who ordinarily cannot detect violations of if-then rules can do so easily and accurately when that violation represents cheating in a situation of social exchange/contract Rule: "If you are drinking alcohol then you must be 21" 17 21 Drinking Beer Drinking Coke Indicate only those card(s) you definitely need to turn over to see if any of these people violate this rule. 17 & drinking beer – most people get this right! Reasoning instincts: An example Wason Selection Task: Subject is asked to look for violations of a conditional rule of the form If P then Q. Rule: "If a card has an even number on one face, then its opposite face is red”. Which card(s) must be turned over to see if this rule has been violated. ‘8’ and brown cards – only ~25% of subjects get this right! Reasoning instincts: An example Wason Selection Task: Subject is asked to look for violations of a conditional rule of the form If P then Q. Which of the following cards do you need to turn over to either confirm or falsify the hypothesis that “if a card has an even number on one side, it has a vowel on the other?” 1 2 A B ‘2’ & ‘A’ cards – only ~25% of subjects get this right! Reasoning instincts: An example Social contract form again… Which of the following cards do you need to turn over to either confirm or falsify the hypothesis that If you charge a purchase on your credit card, you must pay the bill. Person charges purchase Person doesn’t charge Person pays bill Person doesn’t pay bill Most people get the right answer! Cheater Detection & Social Contracts • For altruism without kin selection to work, need reciprocity • Useful to have the payoffs delayed • I’ll do this for you now if you agree to do that for me (or my children) later • Don’t want to make such deals with cheaters, so its necessary to have a means of detecting cheaters • Conclusion: natural selection for a cheater detection module! General Processes vs. Modularity From Descartes on, strong emphasis on unity of mind • Flourens’ opposition to phrenology • Opposition to brain localization in 20th century: Lashley, Head et al • Behaviorists’ general learning principles But cognitive psychology has tended to emphasize the division of the mind into specific processors, responsible for different cognitive processes • Memory, language, object recognition, etc. • Strategies for dissociation designed to separate processing components functionally (and structurally in neuropsychology) Chomsky’s mental organs proposal “We may usefully think of the language faculty, the number faculty, and other ‘mental organs,’ as analogous to the heart or the visual system or the system of motor coordination and planning. . . . In short, there seems little reason to insist that the brain is unique in the biological world, in that it is unstructured and undifferentiated, developing on the basis of uniform principles of growth or learning—say those of some learning theory, or some yet-to-beconceived general purpose learning strategy—that are common to all domains” (1980, p. 3). Fodor’s Modularity of Mind Distinction between horizontal and vertical modules. Vertical modules: • domain-specific • mandatory in their operation • allow only limited central access to the computations of the modules • fast, • informationally encapsulated • have shallow outputs • associated with fixed neural architectures • exhibit characteristic and specific breakdown patterns • exhibit a characteristic pace and sequencing in their development Fodor’s Modularity of Mind informationally encapsulated Challenges to Fodorian Modularity Evidence for top-down (as opposed to bottom-up) processing Speech processing • Word recognition based on acoustic and phonetic information alone—syntax and semantics have no influence • Evidence from shadow speech—people restore the correct word despite distortions, which they do not do when the sound is presented in isolation • Controversial case: McGurk Effect McGurk Effect • Seeing someone say “ga” while hearing “ba” results in perception of intermediate sound. • Could be entirely within language module (motor theory of speech perception) • Massaro: rather invokes more general processing: integration of information and top-down as well as bottom-up processing McGurk Effect • Seeing someone say “ga” while hearing “ba” results in perception of intermediate sound. • Could be entirely within language module (motor theory of speech perception) • Massaro: rather invokes more general processing: integration of information and top-down as well as bottom-up processing http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G-lN8vWm3m0 Evolutionary Psychology: Modules all the way through “We have all these specialized neural circuits because the same mechanism is rarely capable of solving different adaptive problems. For example, we all have neural circuitry designed to choose nutritious food on the basis of taste and smell – circuitry that governs our food choice. But imagine a woman who used this same neural circuitry to choose a mate. She would choose a strange mate indeed (perhaps a huge chocolate bar?). To solve the adaptive problem of finding the right mate, our choices must be guided by qualitatively different standards than when choosing the right food, or the right habitat. Consequently, the brain must be composed of a large collection of circuits, with different circuits specialized for solving different problems. You can think of each of these specialized circuits as a minicomputer that is dedicated to solving one problem. Evolutionary Psychology: Modules all the way through “Such dedicated mini-computers are sometimes called modules. There is, then, a sense in which you can view the brain as a collection of dedicated mini-computers – a collection of modules. There must, of course, be circuits whose design is specialized for integrating the output of all these dedicated mini-computers to produce behavior. So, more precisely, one can view the brain as a collection of dedicated mini-computers whose operations are functionally integrated to produce behavior.” Cosmides & Tooby, Evolutionary Psychology: A Primer