DNA_Project - Berkeley Cosmology Group
advertisement
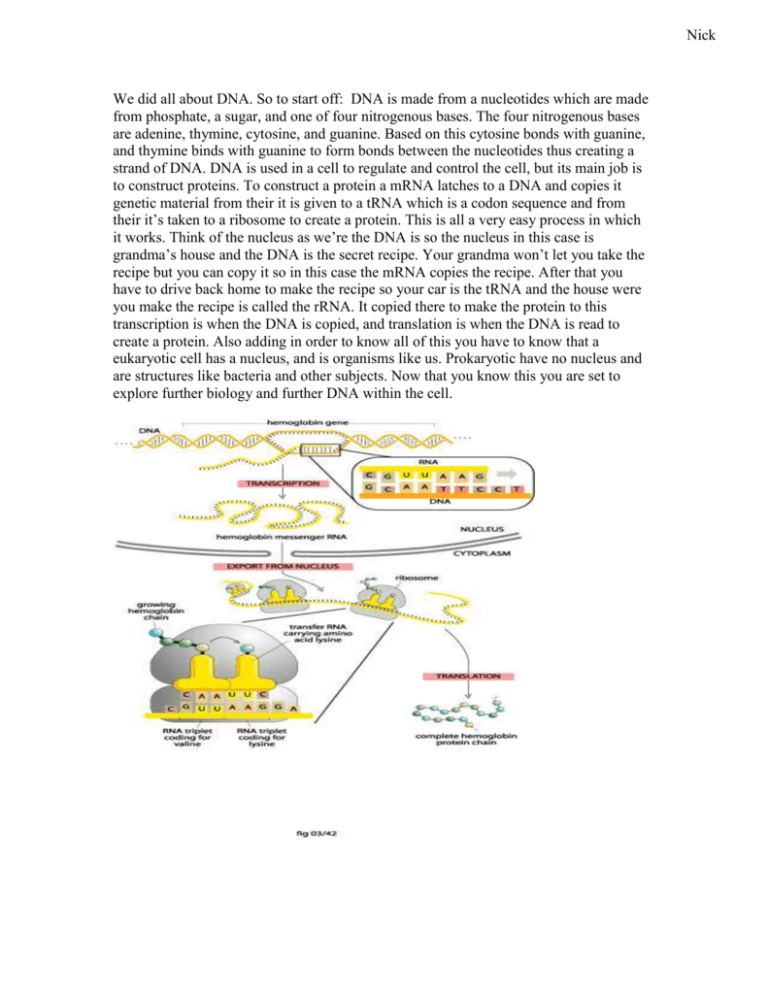
Nick We did all about DNA. So to start off: DNA is made from a nucleotides which are made from phosphate, a sugar, and one of four nitrogenous bases. The four nitrogenous bases are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. Based on this cytosine bonds with guanine, and thymine binds with guanine to form bonds between the nucleotides thus creating a strand of DNA. DNA is used in a cell to regulate and control the cell, but its main job is to construct proteins. To construct a protein a mRNA latches to a DNA and copies it genetic material from their it is given to a tRNA which is a codon sequence and from their it’s taken to a ribosome to create a protein. This is all a very easy process in which it works. Think of the nucleus as we’re the DNA is so the nucleus in this case is grandma’s house and the DNA is the secret recipe. Your grandma won’t let you take the recipe but you can copy it so in this case the mRNA copies the recipe. After that you have to drive back home to make the recipe so your car is the tRNA and the house were you make the recipe is called the rRNA. It copied there to make the protein to this transcription is when the DNA is copied, and translation is when the DNA is read to create a protein. Also adding in order to know all of this you have to know that a eukaryotic cell has a nucleus, and is organisms like us. Prokaryotic have no nucleus and are structures like bacteria and other subjects. Now that you know this you are set to explore further biology and further DNA within the cell. Desiree So basically genes are a segment of DNA that codes for a protein within the cell. Exons are the protein coding segments of a gene only in eukaryotes. Which are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus. And introns are what get spliced out in a gene. This all comes together in DNA splicing. That is because you have your strand of DNA with exons and introns, the introns are what need to be cut/spliced out during premRNA. That is because in order to be read during mRNA it needs to be “edited”. Ingrid Splicing The purpose of RNA splicing is to remove the intron sequences from the newly transcribed pre-mRNAs. In other words,for the pre-mRNA to read the gene it needs to cut out the introns in order to read the exons. Introns are segments of gene located between the exons, which don’t work in coding for protein synthesis. Exons are segments of a gene that does code for protein synthesis that is transcribed to messenger RNA. Both introns and exons sequences are transcribed into RNA. RNA splicing is done by spliceosomes, which are large group ofRNA and protein molecules that performs pre-mRNA. The introns are taken out of that sequence, this processis called RNA splicing. Every time introns are being removed transesterifications occur and exons are brought together. The point of taking out large numbers of introns through RNA splicing is because this helps the creation of a new and efficient protein. Spliceosomes go through many changes because by doing this it lets the checking and rechecking of RNA sequences previously of the chemical reaction that will happen. This increases the accuracy of splicing. Jaskiranjeet Phylogenetic Trees A phylogenetic tree is a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various species that are believed to have a common ancestor. A phylogenetic tree is a specific type of cladogram where the branch lengths are proportional to the predicted or hypothetical evolutionary time between organisms or sequences. Cladograms are diagrams that are similar in appearance to family trees. They represent relationships between DNA or amino acid sequences. It is also true that sequence relatedness can predict the relatedness of species. However, these diagrams cannot be completely considered to be accurate descriptions of the history of any organism. There are a number of pathways an organism can take that could also produce the same result.








