key to sample questions test 2
advertisement

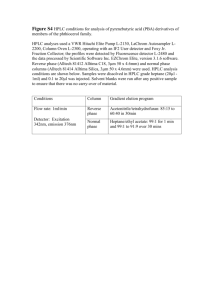
KEY Questions – Test 2 1 Circle the best answer. a. Increasing the flow rate in a gas chromatograph always increases resolution decreases resolution reduces the effects of diffusion improves equilibrium between the mobile and stationary phase. b. Which is NOT true about a capillary column in GC it is easy to overload the column capillary columns tend to have poorer resolution that packed columns very sensitive detectors are needed they can be used with mass selective detectors c. As compared to HPLC, capillary electrophoresis is slower and more easily interfaced to MS more easily used for electrically neutral compounds slower and has poorer resolution faster and has higher resolution d. Which factors affect m/e in a time-of-flight mass analyzer. voltage and length and voltage and magnetic field time length voltage, time and length e. Which of the following is important for resolution in both electrophoresis and chromatography. electroosmotic flow the length of the column equilibrium between the mobile and stationary phase longitudinal diffusion f. Which of the following detectors does NOT destroy the sample? mass selective detector FID thermal conductivity flame photometric detector g. Which of the following is NOT a common GC detector? FID UV detector electron capture detector thermal conductivity detector h. Which of the following is not a strategy for improving resolution in GC? use temperature program change flow rate change column change detector 1 KEY Questions – Test 2 i. What resolution is required to separate peaks with masses 114.53 and 114.55? 114.54 2863.5 11454 5727 j. Which term(s) in the Van Deemter equation that depend on flow rate? A and B A and C B and C A and C k. In a mass spectrometry, the usually sequence of events is: ionization, acceleration to constant energy, mass analysis acceleration to constant energy, mass analysis, ionization acceleration to constant energy, ionization, mass analysis ionization, mass analysis, acceleration to constant energy l. Which factor does NOT affect separation in electrophoresis? charge viscosity of solvent equilibrium voltage m. Which type of compounds is expected to have mass spectra with prominent peaks separated by 14 m/e units. compounds with aromatic rings compounds with long alkyl chains compounds with double bonds compounds that have been enriched with 14C n. In which ionization method is the sample is mixed in 1000:1 ratio with low MW gas (CH4, N2,etc) and very little fragmentation is observed in the mass spectrum. EI MALDI ESI CI o. Which is NOT true of exclusion chromatography ? separation is based on the size of the molecules the method is commonly used to separate proteins a given column can be used to separate any mixture as long as you wait long enough there are some columns that are used for low molecular weight mixtures p. Which of the mass analyzers below usually gives the best resolution? quadrupole TOF double focusing q. r. Which detector would NOT be appropriate with a capillary column? FID electron capture thermal conductivity detector detector Which is a common detector in mass spectroscopy? photomultiplier TCD electron multiplier MS-MS MSD FID s. Which of the following is TRUE for a mass spectrum? the parent peak is always strong the fragmentation pattern is not affected by the acceleration voltage very accurate quantitative determinations are difficult isotope effects are not important t. A process that is important for packed columns but NOT for capillary columns is diffusion equilibrium volatilization eddy currents 2 KEY Questions – Test 2 u. Which of the following detectors would be especially sensitive to chlorine containing compounds? FID thermal conductivity UV electron capture v. w. Which is a MS ionization method that uses a laser in the ionization process? EI FAB MALDI CI Which type of ionization uses a stream of high-energy ions to strike a target holding the sample? electron impact MALDI electrospray FAB x. If a magnetic sector mass analyzer is tuned to pass ions with a m/e of 100, then by what factor will the magnetic field have to be changed to pass ions with a m/e of 25? 2 ½ 1/4 4 y. Which statement is TRUE about capillary versus packed columns? capillary columns are faster but have poorer resolution capillary columns provides better resolution but requires very sensitive detectors, a capillary column is longer than a packed column and therefore resolution is lower, capillary columns provides better resolution but must be operated at higher temperatures z. Which is the quantity that is the equilibrium constant between the mobile and stationary phase? capacity factor retention time selectivity constant partition coefficient aa. Which is FALSE about mass spectra? a fragment that contains an odd number of N’s will have an m/e that is an odd number the parent peak is often not the highest intensity peak in a mass spectrum ions that have charges greater than one are not seen in mass spectra a MALDI spectrum has little fragmentation bb. Which of the following detectors would be especially sensitive to phosphorous containing compounds? FID thermal conductivity electron capture Thermionic cc. In a magnetic sector mass spectrometer, the mass/charge ratio that passes through the exit slit is proportional to the magnetic field strength proportional to the magnetic field strength squared proportional to the accelerating voltage proportional to the accelerating voltage squared dd. In a time-of-flight MS the mass/charge ratio is proportional to the time of flight proportional to the time of flight squared inversely proportional to the time of flight inversely proportional to the time of flight squared 3 KEY Questions – Test 2 2 In one or two sentences, discuss each of the following. a. Why is mass spectroscopy done in vacuum? to prevent recombination of ions b. What is the difference between a packed column and a capillary column? a capillary column is an open bore tube with stationary phase on the inside diameter. A packed column is a much wider tube that is filled with particles coated with the stationary phase. The capillary column generally has better resolution because of the great reduction in eddy diffusion c. How does the mobile phase flow rate affect resolution in chromatography? increasing the flow rate reduces contribution to broadening from diffusion effects but increases contribution to broadening because of poor equilibrium. Decreasing the flow rate has the opposite effects. d. How does column temperature affect resolution in HPLC, GC? Temperature affects retention times because equilibrium constants(partition coefficients change) . Increasing temperature also increases diffusion. In GC decreasing temperature almost always improves resolution at the expense of longer retention times. e. From the periodic table one finds that the mass of Br is 79.9. For a typical bromine compound there is no peak at 79.9 in the mass spectrum. The mass on the periodic table is not the mass of any particular isotope. It is the weighted average for all Br isotopes. f. Why is the parent peak not usually the highest m/e peak in mass spectroscopy? Most mass spectra for small molecules are done by high impact electron ionization which tends to fragment molecules into many small pieces. g. What is gradient elution and why is it used? Gradient elution is used in HPLC to decrease analysis time while maintaining resolution. In gradient elution the solvent composition is changed during the run. 3 For each of the following mixtures, indicate an appropriate type of chromatography or electrophoresis. Also indicate an appropriate detector (GC, normal phase HPLC, reverse phase HPLC, GPC, CZE, CIEF, CGE, IC, TLC) a. a mixture of proteins GPC (UV detector) - detection will be difficult unless concentration is high. A fluorescent tag may me necessary b. a perfume GC (FID) d. a mixture of amino acids IC (conductance) normal phase HPLC (UV) e. a mixture of C8 to C14 alkanes reverse phase HPLC (refractive index detector) f. a mixture of anions IC (conductance) 4 KEY Questions – Test 2 4 (6) Identify the compound that gives the following mass spectrum. The only atoms that could be present are C, H, O, N, Cl, Br. Explain your answer by identifying the fragments. m/e 35 36 37 47 relative m/e abundance 5 51 2 82 2 84 18 85 relative abundance 32 12 92 5 48 49 13 49 86 87 58 2 50 5 88 17 CH2Cl2 m/e relative abundance m/e 35 36 37 47 5 2 2 18 Cl 35 H Cl 37 Cl C35Cl 51 82 84 85 abundance 32 12 92 5 CH237Cl C35Cl2 C35H2Cl2 CH35Cl37Cl 48 49 13 49 CH35Cl C Cl, CH235Cl 86 87 58 2 CH235Cl37Cl CH37Cl2 50 5 CH37Cl 88 17 CH237Cl2 35 37 relative 5 (10) Consider the chromatogram shown below. 45 D 40 C 35 A 30 25 20 E 15 B 10 5 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 time (sec) 5 140 160 180 200 KEY Questions – Test 2 a. Roughly predict the appearance of a chromatogram for the same mixture if the column was changed from non-polar to polar. Consider retention time, peak width and peak amplitude. Assume that the detector responds equally well for each component. The components would probably come out in the reverse order. The peaks coming out later would be broader because of diffusion. b. Why can’t you say conclusively that component D is the most abundant? The peak area depends on the amount of material and on the sensitivity. The detector may be more sensitive to component D than to other components c. Assuming that the figure is a gas chromatogram, what could be done to improve the resolution? change column, reduce temperature d. Assuming that the column is non-polar, which peak corresponds to the most polar component of the mixture? A e. Estimate the resolution for the peaks C and D in the chromatogram. 2 t DR t RC 280 60 RS 1 WD WC 16 24 6.(5)For a given column H = 2 mm. Assume that you want to separate two components with a resolution of 2.0. How long does the column have to be to separate two components that have a selectivity factor of 1.03. Assume that the capacity factor for component B = 2. kB 2 Rs 2 2 1 kB N 16 Rs 1 kB 2 L N H 1.03 H 2 mm 2 N 1.697 10 5 L 339.488 m 7 (12) Fill in the table Detector UV absorption refractive index flame photometric detector fluorescence thermal conductivity electrochemical HPLC or GC HPLC HPLC GC types of samples that can be detected compounds that absorb UV universal organics HPLC GC HPLC fluorescent compounds universal compounds that are electrochemically active. 6