AP Biology
advertisement
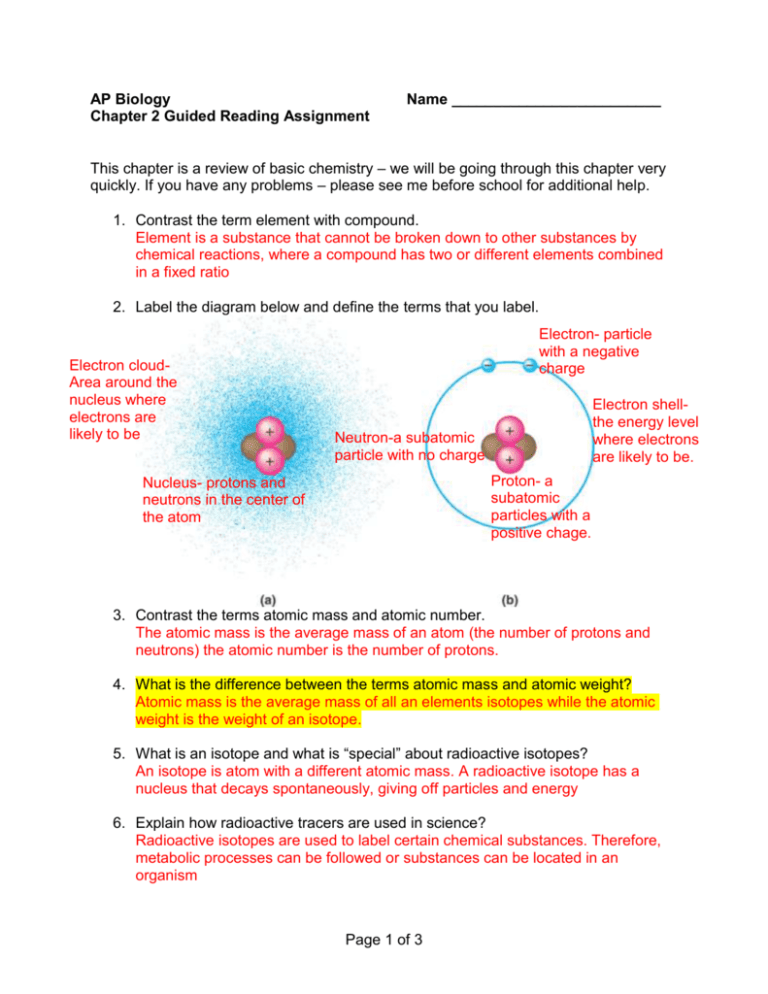
AP Biology Chapter 2 Guided Reading Assignment Name _________________________ This chapter is a review of basic chemistry – we will be going through this chapter very quickly. If you have any problems – please see me before school for additional help. 1. Contrast the term element with compound. Element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions, where a compound has two or different elements combined in a fixed ratio 2. Label the diagram below and define the terms that you label. Electron cloudArea around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be Electron- particle with a negative charge Electron shellthe energy level where electrons are likely to be. Neutron-a subatomic particle with no charge Proton- a subatomic particles with a positive chage. Nucleus- protons and neutrons in the center of the atom 3. Contrast the terms atomic mass and atomic number. The atomic mass is the average mass of an atom (the number of protons and neutrons) the atomic number is the number of protons. 4. What is the difference between the terms atomic mass and atomic weight? Atomic mass is the average mass of all an elements isotopes while the atomic weight is the weight of an isotope. 5. What is an isotope and what is “special” about radioactive isotopes? An isotope is atom with a different atomic mass. A radioactive isotope has a nucleus that decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy 6. Explain how radioactive tracers are used in science? Radioactive isotopes are used to label certain chemical substances. Therefore, metabolic processes can be followed or substances can be located in an organism Page 1 of 3 7. Explain how the movement of electrons relates to the concept of potential energy – use the diagram below to help answer the question. The farther an electron is from the nucleus the more energy it has. Just like the farther an object is from the ground the more potential energy it has. 8. What determines interactions between atoms? Why are valence electrons important? The number of valence electrons determines interactions between atoms. The chemical behavior of an atom depends on its valence electrons. 9. Define the following terms: a. Chemical bond - an attraction between two atoms resulting from the interaction of valence electrons b. Covalent bond - the sharing electrons by two atoms c. Single bond - the sharing of 1 pair of electrons between 2 atoms d. Double bond - the sharing of 2 pair of electrons between 2 atoms e. Valence - electrons in the outer most shell f. Electronegativity – the strength of attraction an atom has for electrons g. Nonpolar covalent bond - when electrons are shared equally by the atoms in a molecule h. Polar covalent bond – electrons are not shared equally by the atoms in a molecule due to differences in electronegativity. 10. What is the difference between a structural and molecular formula? the molecular formula writes the chemical symbol with subscripts while the formula indicates bonds 11. How do ionic bonds compare with covalent bonds? Covalent bonds are stronger than ionic bonds. Ionic bonds are formed by the attraction of an anion and a cation. A covalent bond is formed by sharing valence electrons. Page 2 of 3 12. Compare and contrast hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions. Hydrogen bonds are interactions between positive poles and negative poles of polar molecules like water. Van der Waals interactions are between the positive nucleus of one atom and the negative electron cloud of neighboring atoms. 13. Based on the reading, what is an example, in a living system, of how molecular shape is critical? Molecular shape determines the function of a molecule. If something changes the shape of a molecule, it will no longer function properly. 14. Define a dynamic chemical equilibrium in terms of quantities of reactants and products. This is a critical concept! In a reversible chemical reaction the point at which the rate of the forward reactions and reverse reactions are equal. The reactions are still occurring but with no effect on the amount of reactants or products. Page 3 of 3






