Test 3, 2013
advertisement

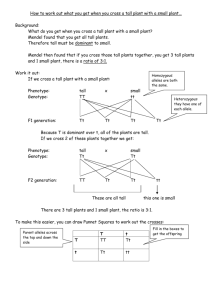
Genetics Test 3, Fall 2012 Name: This test consists of two parts . In Part One, answer 5 of the 6 questions (15 points each). In Part Two, all students must answer the entire question (25 points). Please show all of your work, or you will receive no partial credit for incomplete answers. Part One. Short Answers. Answer 5 of the following 6 questions. Please indicate which questions you want me to grade. (15 points each). Question One. A population (n=300) in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium contains 70% of a dominant phenotype and 30% of a recessive phenotype. Another nearby population (n=180) has an 80% dominant phenotype to 20% recessive phenotype ratio. If 20 individuals from the first population migrate to the second population, what will the allele frequencies in the conglomerate population be? We did not do this this year…but you should be able to give, in general, what you expect the impact on the allele frequencies to be (does the dominant allele frequency go up or down, for example?) Question 2. In mice, the autosomal locus coding for the beta-subunit of hemoglobin is 1 m.u. away from the albino locus (they are linked genes). Assume for a moment that the same is true for humans. Normal skin pigment (A) is dominant to albinism (a) and normal hemoglobin (H) is dominant to sickle cell (h). Since both of these traits are very rare, assume that unaffected parents in the problem below are not carriers. A. A son is born to an albino man with normal hemoglobin and a woman with normal pigmentation and sickle cell anemia. What kinds of gametes will the son form, and in what proportions? Question 3. In the tubular flowers of Foxgloves, wild-type coloration is red while a mutation called white produces white flowers. Another mutation, called peloria, causes the flowers at the apex of the stem to be huge. Yet another mutation, called dwarf, affects stem length. You cross a true-breeding white-flowered, normal-sized flowers, tall plant by a true-breeding red-flowered, peloria, dwarf plant. All of the F1 plants are tall with white, normal sized flowers. You then test-cross the F1 plants to red, dwarf, peloria plants, and get 543 progeny of the types shown: Red, dwarf, peloria. White, tall, normal. White, dwarf, peloria. Red, tall, normal. White, dwarf, normal. Red, tall, peloria. Red, dwarf, normal. White, tall, peloria. 172 162 56 48 51 43 6 5 A. Which alleles are dominant? B. What were the original genotypes of the parents in the original cross? C. Draw a gene map showing all genetic distances Question 4. If the mutation rate for a particular gene is 10-5, the number of individuals in a population is 7000, and the frequency of the dominant allele in the population is 0.7, how many generations of mutation will it take before the frequency of the dominant allele is reduced to 0.5? We did not do this this year…so ignore. Question 5. A population of Yaks has the following proportions: BB (Black). Bb (Gray). Bb (White). 543 254 335 Use Chi square analysis to determine if this population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Question 6. Based on the data below, draw a phylogenetic tree using UPGMA analysis. Species A Species B Species C Species D Species E Species A Species B Species C Species D 1.4 1.7 3.3 2.7 0.6 3.5 2.5 3.7 2.8 0.4 Part Two: All students must answer the questions on the next two pages (25 points) Your lab partner is designing an experiment in which they plan to amplify the ADE1 gene via PCR, then sequence the gene. They have asked you to critique each portion of their experimental design below. The relevant portion of the ADE1 coding sequence is shown. 5' CATCGTGCGC CGGCACAGTG AGTTACCCGA CACGATGAGA GGTTACATTA CATGGCCTGG GCCGATGTTC ATATATCACC GGGCTCTGCC CTCTACCTGC ACTCCGTCTA GCACAGGCTG TGGAAGGAGT CGGGCTGCGT CCAAAGCGGA CAGACCTAAT ACCAGGAGCG GAGTCTGAGG GCAGGGTGCG TGGGCAGGAG 3' 1. Assuming that you want to copy the entire gene above, the forward primer will be CATCGTGCGCGGTTACATTA. Is this correct? If not, give the correct sequence. 2. The reverse primer will be. GAGGACGGGTTAATCCAGAC. Is this correct? If not, give the correct sequence. 3. Generally, forward and reverse primers should have Tm's within 5 degrees of each other. Does this appear to be a good primer pair? 4. You lab partner claims that the length of the resulting PCR fragment will be 160 base pairs. Is this correct? If not, give the correct length. 5. Your lab partner decides to use the forward primer to sequence their DNA using Sanger sequencing. They claim that the first 5 bases of the resulting 200 base par sequence will be GGGCTC. Is the sequence and/or the predicted length correct? If either is incorrect, correct it. 6. Finally, your lab partner does not really understand how sequencing works, because they have never really understood DNA replication. Explain to them how the addition of an incoming base to the 3' end of the growing DNA molecule is critical to both Sanger and Ion Torrent sequencing.