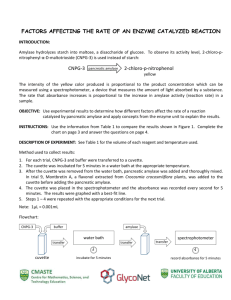
Amylase
advertisement

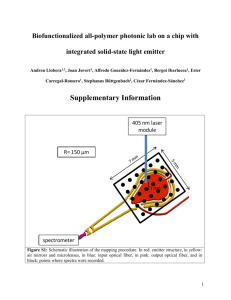
UNIT: Enzymes II (Kinetic / Rate Reaction) Amylase Procedure Thermo Procedure 3.2.1.1 Summary Determination of amylase activity in serum and urine is considered to be useful for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. In acute pancreatitis, the amylase activity in urine samples remains elevated for longer periods than in serum. Some authors recommend the determination of the ratio of the amylase and creatinine clearance is important in following the course of the disease. A decrease in pancreatic amylase is characteristic of pancreatic insufficiency. Principle- see product insert for clarification Amylase hydrolyzes the alpha - 1,4-glucan link in starch and certain other polysaccharides to form maltose. Many of the methods described in the literature for the determination of amylase activity are based on the hydrolytic activity of the enzyme. Procedures based on coupled enzyme reactions have been described for the determination of the enzyme activity. Methodologies which were developed recently, use p-nitrophenylglycosides as substrates for the determination of alpha-amylase activity. In the procedure alpha- amylase hydrolyzes a p-nitrophenylglycoside substrate forming pnitrophenyl and glucose. The p-nitrophenyl absorbs light at 405 nm and following a 2 minute lag period the rate of increase in absorbance at 405 nm is directly proportional to the amylase activity in the sample. Details of the reaction can be found on product insert. Specimen Collection and Storage Unhemolyzed clear serum is the specimen of choice. Heparinized plasma may be used, but plasma from other anticoagulants such as citrate, oxalate and EDTA may inhibit amylase activity. The pH of urine samples (random or timed specimens) should be adjusted to 7 before storing at 2-8 o C. Amylase activity is stable for several weeks when the samples are stored refrigerated 2-8 o C. Materials Required But Not Provided 1. 2. Waterbath or heating block set to assay temperature. Temperature controlled spectrophotometer and cuvets with optical properties suitable for use at 405 nm. 3. Pipetting devices for accurate delivery of volumes required for the assay. 4. Timer & test tubes. Procedure The temperature of the reaction mixture should be maintained at the desired assay temperature of 37o C. 1. Reagent preparation. a. Dissolve contents of each vial in volume of deionized water indicated on vial label. Avoid pipetting by mouth to prevent contamination of the reagent by salivary amylase. b. Stopper vial and immediately mix several times by inversion. DO NOT SHAKE. c. Reconstituted reagent is stable until expiration date when refrigerated. MLT 2401 Lab Manual 1 UNIT: Enzymes II (Kinetic / Rate Reaction) 2. Optimize the spectrophotometer at 405 nm, and cuvet compartment to desired temperature. Use deionized water to zero instrument. 3. Into test tubes marked to identify control(s) and patient(s), pipette 2.0 mL of amylase substrate and place in 37o C waterbath for 5-10 minutes. Also prewarm a dry cuvette. 4. To one (1) tube at a time***, add 0.050 mL of sample. Mix immediately by inversion and return it to the waterbath for 240 seconds to allow reaction kinetics to become linear (zero order). Transfer the mixture to the dry prewarmed cuvette. 5. At the end of the 4 minutes, wipe away any water or marks on the outside of the cuvette and place it in the spectrophotometer. 6. Read and record the absorbance at 405 nm vs water as reference. Start the stopwatch. This is INITIAL ABSORBANCE. 7. Continue incubation by returning the cuvette containing the solution to the waterbath swirling the contents gently. 8. Record absorbance again after exactly 1 minute. Repeat the process and record absorbance at 2 minutes. Repeat the process for all specimens. 9. Calculate the change in absorbance per minute by subtracting INITIAL ABSORBANCE from FINAL ABSORBANCE and dividing by 2. The change in absorbance should be at a constant rate. Calculations The determination of amylase concentration is based on the molar absorptivity of p-nitrophenyl at 405 nm. The complex formula can be viewed in the product insert. A reduction of the formula will result in determination of amylase concentration by the following calculation: Amylase Activity (U/L) at 37o C. = Averaged change in Absorbance per min. x 6406 Example: When a serum sample was assayed for amylase activity, the following absorbance values were obtained at 37o C. INITIAL A FINAL A = 0.110 = 0.340 change in absorbance/min = (0.340 - 0.110) / 2 = 0.115 Amylase Activity (U/L) at 37o C = 0.115 x 6406 = 736 U/L Name Date MLT 2401 Lab Manual 2 UNIT: Enzymes II (Kinetic / Rate Reaction) Amylase Report Form Reaction temperature Spectrophotometer Wavelength Calculation factor Absorbance Initial 1 min 2 min (Final A) average change/min Concentration U/L control 1 control 2 patient 1 patient 2 Example Calculation MLT 2401 Lab Manual 3