I. Why Metric?
advertisement

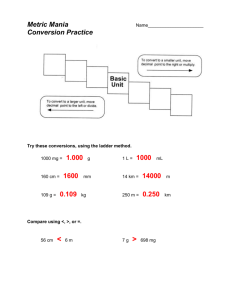
METRIC HANDOUT METRIC! EAPS 100 (for reference purposes) Prof. L.W. Braile January, 2015 I. Why Metric? A. The metric system is much easier. All metric units are related by factors of 10. B. Nearly the entire world (>95%), except the United States, now uses the metric system. U.S. economic competitiveness would be strengthened by converting to the metric system. See more and map of the world showing non-metric countries at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metric_system. C. Metric is used exclusively in science -- therefore, understanding of scientific and technical issues by non-scientists will be enhanced if the metric system is universally adopted. D. Because the metric system uses units related by factors of ten and the types of units (distance, area, volume, mass) are simply-related, performing calculations with the metric system is much easier thus facilitating quantitative analysis and understanding in science. That is, mathematical manipulations using the metric system are easier which leads to fewer mistakes and less confusion and increases the chance that scientific principles and concepts can be understood! II. Comparison of simple conversion operations in the English (customary) and Metric systems Notice the unusual numbers relating the various units in the English system and the simplicity of the powers of ten in Metric. (An English-Metric conversion table is contained in the Appendix of Lutgens and Tarbuck, 2014). ENGLISH SYSTEM METRIC SYSTEM 1. Units of Distance 12 in = 1 ft 3 ft = 1 yd 1760 yds = 1 mi 5280 ft = 1 mi 10 mm = 1 cm 100 cm = 1 m 1000m = 1 km (basic units are m or km) (English-Metric conversions: 1 inch = 2.54 cm; 1 mile = 1.61 km) 2. Units of Area 144 in2 = 1 ft2 43,560 ft2 = 1 acre 640 acres = 1 mi2 10,000 cm2 = 1 m2 10,000 m2 = 1 hectare 100 hectare = 1 km2 (basic units are m2 or km2) (English-Metric conversions: 1 in2 = 6.45 cm2; 1 mi2 = 2.59 km2) 3. Units of Volume 57.75 in3 = 1 qt 4 qt = 1 gal 42 gal (petroleum) = 1 barrel 32 qt = 1 bushel 1 cm3 = 1 ml 1000 ml = 1 liter 1000 liter = 1 m3 (basic units are liters or m3) (English-Metric conversions: 16.39 cm3 = 1 in3; 3.79 liters = 1 gal) 2 4. Units of Mass 437.5 grains = 1 oz 16 oz = 1 lb 2000 lb = 1 short ton 1000 mg = 1 g 1000 g = 1 kg 1000 kg = 1 metric ton (basic units are g or kg) (English-Metric conversions: 453 g = 1 lb; 2.2 lb = 1 kg) (Mass-volume conversions for water, or material of equal density, are also easy because 1 kg of water = 1 liter = 1/1000 m3 and 1 g of water = 1 cm3) 5. Units of Temperature Fahrenheit-Celsius-Kelvin conversions: T(C) = [T(F) - 32] x 5/9 T(F) = T(C) x 9/5 + 32 T(K) = T(C) + 273 (basic units are Kelvin or degrees Celsius/Centigrade) Convenient Equivalences to Help in Remembering Celsius Scale T(F) T(C) -459 -40 0 32 68 82 98.6 104 212 -273 -40 -17 0 20 28 37 40 100 Conditions Zero Kelvin (absolute zero) extremely cold water freezes room temperature warm day body temperature hot day water boils Extensive reference information on units of measurements and conversion factors are contained in the following references: Jerrard, H.G., and D.B. McNeill, A Dictionary of Scientific Units: Including Dimensionless Numbers and Scales, 6th ed., Chapman and Hall, New York, 255 p., 1992. Pennycuick, C.J., Conversion Factors, Univ. of Chicago Press, 47 p., 1988. Weast, R.C. (ed.), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press, Cleveland, OH, 1974. Web sites: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metric_system http://lamar.colostate.edu/~hillger/ www.metric.org http://www.metric-conversions.org/conversion-calculators.htm http://www.sciencemadesimple.com/conversions.html 3 4