Ch. 3 Study Guide - Garnet Valley School District
advertisement

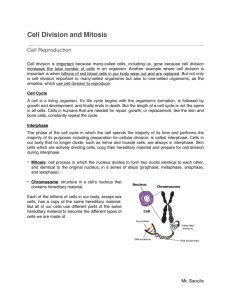
Chapter 3 Science Study Guide Terms to Know: Cell Division: the process that causes multicellular (or many-celled) organisms to grow by increasing the number of cells Cell Cycle: process of formation, growth, development, and death that cells go through Mitosis: process when the nucleus divides to form 2 identical nuclei (also known as cell division) Daughter Cells: the two new cells formed from the process of mitosis Centromere: the center of the chromosome that holds chromatids together Chromosome: structure in the nucleus that contains genetic material Chromatid: identical strands that make up a chromosome Chromatin: relaxed DNA in the nucleus before mitosis begins (“spaghetti”) Asexual Reproduction: a new organism is produced from one parent organism that goes through cell division (mitosis) Rapid rate of reproduction Offspring is identical to parent Sexual Reproduction: a new organism is produced from two parents that go through cell division (mitosis) and other processes Rate of reproduction is slower than rate of asexual reproduction Offspring have genetic information from both parents Nuclei: more than one nucleus (which controls the cell and is where the DNA and chromosomes are located) Centrioles: two small organelles found in animal cells that help the cell divide; they move to opposite ends of the cell during prophase Stages of Mitosis: Interphase stage when the cell duplicates it’s chromosomes and prepares for cell division; cells spend most of their life in this phase Prophase Stage when nuclear Membrane disappears, Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell, and spindle fibers stretch across the cell Metaphase Stage when pairs of chromatids Line up across the center of the cell Anaphase Stage when centromeres Divide, and chromatid pairs Separate and move to opposite Ends of the cell Telophase Cytokinesis: Think chromatIN for INterphase; looks like spaghetti Chromatin pairs off into chromosomes; think P for Pair and Prophase Chromosomes line up in the middle; think M for Metaphase and Middle Chromosomes break apart into Chromatids and spread to opposite sides of cell; think A for Apart and Anaphase Chromatids relax and become chromatin again; two daughter cells are formed. Think T for Two or Twin and Telophase The cytoplasm divides and the two new cells separate; think CYTO for Cytoplasm and Cytokinesis Results of Mitosis: Each new cell except for sex cells have 46 chromosomes Allows for growth and replaces worn out or damaged cells Types of Mitosis: 1. Binary Fission: an organism with no nucleus divides into two identical organisms Example: bacteria (think B for Bacteria and Binary fission) 2. Budding: a small, exact copy of the adult grows from the body of the parent Example: hydras reproduce by pinching off buds 3. Regeneration: a whole new organism grows from each piece of the parent Example: earthworms and starfish Functions of Cell Division: ~Cell division occurs in all organisms, but performs different functions *Unicellular (single-celled) organisms reproduce through cell division * Multicellular (multi-celled) organisms also reproduce through cell division, but cell division for them is involved in growth, development, repair, and reproduction Growth: your cells are the same size, but as you grow older, you grow physically so your cells need to divide into more cells Development: cells need to become specialized to perform different jobs and functions, so they take on different shapes and structures as they develop or mature; some might become skin cells while others become nerve cells Repair: your body needs to repair itself when injuries occur, so your cells divide and make new cells to heal wounds (like broken bones or cuts); also, your cells age and die and are constantly being replaced by new cells