Name

Name: _________________________________________ Date:____________________________
Homework 3
SHOW all work, please BOX your final balanced equation for each set below (numbers 1 and 2) Insert spaces or perform balancing on a separate sheet of paper. Don’t forget to clearly label the ox and red species!
1.) Balance the following chemical reactions as indicated AND identify the reducing and oxidizing species: ( insert spaces as needed or perform on a separate sheet of paper)
Remember, a redox reaction (basic) is balanced like an acidic redox reaction. The half reactions are pulled out. The atoms are balanced as is. Water is used to balance the number of oxygens, hydrogen ions are used to balance the number of H’s. Electrons are used to balance charge. The reactions are multiplied by a factor to make sure that the numbers of electrons lost = numbers of electrons gained. The reactions are added together. THEN OH -1 ions are added to BOTH sides. The number of OH -1 ions added needs to equal the number of H +1 ions present. This will create additional waters (which need to be reduced!) and you will now have an excess of
OH -1 ions on one side indicating the basic solution a.
MnO
4
-1
(aq)
+ SO
3
-2
(aq)
MnO
2 (s)
+ SO
4
-2
(aq)
[basic]
Mn +7 O -2 S +4 O -2 Mn +4 O -2 S +6 O -2
Mn +7 or MnO
4-1
is reduced therefore it is the oxidizing agent
S +4 or SO
3-2
is oxidized and therefore is the reducing agent
MnO
4-1
→ MnO
2
SO
3-2
→ SO
4-2
MnO
4-1
→ MnO
2
+ 2H
2
O H
2
O + SO
3-2
→ SO
4-2
4H +1 + MnO
4-1
→ MnO
2
+ 2H
2
O H
2
O + SO
3-2
→ SO
4-2
+ 2H +1
2(3e -1 + 4H +1 + MnO
4-1
→ MnO
2
+ 2H
2
O) (H
2
O + SO
3-2
→ SO
4-2
+ 2H +1 + 2e -1 )3
6e -1 + 8H +1 + 2MnO
4-1
→ 2MnO
2
+ 4H
2
O 3H
2
O + 3SO
3-2
→ 3 SO
4-2
+ 6H +1 + 6e -1
6e -1 + 8H +1 + 2MnO
4-1
→ 2MnO
2
+ 4H
2
O
3H
2
O + 3SO
3-2
→ 3 SO
4-2
+ 6H +1 + 6e -1
2H +1 + 2MnO
4-1
+ 3SO
3-2
→ 2MnO
2
+ H
2
O + 3 SO
4-2
Now OH -1 needs to be added to BOTH sides. The same numbers of OH -1 will be added as there are H +1 ions.
2OH -1 + 2H +1 + 2MnO
4-1
+ 3SO
3-2
→ 2MnO
2
+ H
2
O + 3 SO
4-2
+ 2OH -1
2H
2
O + 2MnO
4-1
+ 3SO
3-2
→ 2MnO
2
+ H
2
O + 3 SO
4-2
+ 2OH -1
Now cancel any duplicate waters (since you made water by adding H +1 and OH -1 you may now have waters on both sides of the → again – reduce!!)
H
2
O + 2MnO
4-1
+ 3SO
3-2
→ 2MnO
2
+ 3 SO
4-2
+ 2OH -1
b.
Zn
(s)
+ NO
3-1 (aq)
Zn(OH)
4-2 (aq)
+ NH
3 (g)
[basic]
Zn is oxidized and is therefore the reducing agent
NO
3-1
is reduced and is therefore the oxidizing agent
Zn → Zn(OH)
4-2
NO
3-1
→ NH
3
4H
2
O + Zn → Zn(OH)
4-2
NO
3-1
→ NH
3
+ 3H
2
O
4H
2
O + Zn → Zn(OH)
4-2
+ 4H +1 9H +1 + NO
3-1
→ NH
3
+ 3H
2
O
4H
2
O + Zn → Zn(OH)
4-2
+ 4H +1 + 2e -1 8e -1 + 9H +1 + NO
3-1
→ NH
3
+ 3H
2
O
4(4H
2
O + Zn → Zn(OH)
4-2
+ 4H +1 + 2e -1 )
8e -1 + 9H +1 + NO
3-1
→ NH
3
+ 3H
2
O
16H
2
O + 4Zn → 4Zn(OH)
4-2
+ 16H +1 + 8e -1
8e -1 + 9H +1 + NO
3-1
→ NH
3
+ 3H
2
O
13H
2
O + 4Zn + NO
3-1
→ 4Zn(OH)
4-2
+ 7H +1 + NH
3
7OH -1 + 13H
2
O + 4Zn + NO
3-1
→ 4Zn(OH)
4-2
+ NH
3
+ 7H +1 + 7OH -1
7OH -1 + 13H
2
O + 4Zn + NO
3-1
→ 4Zn(OH)
4-2
+ NH
3
+ 7H
2
O
7OH -1 + 6H
2
O + 4Zn + NO
3-1
→ 4Zn(OH)
4-2
+ NH
3
2.) Balance the following chemical reactions as indicated AND identify the reducing and oxidizing species: ( insert spaces as needed or perform on a separate sheet of paper ) a.
ClO
3
-1
(aq)
+ I
-1
(aq)
I
2 (s)
+ Cl
-1
(aq)
Cl +1 O -2 I -1 I 0 Cl -1
[acidic]
Cl +1 or ClO
3-1
is being reduced therefore it is the oxidizing agent
I -1 is being oxidized therefore it is the reducing agent
ClO
3-1
→ Cl -1 I -1 → I
2
ClO
3-1
→ Cl -1 + 3H
2
O 2I -1 → I
2
6H +1 + ClO
3-1
→ Cl -1 + 3H
2
O 2I -1 → I
2
+ 2e -1
6e -1 + 6H +1 + ClO
3-1
→ Cl -1 + 3H
2
O 3(2I -1 → I
2
+ 2e -1 )
6e -1 + 6H +1 + ClO
3-1
→ Cl -1 + 3H
2
O
6I -1 → 3I
2
+ 6e -1
6H +1 + ClO
3-1
+ 6I -1 → Cl -1 + 3H
2
O + 3I
2
6H 1Cl 3O 6 I (+6 + -1 + -6) = -1 6H 1Cl 3O 6 I (-1 + 0 + 0) = -1
b.
Cr
2
O
7
-2
(aq)
+ Zn
(s)
Zn
+2
(aq)
+ Cr
+3
(aq)
[acidic]
Cr +6 O -2 Zn 0 Zn +2 Cr +3
Cr
+6
or Cr
2
O
7-2
is reduced, therefore it is the oxidizing agent
Zn
0
is oxidized, therefore it is the reducing agent
Cr
2
O
7-2
→ Cr +3 Zn → Zn +2
Cr
2
O
7-2
→ 2Cr +3 + 7H
2
O Zn → Zn +2 + 2e -1
14H +1 + Cr
2
O
7-2
→ 2Cr +3 + 7H
2
O
6e -1 + 14H +1 + Cr
2
O
7-2
→ 2Cr +3 + 7H
2
O
6e -1 + 14H +1 + Cr
2
O
7-2
→ 2Cr +3 + 7H
2
O
3(Zn → Zn +2 + 2e -1 )
6e -1 + 14H +1 + Cr
2
O
7-2
→ 2Cr +3 + 7H
2
O
3Zn → 3Zn +2 + 6e -1
14H
+1
+ 3Zn + Cr
2
O
7-2
→ 3Zn
+2
+ 2Cr
+3
+ 7H
2
O
3.) Write the electron configurations – DO NOT USE THE NOBLE GAS CONFIGURATION!! – for the following: a.
Cr 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 4 →
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
4s
1
3d
5 b.
Cu 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 9 → 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6
4s
1
3d
10 c.
F 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5
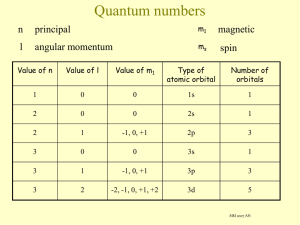
4.) Write a set of quantum numbers (n, l, m l
, and m s
) for the 1 st electron, the 2 nd electron, the 5 th electron, and the 6 th electron for fluorine. (HINT!! Orbital box diagrams might help!)
1
5 6
2
1s 2s 2p
Note: The 1 st and 2 nd electron MUST have the same m l
value because they are in the same “box” (orbital) while the 5 th and the 6 th electron MUST have different m l
values since they are not in the same “box”
(orbital).
1 st e: n = 1 l = 0 m l
= 0 m s
= + ½
2 nd e: n = 1 l = 0 m l
= 0 m s
= - ½
5 th e: n = 2 l = 1 m l
= -1 m s
= + ½
6 th e: n = 2 l = 1 m l
= 0 m s
= + ½
5.) Write the electron configurations – DO NOT USE THE NOBLE GAS CONFIGURATION!! – for the following a.
Cu
+2 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 9 → 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 0 3d 9 b.
Cl -1 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5
→ 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6
6.) Which of the following quantum number sets are allowed? If there is an error identify AND correct it by changing the l number only a.
n= 1 , l
= 1, m l
= 0 NOT VALID: l
cannot be the same numerically as n! Therefore l
= 0 b.
n= 6, l
= 4, m l
= -5 NOT VALID: the m l
value is outside the –
l
to + l
range. Therefore, the l
value must = 5