L5-3 - Louisiana FFA Foundation
advertisement

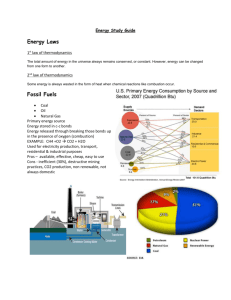
Louisiana Team AgEd Louisiana Agriscience Education Curriculum Course: Agriscience I Unit: Energy Lesson: Alternative Energy Sources for Agriculture LOUISIANA LEARNING STANDARDS AND GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS Learning Standards (LS): The student will be able to recognize the environmental effects of using alternative fuels The student will be able to describe the pros and cons of using alternative fuels Grade Level Expectations (GLE) Explain why ecosystems require a continuous input of energy from the Sun (LSH-E1 Evaluate whether a resource is renewable by analyzing its relative regeneration time (SE-H-B1 PERFORMANCE-BASED LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Instruction in this lesson should result in students being able to: 1. Recognize the environmental effects of using alternative fuels. 2. Describe the pros and cons of using alternative fuels. LIST OF RESOURCES. Teachers may find the following resources useful in planning and teaching this lesson: Textbooks Bernstein/Winkler/Zierdt – Warshw Environmental Science Ecology and Human Impact Addison-Wesley Publishing Company 1996 (Chapters 16 and 17) Christensen, John et.al. Global Science Dubuque, Iowa: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company 2000 (Textbook Chapters 7, 9, and 10) Web Sites http://www.eereenergy.gov http://www.helixcharter.net http://www.biomassenergycentre.org http://www.energyquest.com http://www.findsolar.com http://www.ucsua.org/clean-energy/renewable_energy_basics http://www.howstuffworks.com http://www.freeenergy.com Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 1 of 13 http://windenergyworks.org http://eia.doe.gov http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/alternate/page/renewenergyconsump/figure1.html Other Resources. The following resources will be useful to students and teachers: None TERMS. The following terms are presented in this lesson: Solar Energy – Hydroelectric Power Wind Energy Biomass Fuels Geothermal Energy Nuclear Energy Tidal Energy LIST OF EQUIPMENT, TOOLS, SUPPLIES, AND FACILITIES Computer with power point Projector Internet access Writing Surface INTEREST APPROACH. Use an interest approach that will prepare students for the lesson. Teachers often develop an approach for their unique class and student situations. A possible approach is included here. You and a friend are watching T.V. and view a program about solar energy use and solar homes. After viewing the program your friend is interested in converting his home into a solar home, however he does not know how much the equipment will cost and the savings provided each month. Both of you have heard that solar power is environmentally friendly, but do not want to spend all of your savings on the equipment. In this activity students will research how to convert their current home or example home to a solar power home. Each student will be required to find out the amount of kilowatts and impact a monthly electric bill. This information will plug into the Find Solar web site, www.findsolar.com. Students will be able to determine if conversion is economical and environmental impact of using solar power. Research will be compared/contrasted and debated in class, to determine feasibility. Have each student indicate whether they would convert to solar power, and why or why not. (PS-H-F2), (D9-H) Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 2 of 13 SUMMARY OF CONTENT AND TEACHING STRATEGIES Anticipated Problem: What types of alternative energy sources are available today and in the future for the agriculture industry? 1. Have students view pie chart that shows the amount of energy consumption in the United States as of 2007. a. According to the table alternative energy accounts for at least 15% of all energy consumed. Alternative Energy Sources used in Agriculture Solar Energy – energy form the sun absorbed by the earth and used as a fuel by virtually all organisms. 1. Energy from the sun drives the water cycle, causes winds to blow due to uneven warming of the earth’s surface, waves to move, and impacts the earth’s climate. 2. Provides energy for photosynthesis 3. Produces thermal energy, which is when light energy from the sun that is absorbed by dark colored objects. This energy can be used as a source of heat or electricity 4. Solar energy is stored in plants and animals that died millions of years ago forming fossil fuels. Two types of solar heating systems are passive and active 1. Passive solar heating systems are designed so that the sun’s energy is collected, stored, and distributed naturally in an enclosed dwelling. Passive solar energy is used only as an alternative source of heat, reducing the need for fossil and nuclear fuels. a. This is the simplest and cheapest solar energy system. An example of a passive solar heating system is a greenhouse. b. Uses sunlight to provide light and heat directly, with no circulating fluid or energy conversion systems. c. Many homes in North America have large glass windows facing the south, exposing rooms painted with dark colors. Positioning of a building has a big impact on the efficiency of a passive solar heating system. d. Some of examples of agricultural use of passive solar energy: Hay cut, allowed to dry in the sun, and then stacked or baled for storage. Corn and soybean crops partially dried in the field. Solar drying used to cure crops and dry food for storage. 2. Active Solar Heating uses devices to collect, store, and circulate heat produced form solar energy called flat plate collectors. a. These collectors are installed in areas that will receive maximum sunlight. The base is constructed of black metal and tubes filled with a fluid or air runs Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 3 of 13 across the top of the metal. The top of the collector is made up of glass. The black metal absorbs sunlight, heating liquid is pumped through the tubes, which is stored until use, and clear glass is used to prevent heat form escaping. b. These types of systems can be used for producing heat and hot water. As water-cools it is pumped back to the flat plate collector. Photovoltaic Cells 1. Are the only solar devices that produce electricity? 2. Photovoltaic cells or solar cells are made up of two layers of semiconductor elements such as silicon or selenium. One layer is positively charged and the other is negatively charged as sunlight strikes the cells electrons move form the negative to positive side. As a result of the electron movement electricity is produced. a. Cells are used today on space satellites and produce power for homes and industry. b. They are lightweight and last a long time. Solar Energy can be used to heat building such as greenhouses, livestock buildings to maintain animal health, provide hot water for cleaning pens and equipment, and drying crops. Photovoltaic Systems are used for electric fences, garden lights, water pumps, pond aeration, and small irrigation systems. Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Energy 1. Free and unlimited, clean, nonpolluting, renewable resource, little maintained, little noise and machinery involved. 2. Not a constant source (limited sunlight on cloudy or rainy days), upfront equipment cost for capturing energy expensive, but these are usually offset over time with savings in energy bill. As technology progresses equipment will be more cost effective. Hydroelectric Power – Electricity that is produced form the kinetic energy of moving water. 1. Used for centuries to turn water wheels that would grind grains. In the 1800’s turbines were invented that would produce electricity from flowing water. In 1925 40% of all the worlds’ electricity was generated by flowing water. 2. To generate power from water a dam is built across a waterway to create a reservoir. Water behind the dam is directed toward turbine blades, which causes turbine blades to turn. The coils spin through a magnetic field producing electricity. Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydroelectric power 1. Flood control, free, unlimited, nonpolluting, creates recreation areas, stores water for irrigation. . 2. Alter s natural plant and animal life due to temperature changes. (Water is colder on the upside of dam,) Some aquatic life cannot swim upstream, which Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 4 of 13 interferers with reproduction. Erosion problems on the downside of dam due to water not replenishing soil with nutrients. Hydroelectric Power currently supplies about 24 percent of the world’s electricity. The total amount of electric output in 2007 was about 675 megawatts, which is equal to 36 billion barrels of oil. Tidal energy – Works Similar to hydroelectric energy using kinetic energy in ocean tides converted into electricity by rotating turbines. Water is usually dammed in a reservoir during high tides and released during low tides. As water moves form one source to turbines rotate producing electricity. There are only a few suitable sites for tidal energy generators around the world and a difference between 16 feet are needed between high and low tides. Wind Energy - generated by wind generators operated by wind rotating turbines blades, and using kinetic energy to generate electricity 1. Since the 1870’s farmers have been using wind energy to pump water. During the 1920’s wind power was being used to turn small electric generators, but efforts were abandoned due to electrical grid connections. 2. Windmills used to generate electricity of called aero generators, which have air vanes connected to coils of wire. 3. There are two types of aero generators horizontal and vertical axis. a. Horizontal are shaped like airplane propellers and vertical are shaped like an eggbeater. The vertical shape design allow for the generator turn at lower speeds. 4. Wind farms are sites where many aero generators are located together in open areas where wind conditions are favorable at least 15 mph everyday. For wind generators to work effectively wind speeds must be between 14-15mph. Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Energy 1. Free unlimited, non-polluting, source of income for farmers on land lease without interfering with crops and livestock, can be used to pump water. 2. Takes up a lot of land, zoning regulations, liability setting up to gird systems setup and equipment expensive. According to American wind energy association if may take up to 15 years for a wind turbine to pay for itself. As of 2007 wind there are wind farms in 32 states, they have supported 45,000 jobs provided 1 % of all U.S. electricity and save at least 28 million tons carbon dioxide emissions. Since 1980 cost for wind energy equipment has gone down by 90 percent. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 5 of 13 Biomass Fuels – fuels formed form living or recently living organisms. This includes forest, agriculture, and food processing waste. 1. Examples of forest products – saw dust, bark, paper, pulp, scarp lumber, and wood dust. 2. Examples of Agriculture/Food Waste – Fruit pits, pecan shells, rice hulls, corncobs, manure, and sugar cane residue. 3. Biofuels (also called biomass fuels) are a renewable resource and energy is released form them usually by burning of converting to solids, liquids, or gaseous forms. After conversion the fuel can be used for electric power, heat, chemicals, or other fuels, 4. Sewage treatment facilities can use anaerobic digestion to treat water and produce methane gas, which may be used for heating (Anaerobic – without air) a. Methane is a hydrocarbon, which is the main component of natural gas. As organic materials breakdown methane is produced which can be collected and used for heating? b. Grain crops such as corn and sugar cane can be used to make ethanol which is an alcohol made by yeast during fermentation. Alcohol is also a hydrocarbon. c. Oil-bearing plants, plants with high hydrocarbon contents such as algae have components similar to diesel or other petroleum products. 5. Ethanol a. Alcohol-based alternative fuel. b. Made from corn, barley, wheat or “cellulose” sources. c. Lower engine efficiency and “gas” mileage than gasoline. d. Reduces harmful emissions compared to gasoline. e. E-10 = 10% ethanol and 90% gasoline for all gasoline-powered vehicles. f. E-85 = 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline for use in “flex-fuel” vehicles only. 6. Bio-diesel – Made from vegetable oils, animal fats or recycled restaurant greases. Blends up to B20 (20% bio-diesel and 80% petroleum diesel) for most diesel vehicles. 100% bio-diesel may require vehicle modifications. May not be suitable for wintertime use. Lower fuel economy than petroleum diesel. Domestically produced, renewable, safe, biodegradable, reduced air pollutants. Advantages and Disadvantages of bio-fuels 1. Renewable resource reduces green house gases, low emissions, increase economic growth and employment. 2. May decrease plant biodiversity, may cause food prices to increase due to a decrease in avaible grain, Additional land required, emits more Nitrogen Oxides, must be transported by truck or rail, does not flow well at low temperatures, May be incompatible with internal seals and gaskets in older vehicles. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 6 of 13 Geothermal Energy – Heat energy generated within the earth. 1. Geothermal energy is heat given off by radioactive elements decaying deep beneath the ground. Enough heat is generated to melt rock called magma. This heat contains 50,000 times more energy than oil and natural gas. 2. Geothermal energy in use din regions where the Earth’s crust is thin enough to let heat through. These regions are usually located along the edges of tectonic plates where young volcanoes are found. (Alaska, California, Oregon, Nevada) 3. As water cones into contact with hot rocks it rises to the surface forming hot springs and geysers. This water can be at least 200 degrees Celsius. a. Cool water seeps into the earth’s crust is heated up then rises to the surface and steam is collected. Power plants also drill holes in rock and pump cool water into hot areas, then collect hot water and steam through additional piping, which is used to turn turbines. Water is then returned back to the original source. 4. There are three designs used to collect steam, Dry, Flash, and Binary. The choice of each system depends on how water comes out as steam. a. Dry – steam goes to the turbine is condensed to water and returned back. b. Flash – hot water is depressurized into steam and used to drive turbines c. Binary – hot water heats a second liquid with a lower boiling point and water is returned back to source. Largest U.S. geothermal plant is steam driven and is located North of San Francisco, California. Geothermal Heat Pumps are used to heat and cool houses. These systems transfer heat during winter and absorb heat during summer. Air or antifreeze is pumped through pipes buried underground and recalculated back into the building. These systems are environmentally clean heating/cooling systems Advantages and Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy 1. Used to heat greenhouses, de-ice roads, and dry out fish, heat water for aquatic farms, and heat and cool homes. Ireland gets 50% of energy form geothermal sources. 2. Emits Hydrogen sulfide, which is a toxic gas that produces a rotten egg odor, produces excessive salt and mineral buildup in pipes that must be removed, lack of adequate water to produce steam in some areas. Conditions where water is able to circulate to the surface due to heat is found on only 10% of the Earth’s surface. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 7 of 13 Nuclear Energy – energy in the nucleus of an atom that can be used to generate electricity. 1. energy is released by nuclear reactions or radioactive decay. Once the bonds that hold atoms together in the nucleus are broken an enormous amount of energy is released. This is done by nuclear fission. As of 2006 nuclear energy accounts for 19% of total electricity generated in the United States. There are about 66 million power plants in the United States. A. nuclear fission – atoms are split apart to form small atoms releasing energy to produce electricity. 2. Two types of nuclear reactors are used to generate electricity burner reactors and breeder reactors. Burner Reactors 1. Uranium 235 is the fuel used for nuclear fission. Fission takes place inside a reactor vessel, which is made up of steel walls 15 to 30 cm thick to prevent radiation form escaping. The reactor is contained inside a thick concrete container. 2. At the center of the reactor is the core, which contains long rods filled with ceramic uranium pellets submerged in water. Water acts as a coolant and slows down the chain reaction so uranium can split. Control rods made up of cadmium and Boron are also placed in the reactor. Control rods absorb neutrons these rods can be raised or lowered in the reactor to slow down are speed up the reaction. 3. Uranium is a non-renewable resource but is a common metal found in mined rocks. The U-235 atoms can easily split apart. During the fission process neutrons split the Uranium atoms causing heat and radiation to be released. More neutrons are also released creating a chain reaction, which can be slowed down or sped up by raising or lowering controlling rods. 4. The energy released from the reaction heats water, which is turned to steam and drives turbines that spin a generator to produce electricity. In some reactors steam is generated form a secondary water reservoir so radioactive water never comes in contact with the turbine. Water in the reactor is heated then circulated to a secondary water reservoir, where stored water is then heated by conduction. Water is then circulated back to their original point of origin. Breeder Reactors 1. Of the Uranium mined today a majority is Uranium-238, which is too stable. Breeder reactors use very little U-235 to start the fission process. Space neutrons are captured by U-238, when this happens Plutonium-239 is formed, which is fissionable and can be split by neutrons. 2. After a chain reaction of Pu-239 is produced U-235 is no longer needed. The process of generating electricity is similar to a burner reactor but instead uses liquid Sodium is used in the reactor core as a coolant to keep the chain reaction going. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 8 of 13 Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Power 1. Large amount of energy avaible, shift to nuclear could reduce fossil fuels and dependence on foreign oil, does not contribute greenhouse gases, smoke, or ashes. 2. Mining Uranium is not a clean process and could deplete our Uranium reserves, Cooling towers dissipate heat into the atmosphere and local water bodies called Thermal Pollution, breeder reactors could be used by terrorist groups to make nuclear weapons, Increase in radioactive waste produced. REVIEW/SUMMARY. Use the student learning objectives as the basis for review and summary. APPLICATION. Students will research how to convert their current home or example home to a solar power home. Each student will be required to find out the amount of kilowatts and the impact on a monthly electric bill. This information will plug into the Find Solar web site, www.findsolar.com. Students will be able to determine if conversion is economical and environmental impact of using solar power. Research will be compared/contrasted and debated in class, to determine feasibility. (PS-H-F2), (D-9-H) EVALUATION. See sample test. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 9 of 13 Answers To Sample Test Fill in the blank 1. hydroelectric 2. horizontal and vertical 3. biofuels 4. geothermal energy 5. nuclear Multiple choice 6. A 7. C 8. D 9. A 10. C 11. B 12. A 13. A 14. A Discussion 15,16,&17 Answer to be determined by teacher evaluation of question. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 10 of 13 SAMPLE TEST: Student Name:___________________ Date: _______ Fill in the blank: 1. _________________ is electricity produced from the kinetic energy of moving water. 2. Two types of aero generators are _______________ and ____________ axis. 3. ________________ , fuels formed from living or recent living organisms. 4. __________________________________ heat energy generated within the earth. 5. ___________________________ energy is the nucleus of an atom that can be used to generate electricity. Multiple choices: 6. Energy from the sun absorbed by the earth and used by all organisms. a. solar b. hydroeclectric c. wind d. nuclear 7. The only solar devises that produce electricity? a. active b. passive c. photovoltaic d. hydroelectric 8. For generators to work effectively, wind speeds must be at least how many miles per hour? a. 5 b. 10 c. 1 d. 14 9. E-85 means? a. 85% ethanol & 15% water. b. 85% ethanol & 15% gas. c. 8% ethanol & 5% gas. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 11 of 13 10. Sites where many aero-generators are located together in areas of favorable wind generators. a. wind mills. b. wind sites. c. wind farms. d. electric stations. 11. Hydrocarbon that is the main component of natural gas that can be collected for heat? a. hydrogen b. methane c. oxygen d. nitrogens Read the following paragraph and answer the questions Farming is one the leading industries in the US and it has been one the longest lasting forms of income, and for sustaining life in the history of the US. Without farmers, without their hard work day after day, many millions of Americans would starve without the needed nutritious types of products that farmers provide each of us. Farmers use machinery to cut the hay, to cut the corn, to aid in ways that were never possible before. One can now run a farm with fewer workers and labor because of the use of automated machines, and machinery in cutting the crops, moving the crops and even in storing crops. With all the machinery that is being used by a farmer, the costs of gasoline and diesel can weight heavily on the farmers bottom line. Incentives for farmers to use alternative fuels are increasing. The cost of diesel and of gasoline is constantly on the rise, and the bottom line for the farmer is shrinking as the gasoline is rising. To combat this, many farmers are striking back, creating their own fuels and finding alternatives for the gasoline and diesel they would other wise be purchasing. For every farmer, there is a need to create a better alternative, and farmers are turning to their own crops, and waste to provide their selves with the needed fuel to cut costs. http://www.ezilon.com/articles/articles/11/1/Farming-and-alternative-fuels 12. Which of the following statements would best summarize the intent of the passage? a. Alternative fuels can help our farmers offset the rising cost of fuel b. An individual U.S. farmer does not need a large workforce to maintain his or her operation. c. Alternative fuels are of no benefit for the U.S. farmer d. Alternative fuels are a waste of valuable research and time. Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 12 of 13 13. Which of the following statements would support best support the need for alternative fuel use? a. Rising fuel prices and the increase in fuel consumption has put a strange on the economy, causing consumers to look at alternative fuels. b. Farmers are not affected by the rise of fuel cost due to tax breaks c. Alternative fuels could decrease the need for fossil fuels and stimulate jobs in Local communities. d. None of the following support alternative fuels 14. Which of the following conclusions is probably correct? a. One of the oldest professions is being affected economically by the rising cost of fuel. b. The American farmer can self sustain his or herself with depending on other citizens in all professions are not always affected by rising fuel cost or fuel consumption. d. All of the above Discussion: Answer the following questions in the space provided below. 15. Of all the energy sources discussed give at least five (5) advantages and disadvantages of each alternative source. 16. Explain how alternative sources of energy can benefit the field of agriculture. 17. Which of the alternative energy sources would benefit our geographic area and what would be the environmental and economic impact is to the local community? Louisiana Team AgEd - Agriscience Education I Curriculum - Page 13 of 13