SKILLS LADDERS
advertisement

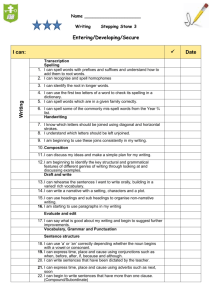
Writing Skills Ladder SKILLS LADDERS Writing Outcomes/ Level Descriptors Outcome 1 Outcome 2 Outcome 3 Outcome 4 Level 1 Outcome 5 Level 2 Outcome 6 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Children begin to ‘draw’ using their preferred hand and experiment with mark making. Children try out a variety of instruments to make marks and shapes on paper or other appropriate material. Children begin to recognise the alphabetic nature of reading and writing and understand that written symbols have sounds and meaning. They hold writing instruments appropriately, discriminate between letters and begin to write in a conventional way. Children’s writing communicates meaning through simple words and phrases. In their reading or writing, they begin to demonstrate an understanding of how sentences work. Children form letters which are usually clearly shaped and correctly orientated. They begin to understand the different purposes and function of written language Children’s writing communicates meaning. They use appropriate and interesting vocabulary showing some awareness of the reader. Ideas are often developed in a sequence of connected sentences, and capital letters and full stops are used with some degree of consistency. Simple words are usually spelled correctly, and where there are inaccuracies, the alternative is phonically plausible. In handwriting letters are accurately formed and consistent in size. Pupils’ writing communicates meaning in both creative and factual forms, using appropriate and interesting vocabulary, and showing some awareness of form and the reader. Ideas are developed in a sequence of sentences, sometimes demarcated by capital letters and full stops. Simple, monosyllabic words are usually spelled correctly, and where there are inaccuracies the alternative is phonetically plausible. In handwriting, letters are accurately formed and consistent in size. Children’s writing is often organised, imaginative and clear. The main features of different forms of writing are used appropriately. Words are chosen for variety, interest and effect. The basic grammatical structure of sentences is usually correct. Punctuation is generally accurate. Spelling is usually accurate. Children produce legible writing. Pupils’ writing is often organised, imaginative and clear. The main features of different forms of writing are used appropriately, beginning to be adapted to different readers. Sequences of sentences are used to develop ideas and words are sometimes chosen for variety and interest. The basic grammatical structure of sentences is usually correct. Spelling is usually accurate, including that of common, polysyllabic words. Punctuation to mark sentences – full stops, capital letters and question marks – is used accurately. Handwriting is legible and work is appropriately presented. Pupils’ writing in a range of forms is lively. Ideas are often sustained and developed in interesting ways and organised appropriately for the purpose and reader. Opinions are stated and supported with some reasons given. Vocabulary choices are often adventurous and words are sometimes used for effect. Pupils are beginning to extend meaning and use different sentence structures. They organise their writing into paragraphs. Spelling conforms to regular patterns and is generally accurate. Full stops, capital letters and question marks are used accurately and pupils are beginning to use punctuation within the sentence, including inverted commas for speech. Handwriting is clear and legible and, where appropriate, presentation is adapted according to the task. Pupils’ writing is varied and interesting, conveying meaning clearly in a range of forms for different readers, using a more formal style where appropriate. They express opinions, supported by reasons. Vocabulary choices are imaginative and words are often used precisely. Simple and complex sentences are organised into paragraphs. Words with complex regular patterns are usually spelled correctly. A range of punctuation is generally used accurately. Work is legible and well presented. Communicate meaning in a lively way, showing an awareness of the readers. Select form appropriate for their purposes (narrative and nonnarrative). Link Ideas and/or events. Reflect the purpose of the writing in the organisation. Make ambitious word choices although may include inaccuracies with some words used for effect. Use vocabulary that is appropriate to the subject matter, eg use of technical words. Show awareness of a wide range of stimuli, e.g. visual and audio. Plan and review their writing and present it clearly in order to communicate their meaning effectively Write with clear organisation and structure. Use text forms appropriately and consistently. Extend ideas logically in sequences using connectives like also, as well, because, but. Show awareness of appropriate layout conventions, eg use of main heading, introduction and conclusion. Show the beginnings of a conscious written style. Choose vocabulary that adds interest, clarity or variety. Respond to a wide range of stimuli e.g. visual and audio Use the structure and linguistic features of a text type accurately. Use the layout of the text appropriately in ways the support the purposes of the writing, eg use of subheadings and diagrams. Organise ideas appropriately for both purpose and reader and develop them in interesting ways. Produce thoughtful and coherent writing with the main points sustained and developed in a logical way. Present information clearly. Write in response to a wide range of stimuli e.g visual and audio Organise their writing into paragraphs State opinions with some reasons Write in a lively, interesting way in a range of forms Use layout to support the coherent organisation of ideas into paragraphs and/or other layout features. Produce text that is well written in respect of all structural and linguistic characteristics of the chosen text type. Show sustained awareness of the reader, both through the way the text is structured and presented and through the convincing use of language chosen to entertain, persuade, interest, etc. Use a varied vocabulary confidently to create effects, appropriate to the form and purpose of the writing. Choose an appropriate formality and style that is sustained throughout. Choose an appropriate tone and demonstrate control over the language. Engage in extended writing in response to a wide range of stimuli e.g. visual and audio Express opinions supported by reasons Pupils’ writing communicates meaning through simple words and phrases. In their reading or their writing, pupils begin to show awareness of how full stops are used. Letters are usually clearly shaped and correctly orientated. Writing (Text Level) Are the children able to…? Draw marks or symbols to represent familiar people and ideas. Adv/MH/misc/Skills Ladder – Writing February 2011 Communicate meaning through marks, shapes and pictures. Understand that marks and symbols convey meaning. Discriminate between print and pictures. Explain simply what they are ‘writing’ about when making marks in response to their interests. ‘Play’ with writing in familiar contexts. Write some distinguishable letters and simple familiar words. Produce meaningful print or marks linked to their own interests. ‘Play’ with writing in different contexts as a means of developing their language and communication skills. Show a growing awareness of the different purposes of writing. Use phrases and longer statements which convey ideas to the reader. Order their writing from left to right and from top to bottom. Show a growing awareness of the different purposes of writing. Writing Skills Ladder Grammar (Sentence level) Are the children able to …? Spelling (Word level) Are the children able to…? Handwriting and Presentation Draw using their preferred hand and experiment with mark making. Are the children able to …? Adv/MH/misc/Skills Ladder – Writing February 2011 Make sequences of marks that represent short sentences or phrases e.g. wavy lines to show a list of items on a shopping list. Write their own names. Write familiar short words for captions and labels. Begin to use simple words and phrases to convey meaning. Show some evidence of word order being consistent with Standard English. Show how full stops and capital letters are used in writing for demarcating sentences. Link ideas using ‘and’. Vary sentence structure, eg by using a variety of sentence beginnings. Use connectives other than ‘and’. Use some descriptive phrases for detail and emphasis. Punctuate most simple sentences correctly (capital letters to demarcate sentences and identify proper nouns and full stops). Use commas to separate items in a list Recognise nouns in sentences and discuss their function Differentiate between common and proper nouns Recognise and use collective nouns. Recognise verbs in sentences. Discuss the function of verbs. Understand difference between verbs in the first and third person Compose sentences where the subjects and verbs generally agree. Compose sentences using past and present tense consistently. Recognise adjectives in sentences and define their function. Recognise adverbs in sentences and define their function. Use simple adjectives and adverbs to add interest and enhance the meaning of the writing. Use punctuation to mark sentences – full stops, capital letters, question marks and exclamation marks – accurately. Construct simple and complex sentences accurately Show time, reason and cause through correct subordination and connectives. Compose sentences using adjectives, verbs and nouns for precision, clarity and impact. Clarify meaning through the correct use of speech marks. Identify and use prepositions to clarify description. Identify pronouns and write appropriate pronouns for a previously named subject or object. Vary sentence structures including longer compound sentences. Use a range of complex sentence types including sentences with adverbial and adjectival clauses with some awareness of how these can affect the reader. Adapt sentence structures so that they are appropriate for text types, purpose and audience. Use connectives confidently to impose order and give emphasis. Choose words and phrases carefully and confidently to add shades of meaning and provide interest for the reader. Use adventurous vocabulary and, where it is used, its use is appropriate to the task, audience and purpose. Use punctuation within sentences usually accurately (commas, and slightly less securely apostrophes, speech marks, colons and semicolons). Punctuate almost all sentences correctly. Use a range of punctuation correctly to vary pace and clarify meaning in narration and direct speech. Use commas within sentences, to avoid ambiguity in relating elements or to show division between clauses. Occasionally use colons, dashes or brackets to structure long sentences. Use a range of sentence lengths and structures confidently to create effects appropriate to the form and purpose of the writing. Vary sentence lengths to enliven the writing, eg word order may be altered to develop themes and sustain the interest of the reader. Make vocabulary choices that are appropriate for the task. Use minor sentences for effect e.g. Fire! Goal! War! Hear and imitate sounds of different lengths and pitches (sound discrimination). Group marks or symbols together showing a growing awareness of words Link sounds to letters, naming and sounding the letters of the alphabet. Hear and say sounds in words in the order in which they come. Produce recognisable letters often linked to their own name. Group letters together showing an awareness of how words are made up. Write a few familiar words in a conventional way. Spell some h/f words correctly. Spell CVC words correctly consistently. Spell words with consonant clusters correctly sometimes. Recognise common digraphs Attempt to spell unfamiliar words using a phonic strategy. Make collections of new words linked to personal interest or particular topics. Spell common polysyllabic words accurately. Spell less common graphemes including trigraphs. Recognise a range of prefixes and suffixes Locate apostrophes in words and discuss their function to show possession. Distinguish the meaning and spelling of common homophones. Recognise compound words and discuss the use of the hyphen to join the parts. Develop a range of personal strategies for learning new and irregular words Spell polysyllabic words usually accurately following simple rules. Spell words containing unstressed vowels Know and use less common prefixes and suffixes as aids to word building and spelling Spell with increasing accuracy and confidence, drawing on word recognition and knowledge of word structure and spelling patterns. Usually spell words with complex regular patterns correctly. Reflect on what they have learned about correct vowel choices, pluralisation, prefixes, word endings and h/f words Use a range of appropriate strategies to spell difficult and unfamiliar words Record and learn from personal errors, corrections, investigations, conventions and new vocabulaty Make marks, shapes and lines in response to sounds of differing length, volume and pitch. Make marks using a variety of tools on paper and other materials. Trace, overwrite then copy lines and shapes. Hold a writing implement in a conventional way. Trace, overwrite and form letters. Form some letters with a clear shape independently. Form letters with left to right orientation. Write upper and lower case letters appropriately. Attempt the majority of letter shapes though there may be inconsistencies in size and orientation. Space most words regularly. Discuss word structures. Locate apostrophes in words and discuss their function to show omission. Use plausible phonic or pattern strategies. Show some recall of visual patterns. Spell some common monosyllabic accurately. Spell longer polysyllabic words in a way that is phonically plausible. Make collections of new words linked to personal interest or particular topics and try out strategies to spell them correctly. Produce clear handwriting – with ascenders and descenders that are distinguishable. Differentiate between upper and lower case letters. Produce letters that are accurately formed and consistent in size Write with consistency in the size and proportion of letters, and spacing within and between words. Write consistently with neat, legible, fluent writing. Produce handwriting that is clear and fluent and, where appropriate, is adapted to a range of tasks. Present their work appropriately for the task e.g. using printing or italics.