Responding to global climate change_Scheme of Work
advertisement

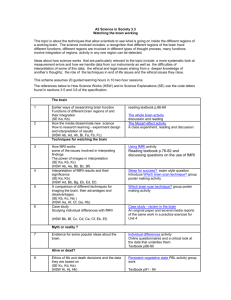
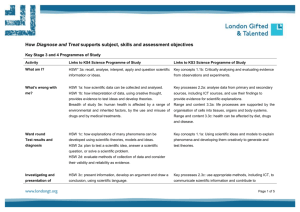
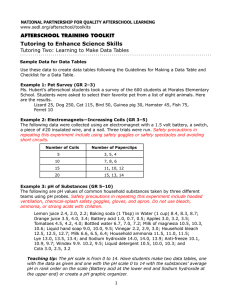
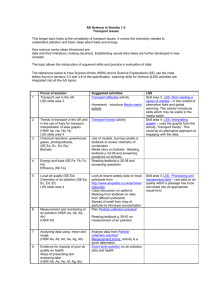
A2 Science in Society 3.4 Responding to global climate change The topic of Climate change is a pressing contemporary policy problem. The topic is explored under four main headings: the evidence that scientists have gathered from a variety of sources to show how climate has changed in the past and why current changes provide evidence for the impact of human activities the way that scientists have developed dynamic models to see how well the science can account for past changes in climate and to make projections about the future the impacts of climate change and their implications for the natural environment and human society. policy responses to climate change across the world taking into account economic as well as technical issues and exploring whether or not it is appropriate to adopt a precautionary approach. In this topic the science explanations are used to show how it is that human activities can change the climate globally. The key ideas are: the cycling of elements between the Earth’s spheres the natural and human-induced processes that affect the carbon cycle such as the burning of fossil fuels the properties of electromagnetic radiation and the interactions of the radiations from the Sun and the Earth’s surface on the atmosphere. There are four main areas of how science works covered in this topic: the way in which scientific explanations develop and are tested the use of dynamic models to test explanations and make predictions the collaborative nature of international science, and the validation of scientific explanations leading to consensus evidence-based policy making under conditions of uncertainty. This scheme of work is divided into ten 2-hour sessions. This can easily be reorganized to match other timetables for the course. In some session there are more suggested resources than could be completed in the time. This offers choice for teachers to match the needs of their students. The references below to How Science Works (HSW) and to Science Explanations (SE) use the code letters found in sections 3.5 and 3.6 of the specification. Focus of session Suggested activities Climate change 1 News items and topical stories about climate change. Impacts on people and the environment around the world (HSW Fb, Ha, Hh) Activity: Climate change in the news Activity: Living with climate change Explaining and modelling climate change 2 3 Greenhouse science, radiation and the greenhouse effect using PowerPoint presentations to explain key terms and ideas (SE: Na, Nb, Nc, Nd, Ne, Nf, Ob) Dynamic modelling, including the role of feedbacks, through manipulation of very simple models (HSW Da, Db, Dc, Dd, De, Ob) Presentation: Climate science Presentation: Earth’s energy budget (CPDN) Textbook p. 99-108 (and p 77) following the presentations students answer the questions in the related section of the textbook. Activity: Dynamic modelling investigating some simple models using excel Activity: A simple climate model (CPDN) using excel to find an equilibrium temperature when variables are changed 4 Modelling climate change Testing models The use of scenarios (HSW Da, Db, Dc, Dd, De, Df, He) Textbook p. 117-122 Activity: climateprediction.net results so far (CPDN) to investigate climate sensitivity Activity: Greenhouse gas emissions forecasts (CPDN) the use of the model to predict the outcomes of different scenarios Questions and discussion on data from models 5 6 Investigating the past through proxy records. Examining the evidence. Using the data to test models and make projections. (HSW Cc, Cd, Ce, Cf, Ch Da, Db, De, Df) PowerPoint presentation Investigating past climates and Activity: Clues from the past Textbook p. 109-117 The science of the carbon cycle, feedbacks and climate forcing (SE Ma, Mb, Mc, Md, Na, Nb, Nd, Ne, Nf) Activity: Why is carbon dioxide so important? (CPDN) (Note: this might be omitted or done as homework) Case study – covering the use of computer models to explain changes to the climate in a particular region. (SE Mb, Nc, Nd, Ne, Ob) (HSW Bd, Cd, Da, Db, Dc, De, Df, Ea, Eb, Ec, Ed, Ee, Ef, Eg, Fd) Power Point presentation Feedback and forcing discussion of questions in presentation and in textbook p. 102-107 Case study – Why is the Arctic warming so fast? Responding to climate change 7 Impacts and their consequences Characteristics of media reporting of the issues. (HSW Fb, Gf, He, Hf) Activity: Climate change impacts independent research and presentation of findings Textbook p. 125-130 8 Start problem-based learning task – local and regional responses to climate change (HSW: Gf, Hb, Hd, He, Hf) PBL - The climate change challenge 9 Responses to climate change from economists and politicians. The role of international agreements and of economic factors in policy making (HSW Fa, Gf, Hb, Hd, He, Hf) Textbook p. 130-134 Presentation: Political responses to climate change Activity: A debate on the issues watching video and analysing the arguments Activity: International decision-making 10 Complete problem-based learning task PBL - The climate change challenge Question covering some key ideas in the topic. (SE Ma, Mb, Mc, Md, Na, Nb, Nc, Nd, Ne, Ob) (HSW Ad, Ag, Db, Df, Fa, Hb, He) Exam style question: Emissions scenarios July, 2011