Semester 2 Exam Review Sheet
advertisement

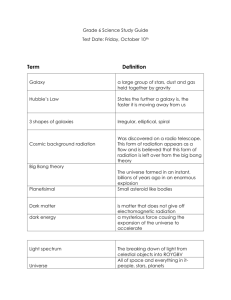
CPE Semester 2 Review 2012-2013 Format & materials: ~140 questions, all multiple choice on Scantron You will need a pencil and eraser You will be given a periodic table with polyatomic ions Any equations you may need (density, solubility) will be given to you. Bring something to do afterward. The test is constructed in order with each unit labeled. That is, the questions are not all mixed up. The number of questions for each unit is proportional to the time spent on the unit. Units that went by pretty quickly don’t have a whole lot of questions, compared to longer units. How to prepare: You will be given all of the formulas on a separate sheet but you need to know what the symbols stand for. Use this packet to determine what to review. Go through this sheet and fill in definitions/answers. Study this material. Review your notes, quizzes, pre-tests, and labs from each chapter. You should be preparing for this test just as you did for each individual chapter test. The pre-test answer keys are available on SchoolPointe. Look back at your test reflections. What did you have trouble with? Be sure to review those things. The test reflection also has ideas for what you should be doing to review at the top of the page. Try some of those things. If you’d like to come in and look at your old tests again you can set up a time with me before or after school. Do a little at a time. Don’t wait until the night before the exam and try to relearn it all. I’ve planned one day in class for us to review together. This will be a question/answer session like we normally do before tests. You should study before this day so that you can have a prepared set of questions to ask me. Ch 20.2 & 20.3: Origins of the Universe Terms: Hypothesis Scientific Law Red shift CBMR (cosmic background microwave radiation) Dark matter Light year Singularity Hubble Hoyle Galaxy Elliptical galaxy Cluster Scientific Theory Universe Blue shift Doppler Effect Supernova Big Bang Lemaitre Einstein Penzias & Wilson Spiral galaxy Irregular galaxy Things you should be able to do: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. R. S. T. U. I can recognize and describe the similarities and difference between Theory, Law, and Hypothesis I can define what a galaxy is I can differentiate between elliptical, spiral, and irregular galaxies I can explain what constitutes good scientific theory and evaluate Big Bang Theory accordingly I can describe the Big Bang as the creation and expansion (rather than an explosion) of space, time, matter and energy I can identify the originator of Big Bang Theory I can identify the individual whose theories lead to the demise of the idea that the universe is “static” and unchanging I can describe cosmic background radiation is and relate it to events as described by Big Bang Theory I can identify when/who discovered CBR I can relate the findings from the WMAP project about CBR to the evolution of the universe I can describe the concept of an expanding universe and relate it to Big Bang Theory I can identify when/who discovered evidence of the universe expanding I can explain the evidence leading to a conclusion that the universe is expanding (explain Red Shift/Blue Shift/Doppler effect of light in terms of perceived frequency and wavelength) I can trace the major events that occurred in the evolution of the universe according to Big Bang Theory (know what the theory describes) I can identify/describe 3 possible outcomes for the fate (end) of the universe based upon the balance between mass and gravity I can identify the characteristic property of matter that will ultimately determine the fate of the universe I can describe where the light matter (hydrogen and helium) come from according to BBT I can describe where heavier elements up to iron come from according to BBT I can describe where elements heavier than iron come from according to BBT I can describe the age of the universe according to BBT Describe the nature of dark matter and its relevance to the evolution of the universe Things to ask Mrs. Nenadal about: Ch 2, 3.1: Properties of Matter Terms: - Matter - Element - Atom - Compound - Molecule - Pure Substance - Mixture - Density - Physical Change - Chemical Change - Homogeneous - Heterogeneous - Suspension - Endothermic - Alloy - Physical property - Kinetic Theory - Solution - Gas - Solid - Liquid - Plasma - Evaporation - Condensation - Sublimation - Melting - Boiling - Freezing (solidification) - Exothermic - Flammability - Reactivity - Chemical property Equations you should know: Density = Mass / Volume Things you should be able to do: - Define/discuss the terms listed above Classify mixtures as homogeneous or heterogeneous Classify properties of matter as either physical or chemical Classify changes in matter as either physical or chemical Classify substances as pure substances or mixtures Understand how matter is organized (the matter tree) Summarize the main points of the kinetic theory of matter Solve problems relating to density Interpret and analyze change of phase information presented in a graph Discuss what happens at the particle level as a substance absorbs/loses heat energy and undergoes changes of phase (relate to kinetic theory) Things to ask Mrs. Nenadal about: Ch 7: Solubility and Concentration Terms: Solubility Insoluble Solute Saturated Unsaturated Dilute Polar Hydrogen bonding Soluble Solution Solvent Supersaturated Concentrated Concentration Non-polar Equations: Concentration = mass of solute / volume of solvent ***Don’t forget you can always set up problems as a proportion m1 = m2 v1 v2 Things you should be able to do: Identify and explain how shaking a mixture can influence the dissolving process Identify and explain how heating a mixture can influence the dissolving process Identify and explain how breaking up the solute can influence the dissolving process Describe how water is capable of dissolving so many different solutes (what does it mean to be polar?) Solve problems relating to concentration, including using a proportion Interpret and analyze solubility information from a graph of solubility vs. temperature o Determine amounts that can dissolve o Determine required temperatures for dissolving o Determine whether a given solution is saturated or unsaturated o Determine the state of matter of a solute and explain your conclusion Describe how to tell if a substance is polar or nonpolar Describe how to tell if a solution is unsaturated, saturated or supersaturated Explain the phrase “like dissolves like” Things to ask Mrs. Nenadal about: Ch 4: Atomic Structure & the Periodic Table Terms: Atom Democritus JJ Thomson Niels Bohr proton neutron electron nucleus energy level group/family semiconductor metal atomic number valence electron - element - John Dalton - Ernest Rutherford - Mendeleev - ion - Bohr model - Lewis diagram - periodic table - quantum model - period - metalloid - non metal - atomic mass - isotope Formulas: #p+ = atomic number #e- = #p+ in a neutral atom #n0 = atomic mass (rounded off) – atomic number Things you should be able to do: Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons for any element Explain the relationship between atomic mass and isotopes of an element Relate the organization of the Periodic Table to the arrangement of electrons within an atom Draw/analyze and interpret Bohr models for elements 1-18 Draw/analyze Lewis dot diagrams Explain the organization of the periodic table in terms of electron arrangement Tell the number of valence electrons in a group/family Determine the number of valence electrons for any element given its column on the periodic table (not including columns 3 -12) Locate and recognize characteristics of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids Given a description of an element’s properties, identify the atom’s family Relate the number of valence electrons to chemical properties Determine the number of energy levels based on row in the periodic table Describe the contribution of different scientists to our understanding of the atom by describing their model of the atom Compare and contrast older models of the atom to the current quantum theory. Things to ask Mrs. Nenadal about: Ch 5, 6.3: Compounds and Reactions Terms you should know: - chemical formula ionic bond covalent bond ion diatomic molecule polyatomic ion subscript - oxidation number - valence electrons - Lewis diagrams - reactants - products - balanced chemical equation - coefficient Things You Should Be Able To Do: - Determine the charge associated with ion formation of various elements; relate this to its position on the Periodic Table Determine the number of atoms of any element in a compound given the chemical formula Distinguish between what happens in an ionic and covalent bond Identify element combinations as either ionic or covalent Draw Lewis diagrams that represent ionic bonds Draw Lewis diagrams that represent covalent bonds Write chemical formulas for given combinations of elements and/or polyatomic ions (given elements, write the compound) Given the chemical formulas, name simple ionic compounds (including ones containing polyatomic ions) Given the chemical formulas, name covalent compounds Write chemical formulas given the compound name Balance chemical equations given the formulas Given the names of compounds in a chemical reaction, write the formulas for the compounds and balance the equation Things to ask Mrs. Nenadal about: Ch 8: Acids and bases Terms: acid base electrolyte strong acid/base weak acid/base titration equivalence point dissociate salt hydroxide ion hydronium ion pH antacid neutralization ionize indicator Things you should be able to do: Describe the ionization of acids and dissociation of bases Explain the difference between strong acids and weak acids Describe and interpret the pH scale Relate the pH scale to concentration of hydronium ions in a solution Give examples of common household acids and bases Predict the product of a neutralization reaction Compare relative strengths of acids and bases on the pH scale Predict the reaction of common indicators to acids and bases (e.g. litmus paper, phenolphthalein) Things to ask Mrs. Nenadal about: Ch 9: Nuclear Changes Terms: isotope radioactivity alpha particle gamma ray fission strong nuclear force radioactive tracer mass number radiation beta particle half life fusion repulsion force background radiation Things you should be able to do: correctly write/interpret the formula for any isotope identify the types of nuclear decay and their products calculate the half-life of an element, mathematically and/or graphically distinguish between fission and fusion and give examples of each explain the relationship between mass and energy in a nuclear reaction describe what strong nuclear force does in the atom describe sources of natural nuclear radiation describe benefits/risks of nuclear energy Things to ask Mrs. Nenadal about: