Observing Academic Communicative Competence I
advertisement

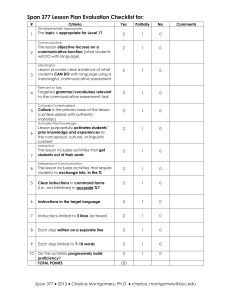
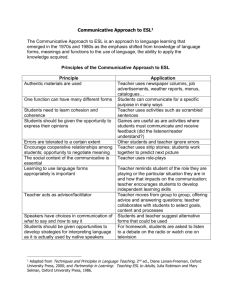
UMEI004C Spring 11 1 Observing Academic Communicative Competence II Observing Academic Communicative Competence Lecturer Name: Name: Date: Time: Sociocultural Class setting (number of students, gender distribution, seating arrangement, lighting, technology, audio-visual materials) Class identities/participant roles (e.g. facilitator, elicitor/questioner, elaborator, collaborator, competitor, clarifier, etc.) Nonverbal behavior/body language Values/beliefs shared by participants (e.g. critical thinking, domain knowledge/expertise, genre knowledge, literacy, openmindedness, respect, competition, cooperation, collaboration, etc.) Notes: Cognitive Outside class reading/writing preparation/tasks (e.g. chapter, article): UMEI004C Spring 11 2 Observing Academic Communicative Competence II Outside class listening/speaking preparation/tasks (e.g. lecture, film): In-class reading/writing/listening/speaking tasks (e.g. article, text excerpt, writing prompt, lecture, group discussion, etc.): In-class academic tasks (e.g. comprehension, analysis, synthesis, evaluation, elicitation/questioning, elaboration, argument, counterargument): Sequencing of academic tasks: Class discussion/lecture topic(s): Sequencing of discussion/lecture topic(s): Notes: UMEI004C Spring 11 3 Observing Academic Communicative Competence II Pragmatic Genres used to organize class discussion(s). Note: genres are related to communicative purposes, and academic speech commonly uses more than one genre to accomplish its communicative goals. What genres are used to organize the discussion(s)/lecture(s)? □Summary □Comparison/contrast □Summary/Response □Narrative □Exposition □Classification □Extended Definition □Argument □ Exemplification □Problem/Solution □Analogy □ Description Lexicogrammatical Lexical bundles/fixed expressions . Record the most common lexical bundles or fixed expressions used in the speech you hear. (The last page has a list of some of the most commonly used in academic speech according to MICASE) i Grammatical Which grammatical structures were most commonly used? Why do you think this is the case? □Passive voice □Present tense narrative □Active voice □Past tense narrative UMEI004C Spring 11 4 Observing Academic Communicative Competence II □Modality Which were the most common forms of modality used to express degrees of certainty? Why? What does modality tell us about the discourse community? Prosodic/Music Intonation and pitch Intonation and pitch communicates a very important part of meaning. Which intonation and pitch patterns were most prevalent in the discussion? Why? □Falling (statements) □Falling (commands) □Rising (incomplete thoughts across an utterance chunk) □Rising (questions) Notes: Register What register(s) were most prevalent in the discussion? Why? □Formal/general academic □Formal/discipline-specific technical □Formal/discipline-specific scientific □Informal/general academic □Informal/conversational Notes: Examples of common lexical bundles/collocations in academic discourse from MICASE □you can see □and so on □and in fact □in your mind UMEI004C Spring 11 5 Observing Academic Communicative Competence II □what I mean □in this case □I was like □you don’t know □so you have □point of view □you know what I mean □you don’t know □all of these □the first/second, etc. one □does that make sense □how do you know □other □in the book □it doesn’t matter □do you see □what I’m saying □how do you know □so that’s why □in this class □in this one □it turns out □in some sense □in the same way □look at it