unit 3 test review - Doral Academy Preparatory
advertisement

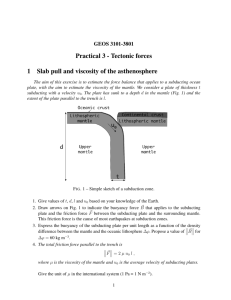
LAYERS OF THE EARTH, PLATE TECTONICS & SURFACE FEATURES STUDY GUIDE Heat from Earth's mantle and core causes convection currents to form in the ___________ In 1910, a young German scientist named Alfred __________ became curious about the relationship of the continents. He formed a hypothesis that Earth's continents had moved!? Describe two examples of evidence Alfred Wegener used to support his theory of continental drift. What was the main reason scientists rejected Wegener's theory of continental drift? In 1960, American geologist Harold Hess proposed a radical idea. He suggested that the ocean floors move called ___________, carrying the continents along with them. What is the evidence for sea-floor spreading? How do the processes of sea-floor spreading and subduction affect the Earth’s oceans? What is the theory of plate tectonics? Where would you expect to find the oldest rock on the ocean floor? Explain your answer. Describe the three types of plate boundaries. As the plates move, they collide, pull apart, or grind past each other, producing spectacular changes in Earth's surface. These changes include __________, ______________, and ______________ List the three kinds of convergent plate boundaries What evidence of Earth's climate in the past supports the theory of continental drift? What are the 5 types of mountains? Give a brief description of each. The mountain range where the world’s largest mountain is found (Mount Everest) is on what continent and is called what? What are the 5 types of volcanoes? Give a brief description of each. Which type of volcano has the most violent eruptions? Which volcano destroyed the city of Pompeii and what happened to the people? What is the Richter scale? Explain a Tsunami and how it forms in the Ocean. Be able to give an example of one of the most famous disastrous Tsunami’s that occurred in 2004. * IMPORTANT WORDS THAT WILL BE ON YOUR TEST* Crust The layer of rock that forms Earth's outer surface. Mantle The layer of hot, solid material between Earth's crust and core. Lithosphere A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. Asthenosphere The soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats. Outer core A layer of molten iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core of Earth. Inner core A dense sphere of solid iron and nickel in the center of Earth. Pangaea The name of the single landmass that broke apart 225 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents. Continental drift The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth's surface. Mid-ocean ridge The undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary. Sea-floor spreading The process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor. Deep-ocean trench A deep valley along the ocean floor through which oceanic crust slowly sinks toward the mantle. Subduction The process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary. Plate A section of the lithosphere that slowly moves over the asthenosphere, carrying pieces of continental and oceanic crust. Theory of plate tectonics The theory that pieces of Earth's lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. Transform boundary A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions. Divergent boundary A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other. Convergent boundary A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.