Specialization nr 13: Veterinary Radiology
advertisement

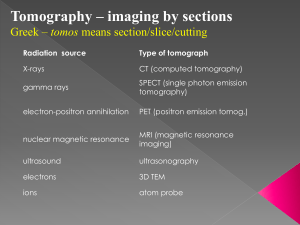
Specialization nr 13: Veterinary Radiology The national managerin term of office 2008 – 2012 Tadeusz Narojek DVM Duration of training–6 semesters 4 semesters – lectures, exercises, seminars 2 semesters - clinical training Lectures – 126 hours Seminars – 56 hours Clinical training – 120 hours Lectures 1. History of veterinary radiology, radiation safety, radiographic techniques, radiographic processing, principles of clinical anatomy –16 hours 2. Diagnosis of thorax diseases – 16 hours 3. Diagnosis of abdomen diseases – 16 hours 4. Diagnosis of appendicular skeleton diseases – 16 hours 5. Ultrasound diagnostics, examination techniques, interpretation ultrasound images –16 hours 6. Diagnosis of nerves system diseases, radiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance – 16 hours 7. Endoscopy, imaging of exotic animals and birds, legal issues in veterinary practice – 16 hours Seminars 1. 2. 3. 4. Performance of imaging examination in X-ray and ultrasound lab. – 14 hours Interpretation of X-ray and ultrasound images – 14 hours Presentation of their own cases – 14 hours Presentation of their own articles, lectures – 14 hours Clinical training – 120 hours Examination small and large animals using X-ray and ultrasound equipment, documenting those tests, processing images diagnostic References Wojciech Empel „Radiodiagnostyka weterynaryjna” A. Coulson, N. Lewis „Atlas interpretacji obrazów radiograficznych anatomii psa i kota” (tłumaczenie na język polski) T. Nyland, J. Motton „Diagnostyka ultrasonograficzna małych zwierząt” Kealy J.K., McAllister.: „Diagnostyka radiologiczna i ultrasonograficzna psów i kotów” Individual training is not envisaged THE DESCRIPTIVE PART A. General I. Introduction 1. History of discoveries related to the diagnostic imaging 2. History of diagnostic imaging in Poland II. Principles of radiographic techniques 1. Physics of X-rays 2. Characteristics of X-rays important from the point of view of the veterinary diagnostic 3. Construction of X-ray tube 4. Construction of X-ray machine 5. Methods of radiology examination - Radiography - Radioscopy - X-ray TV - Tomography - Computed tomography III. Radiography as a primary diagnostic imaging in veterinary practice 1. Projection using in X-ray examination 2. X-ray picture a. Quality of radiogram b. Artifacts 3. Principle of X-ray picture interpretation 4. Indications and contraindications to X-ray examination 5. Contrast agents using in X-ray examination 6. Technique of procedures utilize contrast agents IV. Tomography 1. Projection using in tomography 2. Tomography picture a. Quality of tomogram b. Artifacts 3. Principle of tomogram interpretation 4. Indications and contraindications to tomography examination V. Computed tomography Principle of action computed tomography Construction of CT machine Technique of CT examination Creation of CT image Processing of CT image a. Selection of image parameters b. Multiplanar reconstruction c. Three dimensional reconstruction d. Virtual endoscopy 6. Principle of CT pictures interpretation 7. Use contrast agents in computed tomography 8. Indications and contraindications to CT examination 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. VI. Ultrasonography Physics of ultrasound. Piezoelectric effect Producing a sound wave, receiving the echoes, forming the image Echo effect, Doppler effect Principle working ultrasound machine Ultrasound picture - sonogram a. Modes of sonography b. Principle of sonogram interpretation c. Artifacts 6. Ultrasound machine a. Type of ultrasound machines b. Ultrasound transducers – choice to veterinary practice 7. Indications and contraindications to ultrasound examination 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. VII. Magnetic resonance tomography 1. 2. 3. 4. Magnetic resonance effect Construction of MR machine Processing of MR image Artifacts 5. Indications and contraindications to MR examination VIII. Safety at work. Protection of staff, patient, owner against radiation 1. Dangerous to use X-ray examination. Radiation safety rules diagnostic radiography 2. Safety of ultrasound examination 3. Dangerous during magnetic resonance examination B. Specifics I. Diagnostic imaging od the abdomen 1. Imaging way of abdomen a. Radiography b. Ultrasonography c. Computed tomography d. Magnetic resonance 2. Indications and contraindications to use particular examination type 3. Normal and abnormal image of: a. Abdominal wall b. Peritoneum c. Liver, gall bladder d. Spleen e. Pancreas f. Alimentary system i. Pharynx ii. Esophagus iii. Stomach iv. Intestine g. Adrenal gland h. Urinary tract i. Kidney ii. Ureters iii. Urinary bladder iv. Urethra i. Female genital tract i. Ovary ii. Uterus iii. Vagina j. Specificity imaging of female genital tract in large animals k. Male genital tract i. Prostate ii. Testis iii. Penis l. Specificity imaging of male genital tract in large animal II. Diagnostic imaging of the thorax 1. Imaging way of thorax a. Radiography b. Ultrasonography c. Computed tomography d. Magnetic resonance 2. Indications and contraindications to use particular examination type 3. Normal and abnormal image of: a. Thoracic wall b. Pleura c. Trachea d. Bronchi e. Lungs f. Diaphragm g. Mediastinum h. Cardiovascular system i. Heart ii. Vessels III. Diagnostic imaging of the head and neck 1. Imaging way of head and neck a. Radiography b. Ultrasonography c. Computed tomography d. Magnetic resonance 2. Indications and contraindications to use particular examination type 3. Normal and abnormal image of: a. Nasal cavities b. Frontal sinuses c. Teeth d. Throat e. Larynx f. Hyoid bone g. Cervical trachea h. Thyroid gland i. Parathyroid gland IV. Diagnostic imaging of themusculoskeletal system 1. Imaging way of musculoskeletal system a. Radiography b. Ultrasonography c. Computed tomography d. Magnetic resonance 2. Indications and contraindications to use particular examination type 3. The bone a. Bone development b. Normal image of the bone c. Diseases of the bone i. Developmental malformation ii. Metabolic diseases iii. Ostechondrosis iv. Bone inflammatory v. Bone neoplasia vi. Posttraumatic changes 4. Joints a. Normal image of the joint b. Joints diseases i. Developmental anomaly ii. Inflammation iii. Neoplasia iv. Posttraumatic changes V. Neuroimaging 1. 1. Imaging way of musculoskeletal system a. Radiography b. Ultrasonography c. Computed tomography d. Magnetic resonance 2. Indications and contraindications to use particular examination type 3. The skull a. Normal image of the skull b. Diseases of the skull i. Developmental malformation ii. Metabolic diseases iii. Bone inflammatory iv. Bone neoplasia v. Posttraumatic changes 4. Spinal cord a. Normal image of the spinal cord b. Diseases of the spinal cord i. Developmental malformation ii. Degenerative disease iii. Discopathy iv. Inflammatory v. Neoplasia vi. Posttraumatic changes 5. The brain a. Normal image of the brain b. Diseases of the brain i. Developmental malformation ii. Degenerative disease iii. Inflammatory iv. Neoplasia v. Posttraumatic changes