Electron Tomography
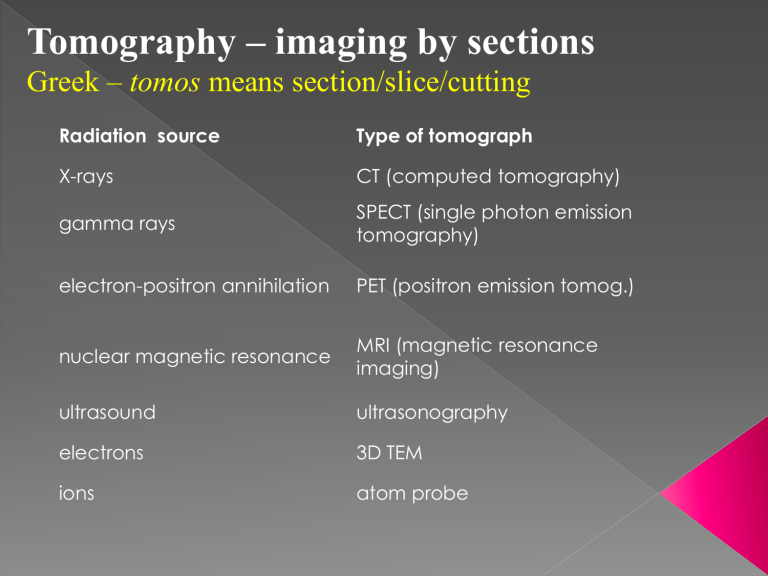
Tomography – imaging by sections
Greek – tomos means section/slice/cutting
Radiation source
X-rays gamma rays
Type of tomograph
CT (computed tomography)
SPECT (single photon emission tomography) electron-positron annihilation PET (positron emission tomog.) nuclear magnetic resonance ultrasound electrons ions
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) ultrasonography
3D TEM atom probe
Three dimensional imaging in TEM
Serial
Sectioning
Alignment of adjacent sections is one of the most difficult aspects of serial reconstruction
Registration points are often used to assist alignment (registration)
Electron Tomography
Electron Tomography
An object viewed from many different angles will generate slightly different images.
Object creates multiple images so the inverse is also possible
These images can be recorded and analyzed to create a tomographic rendering of the specimen.
It is computationally easier to carry out the calculations in Fourier space than it is in image space.
Single reverse FFT
-can enhance symmetry
M.ultiple images can be generated in one of two ways:
1) A single object can tilted and viewed from many different angles.
2) A field of randomly oriented identical objects can be image in a tilt pair.
Electron Tomography
Double tilt holder
Gatan cryo-holder allows samples to be placed into the TEM while being kept frozen at LN temperatures
Solid models constructed from various views