Greek & Latin Roots - Clayton Valley Charter High School
advertisement

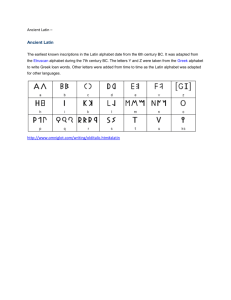
Greek & Latin Roots 1) Photos (Greek): light a. Photograph [graph: write or draw] – picture drawn by light b. Telephoto [tele: distant] – light from far away c. Photometer [metron: measure] – a device which measures light d. Phototropic [tropos: turn] – turning toward light e. Photophilia [philia: love] – love of light f. Photophobia [phobos: fear] – fear or dislike of light g. Photosynthesis [syn: together, thesis: putting] – a process of putting things together by using light 2) Graph [Gram] (Greek): to write or draw a. Photograph [photo: light] – picture drawn by light b. Phonograph [phono: sound] – machine for writing [i.e. recording] sound c. Phonogram [phono: sound] – written symbol for a sound d. Telegraph [tele: distant] writing from far away e. Lithograph [lithos: stone] – drawing made on stone f. Graphite – black carbon used for drawing or writing g. Autograph [autos: self] – to write one’s own name h. Hologram [holos: complete] – a three-dimensional photograph of a whole object 3) Tele (Greek): far away, distant a. Television [video, visum – Latin: see] – seeing distant things b. Telephone [phone: sound] – sound from far away c. Telegraph [graph: write] – writing from a distance d. Telephoto [photo: light] – light from far away e. Telescope [skopeo: look at] – device for looking at distant objects f. Telepathy [pathos: feeling] – knowing how someone far away is feeling g. Telethon [Marathon: a battlefield in ancient Greece] – a telephone fund raiser which runs non-stop, as Pheidippides ran after the battle of Marathon 4) Metron (Greek): measure a. Meter – unit of measure – 39.47 inches long b. Geometry [geo: earth] – measurement of the earth c. Optometry [opsis: sight] – measure eyesight d. Symmetry [sym: same, equal] – measure the same e. Barometer [baros: weight, pressure] – device to measure air pressure f. Thermometer [thermos: heat] – measure heat g. Diameter [dia: through, across] – measuring across h. Centimeter [centum: hundred] – one hundredth of a meter i. Anemometer [anemos: wind] – measures wind speed 5) Tropos (Greek): turning a. Tropics – the area of the earth from the equator north to the Tropic of Cancer and south of the Tropic of Capricorn b. Tropical – the climate of the earth in the tropics c. Phototropic [photo: light] – turning toward the light, as leaves and flowers do d. Heliotrope [helios: sun] – a flower named for its tendency to turn toward the sun e. Tropophilous [philia: love] – plants or trees which like a change or turning of seasons – hot and cold, wet and dry f. Thermotropism [thermos: heat] – turning toward heat, as cats do 6) Philia (Greek): love, friendship a. Philosopher [Sophia: wisdom] – one who loves wisdom b. Philadelphia [adelphos: brother] – city of brotherly love c. Philanthropist [anthropos: man] – one who cares about his fellow man d. Phillumenist [lumen: light] – one who collects match covers e. Philogynist [gyne: women] – one who loves women f. Philtre – love potion g. Anglophile [Angli: English] – one who loves England 1 h. Francophile [Francus: France] – one who loves France 7) Phobos (Greek): fear a. Phobia – irrational fear b. Agoraphobia [agora: field] – fear of open space c. Claustrophobia [claustrum – Latin: lock or bolt] – fear of closed spaces d. Hydrophobia [hydro: water] – disease which makes it difficult to swallow, thought to be fear of water e. Phobophobia – fear of fear itself f. Zoophobia [zoon: animal] – fear of animals g. Toxikophobia [toxikos: poison] – fear of poison h. Phobos – a moon of the planet Mars 8) Syn (Greek): with, together a. Sympathy [pathos: feeling] – to feel with someone else b. Symphony [phone: sound] – sounds that go together c. Synthesis [thesis: put, place] – putting together d. Synthetic – material made by putting chemicals together e. Photosynthesis [photo: light] – process by which light puts plant nutrients together to make green chlorophyll f. Synonym [onoma: name] – two words with the same meaning g. Synagogue [ago: bring] – place to bring people together h. Synchronize [chronos: time] – to do things at the same time. “Synchronize your watches!” 9) Thesis (Greek): put, place, position a. Thesis: a position taken in an argument supported by a set of reasons b. Theme: an essay or composition on a certain subject with a statement and supporting reasons c. Parenthesis [para: beside] – statement beside (or inside) a main sentence d. Synthetic [syn: together] – elements put together to make a material like a natural one (synthetic rubber) e. Synthesizer [syn: together] – instrument which puts sounds together like real musical instruments 10) Kinesis (Greek): movement a. Kinetic: relating to the movement of bodies b. Kinesiology [logos: word or study] – study of human movement c. Kinescope [skopeo: look at] – a machine that shows pictures of movement (old term for television) d. Cinema: motion pictures (Greeks had no “c” – they used “k”) e. Cinamatographer: motion picture photographer 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11) Phone (Greek): sound a. Phonograph [graph: write or draw] – writing with sound b. Telephone [tele: far away] – sound from far away c. Phonogram [gramma: letter] – written sound d. Euphony [eu: well, good] – good or pleasant sound e. Symphony [syn: together] – sounds that go together f. Megaphone [mega: big] – device to make sounds BIG g. Microphone [mikros: small] – device to transmit or record small sounds 12) Sonus (Latin): sound a. Sound – vibrations perceived by our ears b. Sonic – relating to what we can hear c. Sonnet – a form of rhyming Italian poetry d. Sonovox – a machine that makes sound effect voices e. Sonar – device that hears sound under water f. Sonata – an instrumental musical composition with three or four movements g. Sonsonant [con: with] – speech sounds made with lips, tongue, or teeth 13) Skopeo (Greek): look at, inspect, consider, examine a. Scope – all that the eye can see b. Microscope [mikros: small] – device to look at small objects c. Telescope [tele: distant] – device for seeing distant objects d. Periscope [peri: around] – device for seeing around obstacles e. Kaleidoscope [kalos: beautiful, eidos: form] – device for seeing changing beautiful forms or arrangements of small fragments of glass, etc. f. Episcopal [epi: on, over] – overseen by bishops or “overseers” g. Bishop – a church overseer 14) Video / Visum (Latin): see a. Television [tele – G: distant] – machine for seeing things far away b. Videophone [phone – G: sound] – TV screen for seeing the person you are talking to on the telephone c. Montevideo [mons, montis: mountain] – “Mountain View” – a city in Uruguay d. Video – picture portion of television e. Evidence [e, ex: out] – out of what one can see f. Advise [ad: to, toward] – look and tell your view g. Invisible [in: not] – not to be seen 15) Logos (Greek): word, study a. Logic – reasoning to gain knowledge or wisdom b. Geology [geo: earth] – study of the earth c. Astrology [astron: star] – knowledge from the stars d. Biology [bios: life] – study of physical life e. Zoology [zoo: animal] – study of animals f. Technology [techne: art, skill] – study of how to improve an art or a skill g. Anthropology [anthropos: man] – study of mankind h. Psychology [psyche: soul, life] – study of the soul or mental life of a man i. Legend – a story to be read 16) Verbum (Latin): word a. Verb – the action word in a sentence b. Proverb [pro: forward] – a wise or profound saying c. Verbal – of, or pertaining to, words d. Verbiage – use of too many words; chatter e. Verbose [-osus: full of] – wordy, full of words f. Verbatim – word-for-word copy or record g. Verbalize – to express in words h. Verberium – game in which a word is changed into others by rearranging its letters 17) Nomen / Nominis (Latin): name a. Nominate – suggest someone’s name for office 3 b. Nomination – act of naming a candidate for office c. Nominal – in name only; not real or actual d. Nomenclature [calo, calatum: call] – system of names used to classify knowledge; what we call things e. Nom de plume [French] – pen name of an author f. Denomination [de: down from] – names of classes or categories, e.g. religions, money g. Denominator – part of a fraction below the line 18) Pro (Latin): for, before, forward, in place of a. Profess [fateor, fassus sum: admit, reveal] – to admit that one is an expert b. Professional – one who claims to be an expert c. Problem [ballein – G: throw] – anything thrown forward to be worked on, or solved d. Proboscis [boskein – G: feed or graze] – trunk or snout for grazing e. Prologue [logos – G: word or study] – words before beginning of a play or book f. Proclaim [clamo, clamatum: shout] – announce, cry out, publish g. Proceed [cedo, cessurus: move, yield] – move forward h. Pronoun [nomen: name] – word that stands for a noun 19) Prae (Latin): before, in front of a. Predict [dico, dictum: say] – say beforehand, foretell b. Preamble [ambulo, ambulatum: walk] – that which goes before c. Precaution [caveo, cautum: be on guard] – being on guard beforehand d. Precursor [curro, cursum: run] – one who runs ahead e. Prefer [fero, latum: bear, carry] – carry to a forward position or rank f. Pregnant [gigno, genitum: bring forth] – condition before birth g. Prejudice [judicium: judgment] – make judgment beforehand 20) Ad (Latin): to, toward, near, next to a. Adequate [aequus: level, even, flat] – even with or equal to b. Adhere [haereo, haesum: stick to, stay] – stick to c. Adjective [jacio, jactum: throw] – word “thrown at” a noun to modify it d. Admire [miror, miratum: be amazed, wonder] – look at with wonder or amazement e. Admonish [moneo, monitum: warn] – give warning to f. Admit [mitto, missum: send] – send to; allow entrance to a place or to the mind g. Advertise [verto, versum: turn] – turn people to what you are offering 21) Jacio / Jactum (Latin): throw a. Eject [e, ex: out] – throw out b. Interject [inter: between] – throw between c. Object [ob: against] – throw against d. Objection – arguments against a situation e. Project [pro: forward] – throw forward f. Projectile – a thing throw forward (e.g. arrow, bullet, rock) g. Reject [re: back, again] – throw back 22) Pono / Positum (Latin): lay, put, place a. Pose – position or attitude b. Post – fixed or established place; military post c. Postage – payment for messages sent from post to post d. Position – established place e. Deposit [de: down, away from] – lay away; put aside f. Repose [re: again, back] – lie back, pause, rest g. Depose [de: down, away from] – put down from a throne or high office h. Impose [in: in, on, upon] – to put upon i. Component [con: together] – put together 23) Cum (Latin): with, together a. Cooperate [operor, operatum: work] – work with b. Cognate [nascor, gnatus: be born] – born together, having the same ancestors c. Collaborate [laboro, laboratum: work] – work with d. Collect [lego, lectum: gather] – gather together e. Combat [battuo: beat, fight] – fight with 4 f. Commemorate [memoro, memoratum: remember] – remember something together g. Community [munio, munitum: build, fortify] – group which builds together h. Content [teneo, tentum: hold] – held together i. Confection [facio, factum: do, make] – made together 24) Figo / Fixum (Latin): fix, fasten, attach a. Fix – fasten or make firm; set in place b. Fixture – a thing fastened in place c. Crucifix [crux, crucis: cross] – picture, medal, or statue of Christ fastened to the cross d. Áffix (noun) [ad: to] – thing fastened to something; syllable added to a word at either end e. Affix (verb) – act of fastening or attaching f. Prefix [prae: before] – letter or syllable added to the beginning of the word g. Suffix [sub: under] – letter or syllable added to the end of the word 25) Jungo / Junctum (Latin): join, unite, connect a. Join – connect; fasten together b. Joint – place where two parts are connected c. Conjugal – relating to the joining of people in marriage d. Conjugation – a set of verb endings joined with the stem e. Conjunction – word joining two parts of a sentence f. Disjointed [dis: separate] – separated at the joints g. Junction – point of connection; railway crossing h. Subjugate [sub: under] – to connect under the yoke of power 26) Digitus (Latin): finger, toe, inch a. Digit – finger; numerals from 0 to 9; unit of measure the width of a finger (3/4 of an inch) b. Digital computer – computer which uses numerals to mean whole numbers and decimal fractions c. Digitalis – the “foxglove” plant from which heart medicine is made d. Prestidigitation [praesto: at hand, prompt] – a fast-fingered or sleight-of-hand performance of magic or of card tricks 27) Caput / Capitis (Latin): head a. Capital – top of a column; head, chief, or foundation money b. Capitalism – system where the “head money” makes money c. Captain – head of a group of soldiers d. Capitulate – put headings on chapters or divisions in a piece of writing e. Recapitulate [re: again] – to list again the “headings” in a piece of writing f. Cabbage – vegetable “head” 28) Manus (Latin): hand a. Manufacture [facio, factum: making] – make by hand b. Manifest [festus: hit] – to hit by hand; easily perceived c. Manicotti [manica: sleeve] – sleeve-like pasta d. Manuscript [scribo, scriptum: write] – writing, written by hand e. Manumit [mitto, missum: send] – to send forth or release from one’s hand or grasp; to release from slavery 29) Pes / Pedis (Latin): foot a. Pedestal – foot of a column b. Pedestrian – walker, on foot c. Pedal – foot lever d. Peddle / Peddler – house-to-house salesman e. Pedicab – bicycle taxi f. Pedicure [curo, curatum: care] – care for the feet g. Pedigree [“pied de grue”: crane’s foot] – genealogy charts h. Pedometer – measures distance walked i. Pawn (ala chess) – foot soldiers 30) Bracchium (Latin): arm a. Brace – two of a kind (one for each arm) b. Embrace [em: into] – to take into one’s arms c. Bracelet – ornament for the arm or wrist 5 d. Brachiate – to swing by the arms on bars or tree branches e. Brachiopod [podos – G: foot] – two-shelled creature with two “arms” inside with which to bring food f. Bracero – Spanish word for day laborer (with two strong arms) 6 31) Dens / Dentis (Latin): tooth a. Dent – tooth-like notch in gears, locks, etc.; a small depression b. Dentist – tooth doctor c. Dentate – having a toothed edge (leaves) d. Dental – pertaining to teeth e. Dentifrice [frico, fricatum: rub] – toothpaste f. Dentition – development of teeth; teething g. Denture – set of teeth (false) h. Dentiform [forma: shape] – shaped like a tooth i. Indent – set a line of print in from the margin (bite) j. Dandelion [“dent a lion”]: plant called “tooth of the lion” with dentate leaves 32) Corpus / Corporis (Latin): body a. Corporeal – pertaining to the body b. Corps – military division, organized as a body c. Incorporate – to make into a body d. Corporation – legally formed group, a body e. Corpse – dead body f. Corpulence – an excess of body, fat g. Corpus – main body of a fund of wealth, estate h. Corpuscle [diminutive of corpus] – small part of the body 33) Unus (Latin): one a. Unit – one part of a series or of a whole b. Union – act of making one out of many c. E pluribus unum – motto of the U.S.A. “One out of many” states d. United – together as one e. Universe [verto, versum: turn] – star galaxy which turns as one entity, like a cosmic pinwheel f. University [verto, versum: turn] – many colleges joined together to function as one body g. Unicorn [cornu: horn] – mythical horse with one horn on its head h. Unison [sonus: sound] – voices singing or musical instruments playing together the same notes at the same time (as one) 34) Duo (Latin): two a. Duet – music played or sung by two people b. Duplicate [plico, plicatum: fold] – make a second copy c. Dual – two (as in dual purpose) d. Dubious – doubtful, “of two minds” e. Duel – fight between two people f. Duplex [plico, plicatum: fold] – two homes in one building g. Duplicity – two-facedness or to “double cross” 35) Tres (Latin): three a. Trio – three acting or performing together b. Tricycle [cycle: wheel] – a three-wheeled vehicle c. Tripod [podos – G: foot] – a three-legged stand for a camera or other equipment d. Triangle [angulus: corner angle] – a figure with three straight sides and three corner angles e. Triennial [annus: year] – every three years f. Triceratops [keras: horn; tops – G: face] – three-horned face g. Trilobite [lobus: a rounded division] – a prehistoric animal having three rounded divisions of the body (looks like three worms stuck together side-by-side) h. Tribe – early Rome was divided into three family social groups, or clans, called tribes 36) Quattuor (Latin): four a. Quadruped [pes, pedis: foot] – four-footed animal b. Quadricycle [kyclos – G: wheel] – four-wheeled vehicle c. Quadrilateral [latus: side] – having four sides d. Quadragenarian [quadraginta: forty] – person in his/her 40’s e. Quaternity – group of four people 7 f. Quatrain – a stanza or verse of poetry four lines long g. Quadrille – square dance for four couples h. Quadri – prefix meaning four 37) Quinque (Latin): five a. Quinquennial [annus: year] – five-year period or celebration b. Quinquagenarian [quinquageni: fifty each] – person who is 50-59 years old c. Quinquesyllable [syllaba: several letters taken together to make one sound] – a word of five syllables (e.g. quin-que-syl-la-bic) 38) Sex (Latin): six a. Sexennial [annus: year] – six-year period or celebration b. Sexagenarian [sexageni: sixty each] – person who is 60-69 years old c. Sexdigital [digitus: finger, toe] – having six fingers or toes d. Sexcentenary [centum: hundred] – a 600-year period or celebration 39) Septem (Latin): seven a. September – seventh month in the Roman calendar b. Septennial [annus: year] – seven-year period or celebration c. Septangle [angulus: corner angle] – a flat plane figure with seven sides and seven angles d. Septuagenarian [septuageni: seventy each] – person who is 70-79 years old 40) Octo (Latin): eight a. October – eighth month in the Roman calendar b. Octennial [annus: year] – eight-year period or celebration c. Octogenarian [octogeni: eighty each] – person who is 80-89 years old d. Octopus [pous, podos – G: foot] – eight-footed ocean creature e. Octagon [gonia – G: angle] – figure with eight sides and eight corners or angles 41) Novem (Latin): nine a. November – ninth month in the Roman calendar b. Novena – devotions for nine days in the Roman Catholic church c. Novennial [annus: year] – nine-year period or celebration d. Novemdigitate [digitus: finger] – having nine fingers e. Novendial [dies: day] – lasting nine days 42) Decem (Latin): ten a. December – tenth month in the Roman calendar b. Decennial [annus: year] – tenth anniversary or celebration c. Decemdentate [dens, dentis: tooth] – having ten teeth d. Decemfoliate [folium: leaf] – having ten leaves e. Decempedal [pes, pedis: foot] – having ten feet f. Decemplicate [plico, plicatum: fold] – tenfold or ten copies 43) Centum (Latin): hundred a. Cent – one hundredth of a dollar b. Century – a set of one hundred c. Centurion – Roman military officer over 100 men d. Centimeter [metron: measure] – one hundredth of a meter e. Centennial [annus: year] – hundred-year anniversary or celebration f. Percent [per: through] – number of parts in every hundred g. Centipede [pes, pedis: foot] – hundred-footed “bug” h. Centigrade [gradus: step, degree] – temperature scale with one hundred degrees between freezing and boiling 44) Mille (Latin): thousand a. Mile – a thousand paces b. Mill – one thousandth of a dollar c. Millimeter [metron: measure] – one thousandth of a meter d. Millenium [annus: year] – thousand-year period or anniversary e. Millipede [pes, pedis: foot] – thousand-footed “bug” 45) Pyro (Greek): fire a. Pyrotechnics [techne: work, skill] – fireworks 8 b. Pyrotechnician [techne: work, skill] – one who is skilled with fireworks c. Pyre – huge bonfire for burning bodies at ancient funerals d. Pyromaniac [mania: craze] – a crazy person who plays with fire e. Empyrean [em: in] – the heavens f. Pyrometer [metron: measure] – instrument to measure very hot temperatures 46) Ignis (Latin): fire a. Igneous [ous: full of] – pertaining to fire b. Ignite – to set on fire c. Ignition – act of “firing up” or starting an engine; setting anything afire 47) Vulcanus (Latin): Vulcan – Roman God of Fire a. Volcano – a crack in the earth pouring out hot magma and gases b. Volcanic – like or pertaining to volcanoes c. Vulcanize – to treat raw rubber with heat and sulphur to make it harder and more durable d. Vulcanite – hard rubber, treated with heat and sulphur e. Vulcanology [logos: word, study] – the study of volcanoes 48) Hydros (Greek): water a. Hydroplane [planus – L: flat surface] – boat that glides on the surface of the water b. Hydrophobia [phobos: fear] – fear of water c. Dehydrate [de: down or away from] – take water away d. Hydrogen [genos: origin] – a gas which, when burned, produces water e. Hydrophone [phone: sound] – instrument to “hear” under water f. Hydrology [logos: word, study] – study of water g. Hydroelectric [electron: amber] – electricity produced by moving water 49) Aqua (Latin): water a. Aquarium – a pond or tank of water where fish or water plants can live b. Aqueduct [duco, ductum: lead] – a structure for bringing water to where it is needed c. Aquaculture [cultura: till, cultivate] – growing food in water (fish, oysters, seaweed) d. Aquamarine – blue-green color of water e. Aquaplane [planus: flat surface] – surf board f. Aquarius – a constellation called “Water Carrier” g. Aqueous Humor [humor: moisture] – fluid in the eye between the lens and the cornea h. Aquifer [fero, latum: carry] – a layer under the earth where water flows 50) Bonus (Latin): good a. Bonus – something extra good b. Bon Bon [French]: beautifully decorated candy; a good “goody” c. Bonny [Scottish]: good looking d. Boon: a good deed; a favor e. Bounteous [-ous: full of] – plentiful good f. Bounty: plenty or reward g. Bonanza [Spanish: fair weather, prosperity] – rich find in a gold mine h. Debonaire [French: of good disposition] – kindly, jaunty 51) Helios (Greek): sun a. Helios – sun god; also called Apollo or Phaethon b. Heliotrope [tropos: turn] – plant which turns toward the sun c. Helium – light gas used in balloons d. Perihelion [peri: around or near] – closest point to the sun in earth’s orbit e. Aphelion [apo: away from] – furthest point from the sun in earth’s orbit f. Helioscope [skopeo: look] – telescope for looking at the sun g. Heliometer [metron: measure] – instrument for measuring the diameter of the sun 52) Sol (Latin): sun a. Solar – pertaining to the sun b. Solar system – the sun with the objects which revolve around it c. Solarium – a sun dial; a glass-enclosed sun room d. Solaster [astron: star] – a star fish with more than five rays; a sun-star fish e. Parasol [Italian: parare: to ward off] – a light portable sunshade 9 f. Solstice [sisto, statum: set, cause to stand] – stopping or standing still of the sun g. “Old Sol” – folk name for the sun 53) Luna (Latin): moon a. Lunar – of or pertaining to the moon b. Lunatic – mad; affected by the moon c. Lunacy – madness caused by the moon; “moonstruck” d. Clair de Lune (French): moonlight e. Lunambulist [ambulo, ambulatum: walk] – one whose sleep walking is supposedly caused by the moon f. Lunarium – instrument showing the phases and motions of the moon g. Interlunar [inter: between] – time between old and new moon when the moon is invisible h. Lunation – 29 ½ days – a lunar month or the time from one new moon to the next 54) Dia (Greek): through, between, across, apart a. Diabolical [bole: shot, blow] – shot through, possessed (by a devil) b. Diadem [desmos: bond] – bound across the forehead, a wreath or crown c. Diagnosis [gnosis: knowledge] – thorough knowledge d. Diagonal [gony: knee] – line between two non-adjacent corners in a figure of four or more sides e. Diagram [graph: write, draw] – a cross-section drawing f. Diameter [metron: measure] – measure across g. Diamond [a: not + damas: tame] – hardest substance h. Diacritical [krinein: separate] – marks to separate long and short vowel sounds 55) Trans (Latin): across, over, beyond, through a. Transport [porto, portatum: carry] – carry across b. Transaction [ago, actum: do, drive] – trade, exchange c. Transcript [scribo, scriptum: write] – speech put into writing d. Transfer [fero, latum: carry] – carry across e. Transform [formo, formatum: form, shape] – change over to a different form f. Transplant [planta: sprout, plant] – move a plant g. Transparent [pareo: appear] – appear or be seen through 56) Geo (Greek): earth a. Geography [graph: write or draw] – draw the earth (make maps) and write about it b. Geographer: one who makes maps and writes about the earth c. Geology [logos: word or study] – study of the earth and its formations d. Geologist – one who studies of the earth and its formations: rocks, minerals, oil, etc. e. Geometry [metron: measure] – branch of study on ways to measure the earth f. George [ergon: work] – one who works the earth; a farmer 57) Terra (Latin): land a. Territory: land under control of a government or owner b. Terrace: raised platform of earth c. Terra cotta [coquo, coctum: cook] – “cooked earth”; fired clay pottery, tiles, etc. d. Terrarium: garden in a small glass container e. Terrrestrial: pertaining to the earth f. Extraterrestrial [extra: outside] – outside the earth’s atmosphere g. Terrier: small dog which hunts for burrowing game h. Mediterranean Sea [medius: middle] – the sea in the middle of the land 58) Dormio, dormitum (Latin): sleep a. Dormant: sleeping b. Dormant spray: insecticide for plants used in the non-growing season c. Dormitory: place for sleeping d. Dormer window: bedroom window set into a roof e. Dormouse: sleeping (hibernating) mouse f. Dormeuse: railway sleeping car g. Dormitive: something that causes sleep h. Dormition: act of sleeping 59) Hypnos (Greek): sleep a. Hypnosis: sleep-like state controlled by a hypnotizer 10 b. Hypnotize: put into a hypnotic sleep or trance c. Hypnology [logos: word, study] – study of sleep d. Hypnotic: tending to induce sleep e. Hypnotherapy [therapeia: treatment] – treatment of disease by hypnosis f. Hypnophobia [phobos: fear] – fear of sleep g. Hypnos: god of sleep in Greek mythology; Somnus 60) Annus (Latin): year a. Annual: yearly b. Anniversary [verto, versum: turn] – celebration marking the turning of a year c. Biannual [bi: two] – occurring twice a year d. Biennial [bi: two] – every two years e. Triannual [tri: three] – three times a year f. Triennial [tri: three] – every three years g. Centennial [centum: hundred] – every hundred years h. Millennial [mille: thousand] – every thousand years i. Perennial [per: through] – through the years j. Annuity: amount of money paid yearly k. Annals: historical events recorded year by year 61) Lithos (Greek): stone a. Lithograph [graph: write, draw] – picture drawn on stone b. Monolith [monos: one, alone] – lone stone c. Megalith [megas: large] – large stone d. Lithology [logos: word, study] – study of rocks or stone e. Lithosphere [sphaira: ball, globe] – rocky crust of the earth f. Lithic: made of or pertaining to stone g. Eolithic [eo: dawn] – earliest stone age h. Paleolithic [paleo: old, ancient] – ancient stone age after the Eolithic period i. Neolithic [neo: new] – new or late stone age 62) Petros (Greek): rock, stone a. Petrified [facio, factum: make, do] – made into stone b. Petrification: process of making into stone c. Peter: name which means “reliable, like a rock” d. Petroleum [oleum: olive, olive oil] – oil from rocks e. Petroglyph [glyphein: carve] – rock carving f. Petrography [graph: write, draw] – writing about rocks g. Petrous: hard, stone-like, rocky 63) Astron (Greek): star a. Aster – star-shaped flower b. Astronomer [onoma: star] – one who names the stars c. Asteroid [eidos: form] – in the form of a star d. Astrologer [logos: word, study] – one who gains knowledge from the stars e. Astronaut [nauta: sailor] – star sailor f. Diasaster [dis: separation or parting from] – separation from the good influence of friendly stars g. Astral – pertaining to stars h. Astrodome – covered stadium 64) Stella (Latin): star a. Stellar – pertaining to a star, or stars b. Constellation [cum: together] – group of stars c. Interstellar [inter: between] – between the stars d. Stellate: star-shaped e. Stellascope [skopeo (Greek): look at] – instrument for looking at the stars; astronomical telescope f. Stellerid: star fish g. Stellify [facio, factum: make] – transform a person or thing into a star or constellation h. Stella: girl’s name meaning “star” i. Estellita: girl’s name meaning “little star” 11 65) Dendron (Greek): tree a. Rhododendron [rhodos: rose, red] – evergreen shrub with large flowers b. Lepidodendron [lepidos: scale] – extinct prehistoric tree with scaly bark c. Dendrophile [philia: love] – lover of trees d. Dendrometer [metron: measure] – instrument for measuring the height and diameter of trees e. Dendrolite [lithos: stone] – petrified or fossilized trees f. Dendriform [forma: form, shape] – having the shape of a tree 66) Arbor, arboris (Latin): tree a. Arboretum – public garden where trees are cultivated and exhibited b. Arbor Day – day designed for planting trees – usually in March, April, or May c. Grape arbor – grape vines trained to climb on a trellis or open-roof framework d. Arboraceous – full of trees, wooded e. Arboriculture [cultura: tending] – cultivation of trees and shrubs f. Arborvitae [vita: life] – “tree of life”; an evergreen tree of the cypress family bearing cones (conifer) 67) Chronos (Greek): time a. Synchronize (syn: together, same) – do at the same time b. Chronometer [metron: measure] – device to measure time c. Chronology [logos: word or study] – relate events in time sequence d. Chronic – over a period of time; “from time to time” e. Chronograph [graph: write or draw] – device to measure and record time 68) Tempus, temporis (Latin): time a. Temporal – pertaining to time b. Temporary – for a limited time c. Temporize – play for time; stall d. Extemporaneous [ex: out] – speak or act at (or out of) the time without preparation e. Contemporary [cum: together, with] – with the time f. Contemporaries – people who are alive at the same time g. Tempo [Italian from Latin] – time in music; rate of speed at which something moves h. Tense [French: temps] – verb forms which indicate past, present, or future tense 69) Para (Greek): beside, along with a. Parable [ballein: to throw] – to throw a story in for comparison while teaching a lesson or moral b. Parachute [cadere (Latin): to fall] – goes along with you as you fall and slows you down c. Parenthesis [thesis: place] – a statement placed beside (or within) the main sentence d. Paragraph [graph: write] – an editing mark beside a page of print to show needed indentation ¶ e. Parallel [allos: other] – lying along side of another line but not touching 70) Inter (Latin): between, among, amid a. International [natio: nation, race, kindred] – between or among nations b. Interject [jacio, jactum: throw] – throw between c. Interaction [ago, actum: act, perform] – discussion or action between or among people d. Intervene [venio, ventum: come] – come between e. Intergalactic [galactos (Greek): milk] – between stars in the Milky Way f. Interlude [ludus: play] – light entertainment in the midst of serious activities; a “break” 71) Techne (Greek): art, skill a. Technology [logos: word, study] – study of how to do things b. Technical – pertaining to the art or skill involved in all kinds of work, science, sport, business, profession, mechanical arts c. Technique – expert skill in accomplishing something d. Technician – one who is skilled in details of an art or subject e. Architect [archi: chief, master] – a master builder f. Architecture – art or science of building 72) Ars, Artis (Latin): art, skill a. Art – display or application of skill b. Artist – one who acts or creates with skill c. Artistic – pertaining to skillful creation d. Artless – without skill, natural, simple, and sincere 12 e. Artful – full of, or characterized by, skill f. Artificial [facio, factum: make] – made by man; not occurring naturally g. Artillery [artillery (French): equip] – equipment for war h. Inert [in: not] – not skilled; inactive; sluggish i. Inertia – state of inactivity, motion which continues unless altered by an external force 73) Bios (Greek): life a. Biology [logos: word, study] – study of life b. Biography [graph: write, draw] – written life story c. Autobiography [autos: self] – written life story of one’s self d. Microbe [micro: small] – tiny form of life e. Amphibian [amphi: both] – creature who can live both on land and in water f. Bionic – life-like g. Biotic – pertaining to life h. Antibiotic [anti: against] – against living forms which invade the body 74) Vivo, victum (Latin): live a. Vivid – lively, animated, spirited b. Revive [re: back, again] – come back to life c. Survive [sur (French from Latin), super: over] – to live over or beyond a threat of death d. Vivacity – liveliness, vigor e. Convivial [con: with, together] – relating to feasting together f. Viand – food to support life g. Victual – food to support life h. Victim – religious sacrifice of live animal or person 75) Mikros (Greek): small a. Microphone [phone: sound] – device for transmitting a small sound over distance b. Microbe [bios: life] – tiny form of life c. Microcosm [cosmos: world] – a tiny world d. Microfilm [filmen (Anglo-Saxon): thin skin] – tiny film for storing books, records, etc. e. Micrometer [metron: measure] – instrument for measuring small things f. Micron – unit of length 1/1000 of 1 millimeter g. Microscope [skopeo: look at] – instrument for looking at tiny things h. Microwave [wafian (Anglo-Saxon): wave] – tiny electromagnetic wave between 1 and 100 centimeters long 76) Megas (Greek): great, large, big a. Megaphone [phone: sound] – device for making a sound larger [louder] b. Megalith [lithos: rock] – huge rock (such as those in Stonehenge) c. Megalomania [mania: craze] – crazy person with delusions of grandeur or greatness d. Megalophonous [phone: sound] – having a big or loud sound or voice e. Mega – in the metric system, a million times i. Megameter: a million meters ii. Megatons: a million tons 77) Magnus (Latin): big, large, great a. Magnify [facio, factum: make, do] – make larger b. Magnifier: that which makes greater c. Magnitude [-tudo: ness] – greatness d. Magnate – person of great rank or influence e. Magnificent – great in deed or character; lavish f. Mangnanimous [animus: mind, spirit] – great in mind; above what is low, mean, or ungenerous; noble in soul 78) Pater, patris (Latin): father a. Patriarch [archos (Greek): chief] – chief father of a family or of a society b. Patriotism: love for the fatherland c. Patrician: nobly born person; descendent of the founding fathers of Rome d. Patrimony [-monia: condition] – condition or estate inherited from one’s fathers e. Patron: one who acts like a father toward another 13 f. Patronymic [onyma (Greek): name] – a father’s name adapted and given to his children 79) Mater, matris (Latin): mother a. Matriarch [archos: chief] – a woman who rules the family b. Maternal: motherly c. Maternal grandparents: parents of one’s mother d. Matrix: the ground from which some thing or idea springs e. Matriculate: have one’s name entered on the list of students of a school or college f. Alma mater [alma: nourishing, kind] – the “dear old school” from which one graduates g. Matrimony [-monia: condition] – state from which motherhood develops 80) Frater, fratris (Latin): brother a. Fraternal: brotherly b. Fraternity: brotherly association of men c. Fraternize: associate together on friendly or brotherly terms d. Friar: a member of a men’s religious order e. Frere: French word for brother 14