THE EARTHS ATMOSPHERE • Earth`s atmosphere consists of a
advertisement

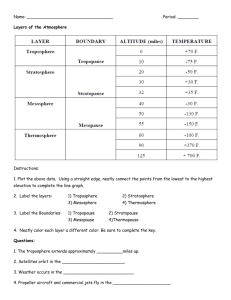
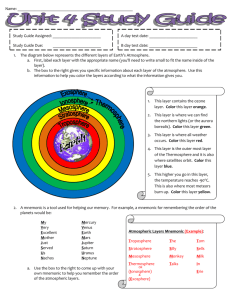
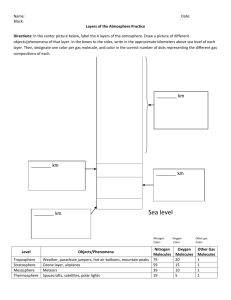
THE EARTHS ATMOSPHERE • Earth’s atmosphere consists of a variety of gases. • The two main gases are nitrogen (71%) and oxygen (16%). • Earth’s atmosphere has several layers. 1. Troposphere 2. Stratosphere 3. Mesosphere 4. Thermosphere 1. The Troposphere the lowest layer of the atmosphere, in which temperature drops at a constant rate as altitude increases • Almost all weather occurs in the troposphere. • The troposphere is the atmospheric layer closest to Earth’s surface. • The troposphere is the densest layer. • The troposphere gets cooler with increasing altitude. • The temperature decreases by 6° C for every kilometer of altitude. • At the top of the troposphere the temperature stops decreasing. • The boundary where this occurs is called the tropopause. • The temperature at the tropopause is -55° C. • The low temperature keeps water vapor from leaving the troposphere. • Cold air can become trapped beneath warm air. • Temperature inversion the atmospheric condition in which warm air traps cooler air near Earth’s surface. • When a temperature inversion occurs, trapped air can become thick with pollution. • As long as a temperature inversion lasts, it is not healthy for people to exercise outside. 2. The stratosphere gets warmer with increasing altitude. a. Stratosphere the upper layer of the atmosphere, which lies immediately above the troposphere and extends from 10 km to about 50 km above Earth’s surface. b. At about 25 km, the temperature begins to increase with altitude until it reaches about 0° C. 3. Mesosphere the coldest layer of the atmosphere, between the stratosphere and the mesopause The mesosphere and thermosphere exhibit extremes of temperature. a. Temperatures in the mesosphere decrease with increasing altitude, to about -80º C. 4. Thermosphere the uppermost layer of the atmosphere, in which temperature increases as altitude increases a. Temperatures in the thermosphere are extremely hot, absorbing intense solar radiation. The ionosphere is used in radio communication and is located in the lower section of the Thermosphere. b. Solar energy absorbed in the lower thermosphere and upper mesosphere forms charged ions. c. This layer is often called the ionosphere. d. Electrons in the ionosphere reflect radio waves. 5. The ionosphere is where auroras take place. 6. Auroras are colorful displays of light formed when energetic ions from the sun hit atoms and molecules in the ionosphere, causing photons to be emitted. 7. When Earth began to solidify, about 4.4 billion years ago, volcanic eruptions released gases. a. The process of releasing gases during volcanic eruptions is called outgassing. b. The gases released by volcanoes did not include oxygen. 8. Photosynthetic plants contribute oxygen to the atmosphere. a. Organisms evolved that used sunlight as an energy source in a process called photosynthesis. b. Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a waste product. c. Gradually the oxygen content increased to what it is today. 9. Animals produce carbon dioxide necessary for photosynthesis. a. Oxygen breathing organisms evolved and released carbon dioxide as a waste product. b. The oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle maintains a balance of atmospheric gases on Earth. 10. Man-made chemicals can deplete the ozone layer. a. Ozone is formed when the sun’s ultraviolet radiation strikes oxygen molecules. b. Ozone absorbs much of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation. c. Without the ozone layer, ultraviolet radiation would damage living cells. 11. Chlorofluorocarbons are chemicals that damage the ozone layer, but are now banned in most countries. 12. The greenhouse effect keeps Earth warm. 13. Greenhouse effect the warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of Earth that occur when carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases in the air absorb and reradiate infrared radiation a. Greenhouse gases trap the sun’s heat and keep Earth’s surface warm. 14. Increased levels of carbon dioxide may lead to global warming. a. If too much heat is trapped the global temperature will rise. 15. Global warming is the gradual increase in temperature on Earth due to an increase in greenhouse gases a. Global warming could cause problems, such as the melting of ice caps, rising of ocean levels, and drought in some areas.