Rules for drawing Pedigrees
advertisement

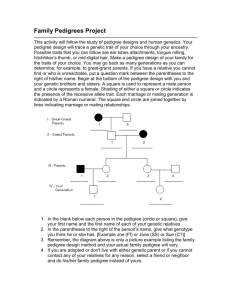
Rules for drawing Pedigrees: 1. To show the gender of an individual: a square is used to represent a male. a circle is used to represent a female. 2. To show the marriage or breeding relationship between couples: a line connecting the male and female is used to represent a breeding couple or marriage. 3. To show the offspring relationships: a line from the breeding couple line indicates children Twins are shown as follows: For example, Identical twins an only child (a daughter) Or two children (a daughter and son) 4. To show which individuals show a particular trait, an individual’s symbol is shaded and this information is shown in a key next to the pedigree chart. Female with trait Male with trait Female without trait Male without trait 5. To show carriers of traits, the symbol may have a dot. Female carrier Male carrier Human Pedigrees: Have you ever heard someone say ‘he got that from his grandfather’ or ‘she’s inherited that from her aunt’? Of course all of your genetic traits have been passed on to you directly from your parents. How then can we explain the appearance of a characteristic in one generation when it seems to have ‘skipped’ the preceding one? A pedigree is a useful way of charting the expression of particular characteristics in families. A pedigree shows the pattern of inheritance of characteristics. When certain patterns are observed over successive generations a mode of inheritance can be determined. The symbols used in pedigrees represent the individuals within a family as well as indicating which individuals possess particular characteristics. A pedigree is usually accompanied by a legend or key that is used to interpret the symbols used. A pedigree (or family tree) is used to show the pattern of inheritance of a particular characteristic. In all pedigrees, each generation is labelled with a roman numeral starting in the first row with I. Any person shaded means that they have the characteristic. Pedigrees: The following pedigree shows a family history for tongue rolling. The shaded squares and circles show those members of the family that can roll their tongue. The gene for tongue rolling (T) is dominant over the gene for non-tongue rolling (t). 1 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 a) How many generations are shown? ______________ b) How many females can roll their tongue? _____________ c) How many grandsons have individuals 1 and 2? _____________ d) What relation is individual 3 and 4? ________________ e) What relation is individual 6 and 7? _______________ f) What is the genotype for person 2? Explain by showing your working out. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ g) Determine the genotype for members 6 and 7. Explain by showing all of your working out. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ h) What is the genotype for person 8? Explain ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Construct the following pedigree. Use a grey-lead pencil and a ruler and carefully measure the lines so that they are evenly spaced and in the required generations. (The order of birth is in the same order that the children are mentioned. A man marries a woman with an allergy to chocolate. This allergy is the affected conduction. They have seven children, four boys and three girls. Two of the boys and two of the girls exhibit the condition. The three girls marry. The unaffected girl has three children, two male and one female, none of whom has the allergy. Of the two affected girls, one has two children, both girls, both of whom are affected. The other has two children and boy and a girl, neither are affected. NAME: ___________________________ Year 10 Genetics Human Pedigrees Assignment TASK: Construct your own family pedigree. Start from the generation comprising your grandparents. Include the next generation (your parents and their brothers and sisters) and also your own generation. Select one trait that is common in your family. Eg. Tongue curling; curly hair; sight impairment etc. Use the correct pedigree conventions Shading in those that are affected Using the correct symbols for males/females etc. Including a key in your pedigree Labelling the generations (also indicate which individual is you!) Assessment Sheet: CRITERIA HIGH Student has included all three generations of their family Selected an appropriate trait to study Correct symbols for the pedigree has been used Shading in those that are affected as appropriate Prepared an appropriate key Labelled the pedigree appropriately Assignment is neat and clear TOTAL: /21 MEDIUM LOW NOT SHOWN Analysis of Pedigrees: The pedigree shown on the next page shows the incidence of polydacyly (fingers and toes) in a family. Use it to answer the following questions. 1. Using the genetic shorthand for generations, what would be the symbol generation that comprises Roberta and Ros? 2. To what generation do Jenny and Juliet belong? 3. How many individuals comprise the III generation (not including the people they marry? 4. How many females in this pedigree are affected by poldacyly? 5. How many males in this pedigree are affected by polydacyly? 6. How many individuals in the II generation are affected? 7. What relation is Joan to Ros? 8. What relation is John to Ros? 9. What relation is Roberta to Diana? 10. What relation is Barbara to Ros? 11. What relation is Jeff to Carl?