Total Parenteral Nutrition

Total Parenteral Nutrition
PATIENT NAME _____________________________________ SOC_________
INITIAL
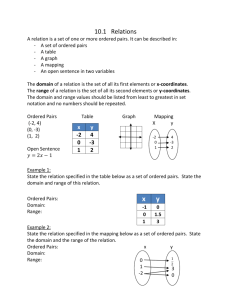
Define total parental nutrition (TPN).
______ ______ A. It is a highly concentrated solution given through a central line to provide all nutrients for the body.
______ ______ B. Various types of solutions may be given:
______ ______ 1. Dextrose and amino acids.
______ ______ 2. Fat emulsions.
______ ______ 3. Lipids premixed with dextrose and amino acids.
Possible reasons for receiving total parental nutrition therapy.
______ ______ A. Inability to absorb or digest food, i.e., severe vomiting or diarrhea, obstruction, severe burns, trauma, cancer, etc.
______ ______ B. Disease, requiring the bowel or other organs to rest (pancreatitis, severe inflammatory bowel disease, etc.).
______ ______ C. Malnutrition.
______ ______ D. Others.
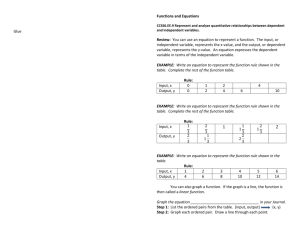
Care for TPN solution.
______ ______ A. Keep TPN solution in refrigerator until about one hour before use, allowing it to warm to room temperature.
______ ______ B. Always check the appearance of the solution by holding it up to the light, and avoid using if discolored, cloudy, or has sediment present.
______ ______ C. Avoid using the solution if the bag is damaged in any way.
______ ______ D. Check the expiration date on the package and avoid using the solution if not current.
Administration of the solution.
______ ______ A. Clean work area with alcohol and assemble equipment.
______ ______ B. Wash hands.
______ ______ C. Read label carefully to be sure it is exactly what the physician prescribed.
______ ______ D. Warm solution to room temperature.
______ ______ E. Prepare solution and tubing as instructed.
______ ______ F. Set the pump to infuse solution at the rate ordered by physician.
______ ______ G. Infuse, beginning at a slow rate, gradually increasing the rate, and then slowly taper rate to discontinue as ordered.
______ ______ H. Flush the catheter as ordered when solution is finished.
General care measures to prevent complications.
______ ______ A. Prevent infection by using strict technique as instructed.
______ ______ B. Inspect catheter insertion site daily for signs of redness, warmth, drainage.
______ ______ C. Monitor for fluid overload swelling in arms, legs, hands, etc.
1
Total Parenteral Nutrition
PATIENT NAME _____________________________________ SOC_________
______ ______ D. Weigh at the same time every day.
______ ______ E. Check urine for glucose and acetone as ordered.
______ ______ F. Provide good oral care frequently.
______ ______ G. Change dressing as ordered.
______ ______ H. Flush catheter as ordered.
______ ______ I. Take temperature as ordered.
Symptoms of complications when receiving TPN.
______ ______ A. Infection: fever redness, or pus at insertion site.
______ ______ B. Catheter related sepsis: fever, chills.
______ ______ C. Hyperglycemia: fatigue, lethargy, confusion, anxiety, weakness, thirst, headache.
______ ______ D. Hypoglycemia: sweating, shakiness, confusion.
______ ______ E. Fluid overload: shortness of breath, fast heart rate, weak pulse, confusion, edema.
______ ______ F. Air embolism: shortness of breath, blueness of nails and around mouth, fast heart rate.
______ ______ G. Catheter occlusion or partial occlusion: lack of flow or decreased flow of solution.
______ ______ H. Fat emulsion reaction: shortness of breath, cyanosis, nausea, vomiting, chest pain, dizziness, headache.
2