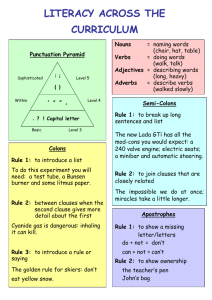
Parts of Speech - המכללה האקדמית אשקלון
advertisement

המכללה האקדמית אשקלון English for Academic Purposes לשימוש פנימי ולצורכי לימוד בלבד 1 CONTENTS - PART 1 - READING STRATEGIES AND GRAMMAR Page 3 UNIT I- VOCABULARY 3 Parts of Speech 5 8 Dictionary Work Word Formation - Affixes 13 Guessing Word Meaning by Using Context Clues 19 Phrasal Verbs 20 Vocabulary Word lists by Category 23 UNIT II- CONNECTORS 24 Connectors by Category 35 Connectors Practice 39 UNIT III- READING COMPREHENSION STRATEGIES 39 Looking for Information 41 Techniques of Skimming and Scanning 47 Inferences 49 UNIT IV- SENTENCE STRUCTURE & GRAMMAR 49 Simple & Compound sentences 53 Noun Modifiers 55 Adjective Clauses 59 UNIT V – PASSIVE VOICE 62 UNIT VI – PARAGRAPH STRUCTURE 62 Main Ideas 64 Patterns of Organization 66 UNIT VII – REFERENCES 69 Appendix: RECOGNIZING QUESTION TYPES 2 Parts of Speech What is a Noun? A noun is a word that names a person, animal, place, thing, idea, or concept. What is a Verb? A verb is a word that shows action or being. Whatever you are doing can be expressed by a verb. A sentence can have only one word as long as that word is a verb. Play! Stop! Run! What is an Adjective? An adjective is a word that tells us more about a noun or a pronoun. An adjective describes or modifies a noun and usually appears before that noun. Adjectives usually answer three questions about the nouns they describe: 1. What kind of? I found a red rose in the cave. -- Red 2. How many? Three tickets, please. -- Three. 3. Which one(s)? I would eat these muffins. -- These. What is an adverb? An adverb is a part of speech that describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, clause, or sentence. Adverbs answer the questions "How?", "When?", "Where?", "Why?", "In what way?", "How much?", "How often?", "Under what condition", "To what degree?" The easiest adverbs to recognize are those that end in -ly. Some adjectives end with -ly also but remember that adjectives can modify only nouns and pronouns. Adverbs modify everything else. An adverb can be placed anywhere in a sentence. 3 In order to guess at the meaning of an unfamiliar word or to look it up in a dictionary, it is necessary to know whether it is a noun, verb, adjective or adverb. This is an exercise that can help you. A] Identify the nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs in the following sentences. (Be ready to explain what clues helped you): 1. The piggle poggled a ponch pouchily. 2. The very seebled siclemere was sickling its stam. 3. Never mankle a moumish with your moup. 4. A denble berdement tobbled its worned penter. 5. Hunking hominously, the normet honkled a few hamps. B] Rewrite the following nonsense sentences using meaningful words. First, identify the nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs: 1. Don’t crunge that quoop! 2. May I plong another redlin into the murking rodget? 3. I broke my bloggers on a flooten klip. 4. The little widget narked our spong. 5. Her musky plips have plinten on the blip. 6. ____________ dibbledumps griggled mibly galong the cloop. NEWSPAPER HEADLINES You can interpret the following headlines in two different ways. What makes the difference in each pair of sentences? 1. Student Protests Increase 2. Record 16,000 for March 3. New York Presses Return to Work 4. Students Attack Ankara Daily 5. Karl Marx Remains in Highgate 4 DICTIONARY WORK When you look up a word in the dictionary, you need to think about some important things. 1. Part of Speech )(חלק דיבר Words can have different meanings when they appear as different parts of speech. Look at the following sentences: 1. a. It is very hot in the desert. b. She deserted her children when they were very young. 2. a. What level are you studying in English? b. The tractor will level the land. 2. Context )(הקשר Words can have different meanings even when they appear as the same parts of speech: 1. You must put a period at the end of a sentence. 2. The Baroque period was a very interesting time. 3. The basic form of the word )(צורה בסיסית של המילה You must take off any endings ) (סיומותthat are on the word. Here are some reminders: a) Take off ED / ING / S / ER / EST. Note the difference between words like "hoping" (You must look for "hope" in the dictionary) and "hopping" (You must look for "hop" in the dictionary) Note that words that end in "sh", "ch" and "X" have ES added on. b) These endings IES / IER / IEST / IED must all change to Y when you look for them in the dictionary. 4. Phrasal Verbs )(פעלי ביטוי Some verbs have different meanings because of the words coming after them. e.g. Look for – לחפש Look forward to – לצפות Look after – לטפל In your electronic dictionary you should enter all the words with a space in between. 5 Exercises 1. Look at the word in bold. What is its Part of Speech? What is its meaning, in the context of the sentence? Part of Speech Meaning 1. a) I would like to draw your attention to the following question. b) Mr. Cohen is always a great draw in our meetings. 2. a) We need to shape our ideas before we start writing the book. b) The shape of this table is very unusual. 3. a) He had an strong drive to smoke cigarettes. b) Her great suffering drives her to alcoholism. 4. a) The teacher will post the grades tomorrow. b) The dog was tied to a post beside the store. 5. a) The man who was injured in the accident is in grave condition. b) When people visit a grave, they often leave flowers. 2. Look at the word in bold. What is its Basic Form? What is its meaning, in the context of the sentence? (Remember to think about Parts of Speech also!) Basic Form Meaning 1. He is potting his plants in beautiful vases. 2. That joke is sillier than the other one. 3. They remedied the problem. 4. She looked at the swatches of fabric. 5. Fleming was the discoverer of penicillin. 6. We are creating new jobs. 7. He had many excuses for being late. 6 DICTIONARY WORK – TRANSLATING The following underlined phrases have been translated into Hebrew. Find a translation error in each of them and correct the translation. 1. Men’s employment rate is increasing every year. עבודת הגברים מעריכות Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 2. Medicine was traditionally a male preserve. באופן מסורתי זכר משמרים Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 3. Average wage rates for women are lower than for men. קצבי השכר הממוצע Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 4. Productivity of labor and capital is reported every year. יצרנות של עבודה ועיר הבירה Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 5. More women than men train as doctors and lawyers. יותר נשים מגברים מאלפים כרופאים ועורכי דין Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 6. Poor investment returns made him lose all his money. השקעה גרועה חוזרת Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 7. Women have paid jobs outside the home. נשים שילמו עבור עבודות Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 8. This company is offering parental leave. מציעים להורים לעזוב Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 9. This plan is a sounder base for long-term growth. בסיס יותר קולי לגדילה ארוכת טווח Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 10. Populations age very quickly. גיל האוכלוסיות Correct translation: _________________________________________________ 7 WORD FORMATION - AFFIXES SUFFIXES Suffixes are added on to the end of a word. They change the part of speech of the word. Suffixes which indicate NOUNS: Suffix Usual meaning Examples 1. ability capacity for, ability to flexibility 2. ance/ence condition of, quality of tolerance, indifference 3. ation, tion condition, action or state ventilation, devotion 4. dom state or condition wisdom 5. ee recipient of an action employee 6. er, or person or thing who / that investor 7. ese language of journalese 8. ess female actress 9. hood state, condition manhood 10. ism action, state anachronism 11. ist person who satirist 12. itis disease of, condition resulting from bronchitis 13. ness quality, state, condition happiness 14. ogy, ology science, study of ecology 15. ship quality, state of leadership 16. tion state, condition addiction Suffixes which indicate VERBS: Suffix Usual meaning 1. ate to make 2. en to make 3. fy to make 4. ize to make Suffixes which indicate ADJECTIVES: Suffix Usual meaning 1. able (ble, ible) capable of being 2. al possessing the quality of 3. ful characterized by, having the quality of 4. ic, ical quality or condition of 5. ious, ous, uous like, full of, having the quality of 6. ish like, somewhat 7. less without, lacking 8. ous, like, full of 9. proof resistant to 10. y having the quality of, some what Examples translate sharpen mystify theorize Examples learnable, edible cylindrical careful magical religious, various reddish thoughtless dangerous waterproof healthy 8 Suffixes which indicate ADVERBS: Suffix Usual meaning 1. ly like, In the manner of Examples happily Suffixes: Exercise Guess the meaning of the word in bold, according to your knowledge of suffixes. 1. He was sitting uncomfortably in his seat on the train. _______________ 2. There was a greenish light coming from the window. _______________ 3. You shouldn't have done that! It was very thoughtless of you. _______________ 4. He didn't pass his exam. He was unsuccessful for the second time. _______________ 5. The team that he supported was able to win the championship. _______________ 6. There is a very high likelihood that they will be late. _______________ 7. I couldn't find any weakness in his theory. _______________ 8. You need to be a highly trained economist to understand this report. _______________ 9. The road was too narrow, so they had to widen it. _______________ 10. He was accused of falsifying the documents. _______________ 11. They had to tranquillize the lion before they could catch it. _______________ 12. He needed to regulate the temperature. _______________ 13. You need a combination of motivation, organization and revision to learn English. _______________ 14. It is very uneconomical to run air-conditioning with the door open. _______________ 15. His arrival has been expected for the last half an hour. _______________ 16. She looked at her reflection in the mirror. _______________ 17. He decided to study journalism at university. _______________ 18. The film was surprisingly good. _______________ 19. The party was disastrous, everything went wrong. _______________ 9 PREFIXES Prefixes are added to the beginning of a word. They change the meaning of the word. Prefix 1. un 2. in (im,il,ir) 3. non 4. de 5. dis 6. re 7. anti 8. co 9. contra 10. en, em 11. ex 12. extra 13. in 14. inter 15. mal 16. mini 17. mis 18. mono 19. uni 20. bi 21. tri 22. multi 23. poly 24. out 25. over 26. post 27. pre 28. semi 29. sub 30. super 31. trans 32. ultra Usual meaning not not not negative, from opposite action again, back against together with against cause to be out of, from beyond, outside into among, between bad, wrong very small wrong, in the wrong way one one two three many many outside, to do better above, beyond, too much after before half under above, more than across, over beyond, very Example uninteresting inefficient, impossible, illogical, irrelevant nonsense defrost disappear renew, reread antibiotics, antiwar cooperation contradict enable, empower exterior extraordinary insight international malnutrition minimarket misunderstand monocycle unite bilingual triangle multilingual polygamy outsider, outrun overhead, overtired postpone prehistoric semicircle submarine, subtitle supermarket transport ultraviolet Prefixes: Exercise Guess the meaning of the word in bold, according to your knowledge of prefixes. 1. The dentist asked if I was feeling a lot of discomfort. _________________ 10 2. He's lost his book again. I don't know where he has misplaced it this time. _______________ 3. I think that you should reconsider. It may not be the best thing to do. _______________ 4. There was a need for postwar construction when the fighting stopped. _______________ 5. It is impolite to talk with your mouth full of food. __________________ 6. He was taken to the hospital because of irregular heart beats. ______________ 7. As a result of too many thieves, there is a new policy of prepaying for gasoline at this gas station. ________________ 8. Do you think Netanyahu will be re-elected for another 4 year term? _____________ 9. The first transatlantic flight was in 1927. ___________________ 10. When are you going to deactivate your Facebook account? _______________ 11. About 30 years ago computer screens used to be monochrome. ___________________ 12. This is really a multilane highway!! There are 8 lanes in each direction!! ___________________ PREFIXES EXPRESSING NUMBERS One of the following lists comes from Latin and the other from Greek. Which words do you know with these prefixes? Meaning One Two Three Four Five Six Seven Eight Nine Ten Hundred Thousand Half Latin uni bi tri quart quint sex sept oct non dec cent mil semi Greek mono di tri tetra penta hexa hept oct ennea ten hecto kil hemi Can you understand the underlined words in the following sentences? Try and answer the questions! 11 1. How many wheels does a monocycle have? 2. Why is a uniform called a uniform? 3. Have you ever heard a string quartet play? 4. What are the sports in a triathlon competition? 5. How many decades has Israel existed? 6. When will the next millennium be? 7. Which U.S. government offices are located in the Pentagon? 8. Why is an octopus called an octopus? 9. How many languages can a bilingual person speak? 10. What is the name for a person who can speak three languages? WORD STEMS Sometimes the stem of the word also contains meaning: Stem 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. anthrop aqua audio auto bibl chron cosm dict graph hydro magni micro phil phobia photo port psych scribe/script solo spec tele viv Usual meaning man water hear self book time order, world say write water great, big small love fear light carry mind write alone see, look far live Example anthropology aqueduct audiologist automatic bibliography chronological cosmopolitan dictation graphologist hydrology magnify microscope philosophy claustrophobia photograph portable psychology inscription, scribe soloist spectator telegram vivid, “Viva!” 12 Guessing Word Meaning by Using Context Clues One of the most useful strategies for dealing with unknown words is to determine whether the meaning of the unknown word is important for understanding the text. So how do you know if a word is important or not? Here are a few guidelines to help you decide: If you cannot understand the main idea without understanding a word, then it is important. If the word is in the title or one of the subtitles, it is probably important. If the word is the subject or main verb of a sentence, it may be important. If the word is repeated several times, it may be important. In these cases there are three vocabulary strategies that can be helpful: A. using the context surrounding the word to guess its general meaning (context clues) B. analyzing the parts of the word to guess its probable meaning (structural clues) C. using a dictionary to look up its exact meaning. A. Context Clues Guessing the meaning of a word from the other words around it, the context, is perhaps the most useful vocabulary skill that readers can have. The ability to use the context clues to guess, or infer, what that word means in a general sense will serve you well in almost every reading situation. Using these clues to understand the meaning of unfamiliar words will help you in the following ways: 1. 2. It saves time because you don't have to look the word up in the dictionary. It gives you a good sense of how a word is actually used. When you meet an unknown word, do not stop your reading to look up the word in the dictionary just yet. You can use different types of context clues as follows: definition, restatement, examples, contrast, cause and effect relationships, modifier and explanation. 1. Definition: The easiest way to guess the meaning of an unknown word is by looking at “definition”, which is given in the sentence by a signal that comes right after or before it. These signals include: o verb “to be” (is, am, are….) o means / mean….. o that is ….. o to be called / is, o are called ….. 13 o refer to …… o to be said to (is/ are said to …..) o punctuation marks; comma ( , ) , dash ( - ) . For example: The time of the year when days and nights are the same length all over the earth is called the equinox. (The equinox = The time of the year when days and nights are the same length all over the earth.) 2. Restatement: In sentences, there are usually phrases or clauses that repeat the idea of the unknown word. In other words, the phrase says the same thing as the unknown word. The unknown word may follow these signal words. o or o that is ( to say) o in other words o punctuation marks such as , ( ) - - .i.e. : For example: All students showed apathy – a lack of interest – in doing exercises on such a hot day. (Apathy = a lack of interest…) 3. Examples: In some sentences, we can guess the meaning of the unknown word by the example given in the sentence. The signal words that show that the sentence is giving an example are: o Such as o For instance o For example o Like o Especially o As o E.g. o Including o Punctuation marks such as - , ; : ( ). For example: Vehicles such as trucks, buses and cars are not allowed in the park. 4. Contrast: In some sentences, we find two words with opposite meanings. If we know the meaning of one word, we will be able to guess the meaning of the other word. The signals commonly used in the sentences are: Conversely On the other hand Even though In spite of Yet Despite But In contrast Though Nevertheless However On the contrary, For example: Melvin was usually on time; yet this morning he was tardy. 14 5. Cause and Effect (Result) relationship: Cause and Effect are the relationship between sentences and clauses, which are “cause” and “effect” to each other. The following are signals of the cause and effect relation: o because / because of o so, so that o due to o therefore o as a result o consequently o since. For example: Linda got drenched during the rainstorm because she left her umbrella at her office. 6. Modifier: Looking at the modifier in the sentences is another way to guess the meaning of the unknown words. Modifier gives a clearer understanding of the unknown word in a sentence by using additional or extra meanings. Usually the modifiers are adjective clauses beginning with – who, which, where, what, and that. For example: Mr. Smith was a racist, who believed his race was better than the others. (A racist is …a person who believed his race was better than the others ……) 7. Explanation: Some signals can give the explanation of the unknown words: o e.g. o In other words o This is because o The reason for this is that o It means that o The cause of this is that o One of the reasons is o This can explain that For example: The police suspected him, but he had an alibi. He was visiting his friends in France when the robbery was committed in Bangkok. B. Structural Clues 1. We use Structural Clues to determine the type or grammatical category of the new word. This tells us the kind of meaning to infer or look for. For example, if you are told that kneaf is a verb, then the sequence, “the sploony urdle kneafed” will begin to make structural sense. You know that urdle must be a noun, since a gap between “the” and a verb must be filled by a noun. You will figure out that sploony is probably an adjective because it is positioned before the noun. 15 Follow these steps: Look at the unknown word and decide its part of speech. Is it a noun, a verb, an adjective, or an adverb? Look at the clause or sentence containing the unknown word. If the unknown word is a noun, what does this noun do, or what is done to it? And what adjectives describe it? What verb is it near? If it is a verb, what noun or nouns does it go with? Is it modified by an adverb? If it is an adjective, what noun does it go with? If it is an adverb, what verb is it modifying? 2. We also use structural clues to break the unknown word into its prefix, root, and suffix, if possible. For example: un-break-able mis-interpret mal-nutrition hope-less-ness out-stand-ing-ly Using Context Clues Exercise 1 Are the underlined words in the following sentences important or unimportant? Do you need to understand these words in order to understand the entire sentence? Leo ate so much fettuccini that he could not eat another bite. He felt like his stomach would explode. Is fettuccini important? yes/no Is explode important? yes/no Exercise 2 Use the context to determine the correct meaning of the underlined words: 1. We have rather lofty expectations for you, son. You will attend college. You will become rich and famous. You will be elected president of the United States before you turn forty. a. high b. shaky c. small d. lowly 2. The signal from the cable is too strong for our television. We’ll have to use a filter to attenuate it. When you attenuate something, you ______. a. watch it carefully b. take good care of it c. make it be less d. get past it 3. “If you knew the gravity of the situation, you wouldn’t be laughing,” Mr. Farmer said quietly. He didn’t have to say more to get everyone’s attention. a. a force that draws different objects toward each other b. seriousness c. humor d. enjoyable, or comfortable 4. Her cardinal rule is this: Be kind to others! She believes that everything else in life will fall properly into place if one follows that rule. a. main, or most important b. red c. like a bird d. not worth remembering 16 5. The owner of the restaurant wouldn’t allow Samantha to walk through the door. “I’m sorry,” she said, “but you started a food fight the last time you were here. You may not have ingress to my restaurant!” a. a kind of bird that lives by the sea b. any food that can be thrown c. a good price for a meal d. the right to enter 6. I looked at the plans for your new house. This is earthquake country. You need to fortify the frame or you’ll have a disaster with the first tremor. a. shake b. build c. strengthen d. destroy 7. Amy was feeling low. Every business she tried lost money or made only pennies a day. Her newest idea was selling chocolate-covered baby shoes. She was convinced that it would be a lucrative business. Her friends tried to warn her that it was not a certain road to riches. a. tasting great with vanilla ice cream b. helping young feet to grow correctly c. showing no careful thought d. bringing in a lot of money, or profit 8. Being unable to write clearly is a liability in a business career. In business, one must often express opinions and ideas in writing. a. drawback b. surprise c. necessity d. penalty 9. Indigenous life forms—the cactus and the camel in the desert, the polar bear and the seal in the Arctic, and so on—are suited to their environment in very specific ways. a. native b. dangerous c. extinct d. recent 10. Studies indicate that a predisposition to schizophrenia is inherited. People who are schizophrenic are more likely than others to have schizophrenic children. a. tendency b. understanding c. fear d. avoidance 11. Manic depression is an emotional disorder in which the patient alternates between feeling delightfully euphoric and being plunged into deep gloom. a. overjoyed b. bored c. exhausted d. curious 12. The thought of eating a rat is abhorrent to most people. a. fun, lively b. horrible, repugnant c. delicious, tasty d. sweet, sugary 13. You can trust the salesmen at that store because they always conduct business in an aboveboard manner. a. honest, open b. sneaky, dishonest c. horrible, repugnant d. strange, unusual 14. The hill was too arduous for us to climb. We had to walk our bicycles up the hill. a. tall, sharp b. fun, exciting c. easy, not challenging d. difficult, steep 15. Fortunately, the dizzy spell was transient. He was able to continue playing within seconds and had no trouble winning the match. a. it sounds like a train b. it is quite harmful c. it helps you win d. it doesn't last long Exercise 3 17 A. Each sentence or paragraph contains an underlined word. Use the context to figure out the meanings of the word. 1. I don’t think the runners can sustain their fast pace throughout the entire race. __________ 2. This course will encompass every fact I know about the art of toe painting. You will be an expert when you are done. . __________ 3. Eddie’s face still smarts hours after being hit by the tennis ball. . __________ 4. The dictator tried to mollify the angry crowd with promises of better living conditions and more rights. . __________ 5. Andy and Sandy have many opposite traits. Andy is an amiable character while Sandy isn’t even slightly friendly. . __________ 6. True learning requires thinking. Indoctrination requires the absence of thought. Don’t allow yourself to be indoctrinated. . __________ B. Use the context to help you understand the underlined words 1. Your fifteen-year-old sister’s manners are deplorable. You should have been there when she ate at our house the other night. She kept reaching across the table for everything without even excusing herself. She burped a dozen times and looked like she was really proud of her achievement. And when we had ice cream sundaes for dessert, she ate hers with her fingers. What does “deplorable” mean? a. awful b. deeply thoughtful c. cute or pleasing d. enjoying good food 2. Randolph is certainly resilient. He lost a fortune when his business failed but now he’s wealthy again. After spending a month in the intensive care unit of the hospital, he’s as healthy and strong as ever. And after all those rumors ruined his reputation, he’s managed to once again be a highly respected member of the community. What does “resilient” mean? a. sneaky b. having a lot of money c. free of sickness d. able to bounce back or recover 18 PHRASAL VERBS Examine the verbs in the following sentences: 1. The goal of the study was to collect the kind of information that does not usually turn up in accident reports … 2. In one instance, a young woman, lost in a suburb, pulls into a driveway and begins dialing a cell phone resting in her lap. 3. … the study found that drivers were overconfident or very poor at predicting when it was safe to look away from the road to perform another task. The word combinations marked in bold are called “phrasal verbs”. In a phrasal verb, a verb is followed by a preposition, which changes its original meanings. Note the differences in meaning: turn turn up turn out turn on turn somebody in pull pull ahead pull back pull into pull off look look after look for look away from turn on turn off pull together look down on somebody/something Look out! Use the dictionary to define the phrasal verbs in the following sentences: 1. The news of her resignation soon got about. ____________________ 2. Elderly people cannot keep up with all the changes in computer technology. _________________________ 3. The thieves made off in a stolen car. _____________________ 4. Have you noticed how he is trying to get in with the boss? ______________________ 5. I cannot go along with you on that point. _______________________ 6. He was done over by a gang after a football match. ______________________ 7. Can you please pick up my shirt from the dry cleaner's? ___________________ 8. Don't make up any more excuses! _______________________ 19 VOCABULARY WORD LISTS BY CATEGORY Reading Comprehension: definition idea topic explain refer cause, reason result, effect former latter quote הגדרה רעיון נושא להסביר מתייחס גורם,סיבה תוצאה הקודם השני ציטוט factor גורם specific infer imply according to מסוים/ספציפי להבין/להסיק מתכוון/מרמז לפי paragraph פסקה mean מתכוון phrase sentence example comparison contrast purpose, aim, goal conclusion משפט דוגמא השוואה ניגוד critical review argument opinion חלק של/קטע משפט ביקורתי בקורת/סקירה נימוק/טעון דעה מטרה belief אמונה מסקנה,סיכום/סיום connectors מילות קשר introduction idiom summary title writer, author passage, text article global reading skim scan intensive reading expressions terms abstract describe event, happening מבוא/הקדמה ניב תמצית/סיכום כותרת/שם כותב/סופר קטע קריאה מאמר קריאה גלובלי לקרוא ברפרוף לקרוא במבט קריאה אינטנסיבית ביטויים מונחים תקציר/תמצית לתאר אירוע 20 Research: population אוכלוסייה interpret לפרש control group variable (dependent) variable (independent) constant קבוצת ביקור measure למדוד משתנה תלוי show מוכיח,מראה משתנה בלתי תלוי hypothesis היפותזה/השערה קבוע theory תיאוריה sample מדגם prove להוכיח method שיטה proof הוכחה results תוצאות conclude להסיק findings ממצאים cause סיבה/גורם evidence עדויות correlation התאמה experiment ניסוי affect להשפיע field שטח effect השפעה laboratory average ממוצע subject מעברה נבדק percent אחוז questionnaire שאלון study מחקר blind objective אובייקטיבי subjective סובייקטיבי placebo עיוור ,להצביע על להראות דמה assume להניח data נתונים/נתון expect לצפות examine לבחון statistic נתון analysis (n) אנליזה,עיבוד random אקראי observe להתבונן,לצפות figures תמונות/מספרים record (v) להקליט,לרשום tables, charts טבלאות characteristics מאפיינים science מדע indicate 21 Vocabulary – Useful Verbs I לקבוע to interpret לפרש to reduce להפחית to increase להגדיל to appear להופיע to persist להתמיד to improve לשפר to prove להוכיח to inform ליידע to perform to determine לבצע to estimate להעריך to deny להכחיש to persuade לשכנע to admire להעריץ to succeed להצליח to challenge לאתגר to consider לשקול to observe לצפות to establish לבסס,לייסד to realize להבין to acquire לרכוש to display להראות to attempt לנסות to be exposed to להיחשף to develop לפתח to recognize להכיר to respond לענות,להגיב to achieve להשיג לסמוך על to remain לטעון to emerge Vocabulary – Useful Verbs II to rely on to claim to decrease to criticize לרדת בכמות to be involved להישאר , לצוץ,לצוף להופיע להיות מעורב ב להעביר ביקורת to correspond להתאים ל to be committed להיות מחויב להתייחס ל to perceive לטפוס,להבין to allow להרשות to support לתמוך to defeat להביס to express להביע to be concerned to regard להיות מודאג להשפיע על to argue לטעון,להתווכח to prevent למנוע to design לעצב to suggest להציע to contain להכיל לחקור להיות,לסמוך על תלוי ב להצביע על to process לעבד to present להציג to influence to investigate to depend on to indicate to benefit from להפיק תועלת מ 22 What are connectors? Connectors are linking words or phrases that connect two ideas, facts, events, etc. They join the ideas but also signal what is coming next, e.g. a contrasting fact or a purpose. These signals help the listener or reader understand the connection between ideas. Connectors can also help answer questions, as you will see in the following examples: Typical questions 1. Question: What two things are contrasted in paragraph 4? Text: Unlike money, there is an endless supply of social reinforcers. 2. Question: The article tells us about the basic functions of any society. They are: a. b. c. Text: Paragraph 2: The essential function of every society- large or small- is to do a better job than any individual can do of providing the necessities of life… Paragraph 3: Over and above the function of providing the necessities of life, society develops a shared set of goals. Paragraph 4: Finally, every society functions in ways that attempt to guarantee that the society itself will survive. 3. Question: Why do we tend not to change our ideas about masculine and feminine talk? Text: Because we think that language also should be divided into masculine and feminine, we have become very skilled at ignoring anything that will not fit our preconception… 4. Question: In what way is paragraph 20 related to paragraph 19? a. Paragraph 20 repeats what was said in paragraph 19. b. Paragraph 20 questions what was said in paragraph 19. c. Paragraph 20 expands on what was said in paragraph 19. d. Paragraph 20 contradicts the main idea of paragraph 19. Text: Paragraph 20 Angela Parker has found that not only do males talk more in class, but that both sexes believe that ‘intellectual argumentation’ in the classroom is a masculine activity. 23 CONNECTORS BY CATEGORY: Contrast but nevertheless, however, while whereas on the other hand, on the contrary, yet, still in fact, although (even) though despite in spite of in contrast to similarly like in the same way just as … (so…) unlike both likewise instead of actually, as … as Comparison Cause and Effect/Result CAUSE EFFECT/RESULT because (of) so since therefore, as as a result, result in for consequently, as a result of lead to result from accordingly as a consequence of thus / hence owing to bring about due to cause thanks to on account of Addition/Reinforcement Explanation/Example and also namely such as in addition (to), as well as in other words for example besides, furthermore, i.e. for instance moreover, in fact, that is e.g. not only…but also first, second, third : -- ( ) 24 1. Contrast Contrast connectors show that two things are different from each other OR that something in the text is different from what we expect it to be. Examples: a. Last year's profits amounted to ten million whereas the previous year's profit was eight million. b. We have not yet received our order in spite of the fact that we contacted you a month ago. Contrast connectors: but nevertheless, however, while whereas on the other hand, on the contrary, yet, still in fact, although (even) though despite in spite of in contrast to unlike instead of actually, Exercise Underline the connector and answer the questions. 1. The interest rate in Israel is 4%, whereas in Canada it is only 2%. What is being contrasted? ____________________________________ 2. Despite difficult trading conditions, the company made a considerable profit. What was unexpected? _______________________________________ Why? ______________________________________________________ 3. On the one hand, reorganization will reduce salary costs but on the other hand, it will increase administrative costs. Two different aspects of ________________________ are being contrasted. 4. Even though it was raining, I didn’t get wet. Did the speaker expect to get wet? __________ 5. While my wife likes to travel abroad, I prefer to stay at home for my vacations. Who is being contrasted? _______________________________ What is the difference? _______________________________ 6. Jerry passed the exam first time; however, I had to retake it three times. What did the speaker expect? _____________________________________ 25 7. Unlike Americans, who form orderly lines to wait their turn, Israelis tend to rush together, especially when they have been waiting for a long time! Who is being contrasted? __________________ and __________________ What is the difference between them? ______________________________ 8. The fire spread all through the factory even though sufficient fire precautions had been taken. What should have happened? ________________________________________ Why? _________________________________________ 2. Comparison Comparison connectors show that two things are similar. You should understand which two things are being compared, and what is similar about them. Examples: a. Just as flowers need rich soil, we need nutritious food. b. Both amateur and professional musicians need to practice every day. Comparison connectors: similarly like in the same way just as … (so…) both likewise as … as Exercise 1 Underline the connector and answer the questions. 1. Similarly to the cat’s need for freedom and independence, some people are very private and minimize their communication with others. Who/what is being compared? _____________________ and __________________ What is similar about them? They both _____________________________________ 2. Like their predecessors, the modern-day Pueblo Indians believe that they are one with the forces of nature. Who is being compared? _________________________ and ___________________ What is similar about them? They both _____________________________________ 3. Both the human beings deprived of socialization and monkeys raised in isolation, demonstrate retarded emotional, social, physical and intellectual development. Who is being compared? _________________________ and __________________ What is similar about them? They both ____________________________________ 26 4. People who move to a foreign country may be compared to the newly-wed, since like the latter, they experience the sense of euphoria which is often remote from the reality. Who is being compared? _________________________ and ___________________ What is similar about them? They both _____________________________________ 5. Human beings are similar to tea bags, whose strength is tested as they get into hot water. What are people compared to? __________________________________________ What does this comparison teach about human nature? __________________________________________________________________ 6. In a recent study, men were found to be more aggressive and more competitive than women. Women are ______________________ and ______________________ than men. 7. As intelligence, personality seems to stem from a combination of genetics and environment. What are the things being compared? ________________ and ________________ What is similar about them? They both ____________________________________ 8. Just as reflexology alleviates people’s tensions, acupuncture calms down the nervous system and reduces the stress of everyday life. Complete the sentence: Both ________________ and ____________________ ________________________________________________________________ Exercise 2 Are the following words used to compare or to contrast ? 1. likewise _____________ 2. although_____________ 3. unlike_____________ 4. similarly_____________ 5. however_____________ 6. in contrast _____________ 7. on the other hand _____________ 27 3. Cause and effect/result Examples: a. Since he wanted to pass the test, he studied all night long. b. The company needs to expand its international business. We therefore recommend the opening up of new markets in Asia. Cause and Effect/Result Connectors: CAUSE EFFECT/RESULT because (of) so since therefore, as as a result, result in for consequently, as a result of lead to result from accordingly as a consequence of thus / hence owing to bring about due to cause thanks to on account of Exercise 1 1. The traffic was heavier than usual, __________ we were late for our appointment. a. owing to b. because c. as a consequence of d. so 2. The company made a loss last year and _______________ did not pay a dividend. a. since b. owing to c. consequently d. result in 3. _____________ my computer froze, I had to restart it. a. Due to b. Because c. As a result of d. Owing to 4. I couldn't get my car to start again, _________________ the battery was dead. a. so b. due to c. because d. as a result of 28 5. _______________ technology is advancing, the company will have to spend more money on upgrading its systems. a. Because of b. Since c. As a result of d. Therefore 6. He had a difficult childhood, _________________his parents’ financial problems. a. therefore b. as a result c. as a consequence of d. since 7. Temperatures were very high during the trip and ______________ damage in the food reserves. a. this resulted in b. therefore c. as a result d. because 8. She said you'd know where the camera was _______________ you were the one who put it away. a. however c. because e. although d. in spite of Exercise 2 Read the sentences and answer the Cause and Effect questions that follow: 1. Nature definitely intended that adults should nap in the afternoons because just as we have a significant drop in body temperature and alertness at night, we also have a similar but smaller drop in the middle of the day. This is why most of us feel particularly tired between 2 and 4 p.m.(14:00 – 16:00). Why do most people feel tired between 2 and 4 p.m.? ____________________________________________________________________ 2. The Piraha people see themselves as different from and better than other people around them. Everything they do is aimed to prevent them from being like anyone else. This is the reason why they have survived as Piraha, while other tribes around them have been absorbed into Brazilian culture. What happened as a result of Piraha’s distancing themselves from other people and cultures? __________________________________________________________________ 3. The variety of cell-phone designs has expanded greatly in the past couple of years as the need for phones with large color screens has grown considerably. This growth is due to 29 cellphone owners’ increasing use of computer services such as surfing the Internet and downloading games. Complete the sentences: As more and more cellphone owners are using the Internet services, _________________________________________. As a consequence, __________________________________________________________________ 4. Occasional liars, which most of us are, really don’t like to lie, but do so every now and then to avoid an unpleasant situation or because they don’t want to admit something bad or embarrassing. List the two reasons occasional liars may tell lies: i. _____________________________________ ii. _____________________________________ 5. The face-to-face, in-person apology is a “killer”. Many people do not like it because they must see the person’s expressions, reveal theirs, and probably receive a verbal reply. Why do people call a face-to-face approach a “killer”? Because the people who apologize in person a. hurt the other person’s feelings b. feel as though they killed somebody c. find it very difficult emotionally d. feel extremely excited 6. Past generations in China never saw dogs because residents could not afford pets and the Communist Party viewed the idea as something that did not fit in with their ideology. Thus, many Chinese with little canine experience are deathly afraid of bigger dogs and do not, for example, recognize that different breeds can have different personalities. a. What are the two reasons past generations in China were not familiar with dogs? 1. _______________________________ 2. _______________________________ b. What is the consequence of this past experience? _________________________________________________________________ 30 4. Addition/Reinforcement Examples: a. The refunds are substantial. In addition, they are easy to claim. b. She wants to be a high level manager as well as being a loving mother. Addition/Reinforcement Connectors: and also in addition (to), as well as besides, furthermore, moreover, in fact, not only…but also first, second, third Exercise 1 1. Oxford is one of England's great medieval cities. ____________, it has been an international center of learning since 1167. a. For example b. Furthermore c. As well as d. Apart from 2. It's often cheaper and quicker to travel by train than by bus or car. __________ , on long journeys it is more comfortable. a. So 3. b. Also c. Similarly d. Except for Not only his love for literature and painting, ________________ his sensitivity to everything beautiful led him to opt for arts as his major field of study. a. in addition b. but also c. although d. because of 4. According to research studies, moderate exposure to sun is very beneficial. First, it improves the mood and reduces depression. _______________, it supplies vitamin D, which is responsible for maintaining of proper levels of calcium in the body. a. However b. Nevertheless c. As a result d. Second 5. _______________ damaging the exceptional views, tourists often damage the economy and the well-being of the local residents. a. Besides b. Moreover c. Consequently d. Yet 6. In order to improve their reading comprehension skills, students should strengthen their vocabulary and learn the proper use of the dictionary. ________________, they ought to practice their guessing skills, i.e. understanding the word in the context. a. As well as b. Still c. Hence d. Moreover 31 Exercise 2 - Read the sentences and answer the questions that follow 1. Hearing loss as a result of the exposure to loud music through headphones is a gradual process. It cannot be detected before it is too late. It can take up to five years of exposure before tests can detect it. What is worse, hearing loss is permanent. What are the two negative results of listening to loud music through headphones? a. ______________________________ b. ______________________________ 2. Forest Schools, a Scandinavian idea that was imported into the U.K. in the 1990s, is now taking off around the country. Many fortunate children from all over the U.K. are now discovering that time spent exploring the woods is good for both the body and the soul. In addition to getting fresh air, children improve their self-esteem, exercise and get a whole new set of skills. How many specific advantages of Forest Schools are mentioned in the paragraph? ____ 3. Now the city of San Francisco is trying to stop fortune-telling frauds. According to the new law, fortune-tellers are required to possess a business license and pay about $500 for a permit. Moreover, fortune-tellers are required to post rate-cards and a phone-number for complaints. List the requirements fortune-tellers have to obey. a. ________________________________________ b. ________________________________________ c. ________________________________________ 4. In China, once a woman is married, she is expected to live with her husband’s family, performing household chores and caring for her in-laws. Not only do her parents lose her services, but also they are usually expected to bear the cost of the wedding as well as provide a dowry of cash and other gifts. Apart from taking upon themselves the wedding expenses, what other disadvantages are there for the parents whose daughter gets married? a. _______________________________________ b. _______________________________________ 5. Despite the dangers they present, the modern-day pirates are difficult to eliminate. Often their host countries tolerate them, attracted by the prospects of increased exports and reduced unemployment, or by the bribes paid to the government officials. In addition, counterfeiters are clever. Sometimes they register brand names in their own countries before 32 the legitimate companies can do so. Then they either sell their goods by exploiting the reputation of the brand names or force the legitimate companies to buy them out. What are the reasons for the difficulty to eliminate modern-day piracy? Complete the sentences: It is difficult to stop commercial piracy because the pirates are ________________ and because piracy brings about _______________ advantages to the host countries. 5. Explanation/Example Examples: a. He is studying ergonomics, namely, the design of equipment to best suit the worker. b. Many composers, such as Beethoven and Mozart, created music, which will be remembered for many generations to come. Explanation/Example Connectors: namely such as in other words for example i.e. for instance that is e.g. : -- ( ) Exercise 1 1. John is a diligent student. _____________, he studies seriously. a. Also b. In other words c. Because Consequently 2. Susan is highly talented in the arts and music. ___________ does she compose music, she also writes the lyrics. a. Even so b. For instance c. Not only d. Moreover 33 3. Tropical fruit ______________ papaya, mango and pineapple are both attractive looking and palatable. a. either b. but c. such as d. i.e. 4. Linguistics _____________ the study of language is taught in all the major universities in Israel. a. such as b. For example c. or d. since 5. Lotem is very confused about his last argument with Adi. _________________, he doesn’t know whether he should apologize or let the things cool down a little. a. In other words b. For instance c. On the other hand d. While 6. Many unusual instruments _________________ the sitar, gamelan and oud are generally not played in the classical orchestra. a. including b. also c. due to d. thus Exercise 2 - Read the sentence and answer the questions that follow 1. Academic cheating, or plagiarism, is becoming easier in the Information Age. However, it is also becoming easier to catch plagiarism. For instance, when students take an exam on-line, some colleges use a program that takes control of the computer’s operating system during the test. What is plagiarism? __________________________________ What does the example presented in the paragraph illustrate? _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Scientists are discovering that dolphins are far from the happy, peaceful creatures that humans think they know. There is emerging evidence that wild dolphins can be cold-blooded killers. For example, in Scotland a scientist watched an adult dolphin repeatedly pick up its young in its mouth and smack it against the water over and over until it sank from view. The example of a dolphin killing its offspring shows that _______________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Female infants speak sooner, have larger vocabularies and rarely demonstrate speech defects. Stuttering, for instance, occurs almost exclusively among boys. Complete the sentence: Stuttering is an example of ______________________, which are more frequent among boys. 34 4. One of the common ways to deal with a conflict is withdrawal, namely, physical or psychological removal from the situation. Withdrawal is negative because it neither eliminates nor attempts to manage the nature of the conflict. For instance, when Tom withdraws physically, Mary may follow him to the basement, where the conflict will be resumed. What is withdrawal?_________________________________________________________ The example of Tom and Mary shows that a positive way to deal with conflict would be ______________ or ____________________________________________________ 5. Food preferences are the most familiar aspect of ethnocentrism. Every culture has developed preferences for certain kinds of food and drink, and equally strong negative attitudes towards others. For example, Americans feel that eating a meal of horse or snake meat is repugnant, while in South Asia the majority of adults don’t drink milk. Similarly, people in India would never eat cow meat, since a cow is considered a holy animal there. Give one example of a food or drink that is acceptable in one culture and rejected in another. _______________________________ PRACTICE: All connectors EXERCISE 1 - Identify the KIND of connector for each sentence below: ADDITION REASON COMPARISON TIME EXAMPLE CONTRAST RESULT 1. While aggregate demand rose, the level of employment actually fell. ___________ 2. Furthermore, confidence in the economy dropped during the crisis. 3. Share prices increased dramatically, thus encouraging further investment. _________ 4. Secondly, the paper will consider reasons for this phenomenon. ___________ 5. One factor, for instance, taxation, may be responsible. ___________ 6. Due to monetary controls, inflation was not significant. ___________ 7. Similarly, other Asian economies experienced rapid growth at the time. ___________ _________ 35 EXERCISE 2 Read the following sentences. Underline connectives and indicate what kind of relationship they express. Choose from the possibilities below: A B C D E Addition Comparison Contrast Cause and result Example 1. At the end of the year, a business fair will be held at which leading Israeli companies will present their products. Several large corporations such as Intel, Elscint, Rafael, Domino’s Pizza and the Postal Service have appointed experts to act as consultants at the event. _________ 2. The Rambam stated that "conflicts between science and religion result from misinterpretation of the Bible _________ 3. Drug abuse among teenagers is increasing at an alarming rate. While the experts have many explanations for this dramatic increase, there is little they can do to solve the problem. _________ 4. People have traditionally prepared for vacations abroad by reading guidebooks. Today Internet provides an additional way of planning trips abroad _________ 5. Squash, a racket-and-ball game played by two people inside a small four-walled court can involve tremendous physical exertion. But fitness alone is not enough -- agility, hand-eye coordination and speed of reaction are also very important. _________ 6. During basic training, infantry soldiers sometimes end up with stress fractures or overuse injuries. These are caused in part by the new recruits' exaggerated motivation to prove they can do above-and-beyond what is asked. _________ 7. Like food producing companies, cosmetic firms are now required to list an expiration date on their products. _________ 8. Internet allows you to see the whole world in the comfort of your own home. The user can, for example, call up the Tokyo subway routes or “sail” in the Bay of Hong Kong without rising from his/her armchair. _________ 9. The pressure from global competition and the increasing demands of consumers have led more and more Israeli businesses to adopt higher standards of service. _________ 10. Although the alcohol industry denies targeting young people in the promotion of its products (they only use adults in the commercials), alcohol commercials often run during programs that young people are likely to see. _________ 36 EXERCISE 3 - Circle the correct answer. 1. Yael was embarrassed _________ she didn’t know the answer to a very simple question. a. due to b. despite c. because d. though 2. _________ her embarrassment, she didn’t leave the restaurant. a. Although b. In spite of c. Even though d. Because 3. We didn’t pay much for the shirts _________ they were made of good quality material. a. even if b. although c. as d. despite 4. Alon managed to fall asleep _________ the noise outside his window. a. in spite of b. because of c. even though d. though 5. _________ his friend’s advice, he joined the rival company. a. Although b. Despite c. Because d. Besides 6. Merav decided to stay at home _________ her illness. a. because of b. because c. although d. since 7. _________ he had prepared for the test, he did not pass it. a. Despite b. Although c. Because d. Owing to 8. _________ Leon liked science so much, he decided to study it at the university, a. In spite of b. Owing to c. Although d. Since 9. _________ unforeseen circumstances, the concert was cancelled. a. Due to b. Because c. Although d. Despite 10. It was late; _________, Dina agreed to help her friend. a. moreover b. nevertheless c. besides d. in addition 11. He had promised to come on time; _________, he arrived late. a. therefore b. but c. although d. however 12. Cindy decided to go sailing _________ she loved the feel of the wind on her face. a. although b. since c. despite d. because of EXERCISE 4 Fill in the blanks with a suitable connector. 1. She woke up late this morning. _________________, she did not miss the bus. 2. She woke up late this morning. __________________, she missed the bus. 37 3. She woke up late this morning. __________________, she had to wait until her daughter was ready. 4. He is a good teacher. __________________, he is not the best teacher in the school. 5. We all enjoyed the movie. __________________, we all enjoyed being at the cinema. 6. __________________, I was very excited about learning in high school. Later, I became less excited. 7. First we went to Danny. __________________, we went to Dana’s place. 8. He loves Geography very much. __________________, his grades are quite low. EXERCISE 5 A. Following are five short textbook excerpts. Circle the best answer that describes the relationship indicated by each underlined transition. 1. The relentless pressures athletes experience may lead them to distance themselves from their studies. The sentence expresses a relationship of a. time b. cause and effect c. illustration 2. Since 1820, more than fifty million people came to live in the Unites States, including some three million slaves who came against their will. The relationship indicated by the transition is one of a. addition b. time c. comparison 3. The number of women in the workforce has increased steadily since the turn of the century due to factors such as World War II, a troubled economy, a high divorce rate, and the women's movement. Yet a pattern of gender inequality on the job continues. The relationship of the second sentence to the first sentence is one of a. contrast b. cause and effect c. illustration 4. As a result of exposure to the various chemicals dumped at Love Canal, nearby residents have an excessive number of serious illnesses, a high incidence of miscarriages, and an unusual number of children born with birth defects. The sentence expresses a relationship of a. addition b. illustration c. cause and effect 5. Speech style affects a speaker’s apparent trustworthiness. For instance, researchers Gordon Hemsley and Anthony Doob found that if, while testifying, videotaped witnesses looked their questioner straight in the eye instead of gazing downward, they impressed people as more believable. The relationship of the second sentence to the first is one of a. contrast b. illustration c. cause and effect 38 Looking for Information WHO? WHEN? WHAT? HOW? WHY? WHERE? UNDER WHAT CIRCUMSTANCES? Which question is answered by each of the underlined words or phrases? Example: Bacteria are the simplest organisms found in most natural environments Answer: WHAT? 1. Bacteria can replicate quickly by simply dividing in two. ________ 2. We should work together to improve the situation. ________ 3. In most competitions, the first three places win a prize. ________ 4. As a result of these investigations, researchers… ________ 5. It is in this space that… ________ 6. The occurrence of unexpected events such as… ________ 7. AIDs was first recognized as a disease in 1981. ________ 8. Knowledge continues to grow at a faster pace than it did during the post-war years. ________ If the question asks why If the question asks what or who If the question asks what happened the answer is a reason the answer is a person or thing involved the answer is a result / effect 39 If the question asks when (time) If the question asks when (under what circumstances) If the question asks how If the question asks where the answer is a date or other time expression the answer is the condition necessary to obtain a result the answer is a description the answer is a place Reading Faster Almost every reader can learn to read faster without sacrificing comprehension. Aside from saving time on homework assignments and doing better on tests, fast readers usually comprehend more than slow readers. Slow, word-by-word readers often miss the meaning of what they are reading because they are focusing on the individual words rather than on the meaning of the sentence. If words are perceived in isolation, they lose their connection to the “message” the author is trying to convey. To receive the message in a sentence, the individual words must be seen in a context. Good readers focus on the ideas of sentences and paragraphs rather than on words in isolation. How can you improve your reading rate? 1. Don’t read one word at a time. Try to “see” several words at a time. 2. Don’t translate each word. Focus on the idea in the sentence. 3. Don’t use your finger or pencil to point to each word. If you like to point, center your pointer in the middle of the column and run it down the column as you read. This will help “pull” your eyes along faster and train them to take in more words at a single glance. 4. Don’t move your lips or say the words to yourself as you read. Talking is slower than reading. If it is difficult to break this habit, try commenting to yourself about the ideas in the passage. For example, “That’s a good idea”, or “This must be the answer to the question,” or “This can’t be true.” 5. Concentrate on speeding up. In the beginning, don’t worry about comprehension. Try reading a passage as fast as you can. Reread it more slowly if necessary. By alternating very fast and slower rates, your “slow” rate will gradually improve. 6. Practice is important. Try to spend 10 or 15 minutes every day practicing fast reading. Make sure you practice on easy material. You won’t be able to read fast if the level of difficulty is high. The exercises in this section are intended as an introduction to read faster. They range from very short and simple passages to longer articles similar to unseen tests. Your teacher will help you use them to focus on various skills and techniques, but if you really want to read faster, you will have to practice on your own as well. 40 Techniques of Skimming and Scanning Readers of academic texts have to carry out different reading tasks. They may want to find a single detail or one idea need to get a general impression of the content of the article, need to have an exact understanding of the writer’s argument and supporting evidence. The techniques that are explained in this section will help you to become a more efficient reader. Scanning for a Specific Detail If we need to find a specific item of information, for example a date, a figure, a name, or a title, we can do so by scanning the paragraph (page) that is by letting our eyes wander over the text. We can locate the information we are looking for without reading all the text. The form of the symbol (capital letters, numbers, punctuation) can help us to focus on the detail that interests us. ACTIVITY 1 Read the questions and see how quickly you can find the answers in the passages that follow. Look for clues that help you to find the information. Passage A 1. 2. 3. 4. What were the export and import figures for the United States in 1974? Which countries are the largest buyers of U.S. goods? From which countries do the imports come? What percentage of goods entered the United States duty free in 1974? The United States carries on trade with most of the nations of the world. In 1974, its exports were valued at approximately $98 billion and its imports at $100 billion. The leading exports are industrial and electrical machinery, chemicals, grain, aircraft and motor vehicles. Canada and Japan are the largest single-country customers, buying about 30 percent of the total. Some of the principal imports are coffee, sugar, tea, petroleum and fuel oil, textiles and motor vehicle products. They come from Europe, Latin America, Asia and Canada. For years, the United States has been following a policy of promoting world trade by lowering tariffs. This has gradually reduced U.S. duties on imports so that in 1974, 2 percent of all goods entered the country duty free. 41 Passage B 1. 2. 3. 4. Who does the author quote to introduce the main point? Which four books are mentioned? Who are the authors? When were the last three books published? “Not acid, speed or junk but school is the most destructive drug in America today”. This is Anatole Broyard’s summation of the theme of Ivan Illich’s Deschooling Society. This revolutionary concept is being heard more and more in a series of reevaluations of the school system. In three books published in the 1960s, we find some of the forerunners of Illich: How Children Fail by John Holt, Compulsory Miseducation by Paul Goodman, and Death at an Early Age by Jonathan Kozol. The three provide us with a comprehensive view of educational trends from Holt’s private school to Goodman’s public school to Kozol’s segregated public school in Boston. All three recognize a failure in the educational system that has perpetrated a heinous crime on the minds and hearts of America’s children. ACTIVITY 2 Scan the next paragraph to find the following information. 1. 2. 3. The name of Laurence Stern’s novel. The year in which the first parts of the novel were published. The way in which the book is described by different critics. Laurence Stern was an English novelist who went far beyond the literary expression of the eighteenth century. Tristram Shandy, whose first parts were published in 1759, is an example of a book that defies categorization. Thought to be “merely a satire” by a leading critic of the time, a “sentimental journal” by a fellow writer, an “epic of Rabelaisian proportions” by a group of distinguished scholars, we are forced to consider it as all of these and more. The scope of Tristram Shandy invites the scholar to read more and classify less. It will be our task to analyze various aspects of Stern’s novel to determine its romantic elements and thus see it as a precursor to the nineteenth-century Romantic revolution. 42 Skimming to Extract Specific Information We use the technique of skimming when we are looking for specific information that is not marked by visual clues or for an idea that is embedded in the text. In such cases, we want to locate the position of the information so we will know at which point to begin close reading. Skimming is a more thorough than scanning. If we are reading to find the answer to a specific question, the words that appear in the question (or synonyms of these words) will probably be in the text. We let our eyes wander over the text until we locate words that express the ideas phrased by the question. We then read that part of the text carefully. ACTIVITY 3 Check off () the questions that are directly answered in the passage that follows them. Note that the same concept (idea) may be named differently in the question and in the text (synonyms or paraphrasing may be used). 1. 2. 3. 4. What factor has hampered the study of humanities? How is literature different from the fine arts? What are two possible ways of viewing literature? Which position does the author take? The study of the humanities has always been hampered by its abstract terminology. Literature, as distinct from the fine arts, deals exclusively with words. Lacking the visual aspect of painting and the audio aspect of music, it remains an ambiguous entity that is constantly being redefined. Definitions of literature often reflect two extreme positions. There are those who see literature as a form of art, as a way of translating experience and others who see it as a social document. ACTIVITY 4 The following are the first lines of several paragraphs of a text. Your purpose in reading this text is to learn more about the specific differences between animal and human behavior. Skim the passage to decide where to begin reading more closely. Check off () the sentence that most likely marks the end of your skimming and the beginning of close reading. The Scientific Method and the Puzzles of Nature The greatest of all the accomplishments of twentieth-century science has been the discovery of human ignorance. 43 It is the admission of ignorance that leads to progress, not so much because the solving of a particular puzzle leads directly to a new piece of understanding but because the puzzle -- if it interests enough scientists -- leads to work…. College students and, for that matter, secondary school students should be exposed very early to the big arguments currently going on among scientists…. There is, for one, the problem of animal awareness. One school of ecologists devoted to the study of animal behavior says that human beings are unique in the possession of consciousness, differing from all of the creatures in being able to think things over, capitalize on past experience and hazard informed guesses about the future. Other lower animals cannot do such things with their minds…. The point about this argument is not that one side or the other is in possession of a more powerful array of convincing facts -- quite the opposite…. This brings me to a second example of unsettlement in biology. This is the matter of chance itself and the role played by blind chance in the arrangement of living things on the planet…. ACTIVITY 5 Your purpose in skimming the first lines of the following text is to learn about the present-day economic policies and their rationale. Check off () the sentence that marks the end of your skimming and the beginning of close reading. Economic Policy In their professional lives, as distinct from their personal lives, economists rarely take a firm stand on the economic policy that should be followed by the country…. Many times, unclear thinking is expressed in jargon, expressions so impressive to laypersons that they believe any recommendations to be scientifically proven and justified. Economists often make value judgments, claiming, for example, that mass unemployment is “bad” and tariffs on foreign imports are “good.”… Here we intend to show the kind of policies that present-day economists prescribe and how far these policies can be justified scientifically…. Economists make their recommendations to the government whose task is to implement or reject proposals…. 44 Skimming for the Main Ideas in a Text Skimming is a useful technique when we want to find out quickly what the text is about. On the basis of the information that we get from skimming a text and reading only a minimal number of sentences, we can usually predict the main ideas and the content of the article. Although not all the texts are organized in the same way, we can find clues that help us. To skim an article for the main ideas, one should 1. Read the title and subtitle carefully. 2. Read the beginning of each paragraph or the first and last paragraphs of an article or chapter. 3. Look for the following words or expressions (they are usually used to introduce important ideas). I/we think / believe / argue / suggest / support / agree / disagree… The principal advantage / disadvantage / objection… The problem / task / hypothesis / premise / point… The results indicate / show / prove… The crucial facts / effects / difficulties / outcomes… ACTIVITY 6 Read the questions below and see how quickly you can find the answers in the text that follows. 1. In which paragraph does the writer compare attitudes in the past with attitudes in the present? _____ 2. In which paragraph does the writer state his idea? _____ 3. In which paragraph does the writer explain the objection to his idea? _____ 4. In which paragraph does the writer present the advantages to his idea? _____ 5. Which of the following alternatives best summarizes the writer’s argument? a. Conditions nowadays are much better than they were a hundred years ago. b. Everybody should receive a minimum amount of money for subsistence for a limited period whenever they want it. c. If people were to receive money for no reason, nobody would want to work. d. The main advantage of the writer’s plan would be to improve interpersonal relationships. The Right to All to a Guaranteed Subsistence 1. A hundred years ago, it was a widely-accepted belief that no one had the responsibility for his neighbor. It was assumed and scientifically “proved” by economists that the laws of society made it necessary to have a vast army of poor and jobless people in order to keep the economy going. Today, hardly anybody would dare to voice this principle. It is generally accepted that nobody should be excluded from the wealth of a nation, either by the laws of nature or by those of society. The rationalizations which were current a hundred years ago, that the poor owned their condition to their ignorance, lack of responsibility -- briefly to their 45 “sins”, are outdated. In all Western industrialized countries, a system of insurance has been introduced which guarantees everyone a minimum of subsistence in case of unemployment, sickness and old age. I would go one step further to argue that even if these conditions are not present, everyone has the right to receive the means to subsist. Practically speaking, that would mean that every citizen could claim a sum, enough for the minimum of subsistence, even though he is not unemployed, sick or aged. He can demand this sum if he has quit his job voluntarily, if he wants to prepare himself for another type of work, or for any personal reason which prevents him from earning money, without falling under one of the categories of the existing insurance benefits; in short, he can claim his subsistence minimum without having to have any “reason”. I would suggest, however, that it should be limited to a definite period of time, let us say two years, so as to avoid the fostering of a neurotic attitude, which refuses any kind of social obligation. 2. This may sound like a fantastic proposal, just as, I think, our insurance system would have sounded to people a hundred years ago. The main objection to such a scheme would be that if each person were entitled to receive minimum support, people would not work. This assumption rests on the fallacy of the inherent laziness in human nature; actually, aside from neurotically lazy people, there would be very few who would not want to earn more than the minimum, and who would prefer to do nothing rather than work. 3. However, the suspicions against a system of guaranteed subsistence minimums are not unfounded from the standpoint of those who want to use ownership of capital for the purpose of forcing others to accept the work conditions they offer. If nobody were forced to accept work in order not to starve, work would have to be sufficiently interesting and attractive to induce one to accept it. Freedom of contract is possible only if both parties are free to accept and reject it; in the present capitalist system this is not the case. 4. But such a system would not be only the beginning of real freedom of contract between employers and employees; its principal advantage would be the enhancement of freedom in interpersonal relationships in every sphere of daily life. ERICH FROMM 46 INFERENCES: Sometimes someone will try to tell you something without coming right out and saying it. He will imply it. When you understand what is implied, you infer. Sometimes you can infer the truth even when the speaker or writer isn’t trying to be helpful. That’s called “reading between the lines.” A. See if you can infer an implied or hidden message in each of the following selections: Turner almost wished that he hadn’t listened to the radio. He went to the closet and grabbed his umbrella. He would feel silly carrying it to the bus stop on such a sunny morning. 1. Which probably happened? a. Turner realized that he had an unnatural fear of falling radio parts. b. Turner had promised himself to do something silly that morning. c. Turner had heard a weather forecast that predicted rain. d. Turner planned to trade his umbrella for a bus ride. “Larry, as your boss, I must say it’s been very interesting working with you,” Miss Valdez said. “However, it seems that our company’s needs and your performance style are not well matched. Therefore, it makes me very sad to have to ask you to resign your position effective today.” 2. What was Miss Valdez telling Larry? a. She would feel really bad if he decided to quit. b. He was being fired. c. He was getting a raise in pay. d. She really enjoyed having him in the office. No, Honey, I don’t want you to spend a lot of money on my birthday present. Just having you for a husband is the only gift I need. In fact, I’ll just drive my old rusty bucket of bolts down to the mall and buy myself a little present. And if the poor old car doesn't break down, I’ll be back soon. 3. What is the message? a. I don’t want a gift. b. Buy me a new car. c. The mall is fun. d. I’ll carry a bucket for you. Bill and Jessica were almost done taking turns choosing the players for their teams. It was Jessica’s turn to choose, and only Kurt was left. Jessica said, “Kurt.” 47 4. We can infer that ________ a. Kurt is not a very good player. b. Jessica was pleased to have Kurt on her team. c. Kurt was the best player on either team. d. Jessica was inconsiderate of Kurt’s feelings. B. For each passage, check () the three statements that are most logically supported by the information given. Although many citizens think of American business as corporate giants like General Motors and IBM, small businesses – defined by the government as any with 100 employees or fewer – are a significant part of the economic scene. Fully one-half of the labor force is employed by small businesses. Small businesses encompass everything from coffee shops to dry cleaners, from law firms to dog-walking services. However, several factors are common to almost all small businesses. Lack of capital is often a problem. Further, small businesses are particularly vulnerable to fluctuations in the marketplace. Even given these problems, however, hundreds of thousands of businesses are found each year. These businesses seem to fit well with the American ideal of independence. (One part of this ideal, however, is hard work, including far more than forty hours of work per week.) _____ a. The health of the American economy depends in large part on the success of small business. _____ b. The author feels the government should provide financial backing to small businesses. _____ c. A large majority of owners of small businesses are good judges of the amount of capital their business will need to get a good start. _____ d. Running a small business generally requires more time than working for one. _____ e. The author feels that people who start a small business are probably partly motivated by the desire to be independent. 48 Sentence Structure Simple sentences: The two main "actors" in the simple sentences are the subject and the verb (or the predicate). Once you recognize them, you should be able to understand the main idea of the sentence. The subject tells us who or what the sentence is about and the verb tells us what the subject does or what happens to the subject. The girl runs. In this sentence, "girl" is the subject and "runs" is the verb (predicate). The little red-headed girl runs towards her friends. In this sentence both the subject (girl) and the predicate (runs) are expanded by the addition of different descriptive words. However, the basic meaning (the main idea) remains the same. Compound sentences: Compound sentences are two or more simple sentences that are connected with and, or, but. Some Israeli youth prefer to begin their college or university education right after the army service, and some young people prefer to go on a long post-army trip first. In this compound sentence, there are two simple sentences connected by “and”. Each of these sentences contains a subject and a verb. Sentence 1: Some Israel youth =subject; prefer to begin = verb Sentence 2: some young people = subject; prefer to go = verb. 49 Identifying Subjects and Verbs What do subjects look like? The subject of the sentence will answer the question "Who?" or "What?". The subject can be a single word, like in the following sentences: John often comes late to class. On Saturdays, she never gets up before 9 o'clock. Before giving a test, the teacher should make sure that the students are wellprepared. The subject can be a group of words: My friend and I both have a dog named Spot. Many parts of the Asian coastline were destroyed by a tsunami in 2004. To interrupt when someone is talking is not polite in North American society. Sitting in a tree at the bottom of the garden was a huge black bird with long blue tail feathers. Note: The subject is not always at the beginning of the sentence. 2) What do verbs look like? Verbs tell us what is happening to the subject. Verbs can be one word: The size of his house amazed me! Her grandchildren bring a lot of joy to her life. Verbs can be a group of words: I should have taken my umbrella to work today. Dinner was being served when we arrived at the house. Exercise 1: Find the subject and the verb in the following sentences. Underline the subject once and the verb twice. 1. Some countries oblige all young people to serve in the army for a certain period of time immediately after they leave school. 2. Accidents occur frequently in the state of New Jersey. 3. Most people have some sort of phobia. 50 4. The bright lights and the colored signs of the fast food restaurants always tempt us to go in. 5. Many sports are closely connected to specific countries and cultures. 6. Parental obsession with winning leaves young athletes feeling frustrated and confused. 7. In the year 2002, Bollywood sold one million tickets more than Hollywood did. 8. The dangerous viruses "GoKar", "Redesi-B" and "Admirer" were transmitted by e-mail. 9. Children throughout the ages have always gone into the woods to light fires, sleep in tents and climb trees. 10. Teachers in America today are using rap – the street-smart, rhyming creations of Shakur, Geto Boys, and others -- to teach history and English. Subject/Noun Clauses The subject can be a "clause" -- starting with the words who, which, when, how, what, where, why, or whose. How you spend your money is your own business. What that man did was wrong. Note: We can see that these are subject clauses because they have no question marks at the end. The following words also mark subject clauses: whoever, whatever, whichever, whether. Whoever wants ice cream should come inside now. Whether she succeeds on this test could change her life. Exercise 2: Find the subject and the verb in the following sentences. Underline the subject once and the verb twice. 1. Whoever ate my lunch is in big trouble. 2. How you will finish all your homework on time is a puzzle to me. 3. The coldest time of year is in the winter. 51 4. That the museum cancelled the lecture disappointed me. 5. Traveling in Europe in the winter can be very unpleasant. 6. Last night I finished my homework, cleaned my bedroom, and spoke to my friend on the phone. 7. The location for the party can be wherever you want. 8. The newest worker on the team should not have spoken so confidently about the project. 9. To retire at age 50 is something we can all hope for. 10. What was said in the argument doesn't matter any more. Adjectives Adjectives, which are single words, come before the nouns they describe. We can have many different adjectives one after the other. The very tall young man joined the basketball team. Sometimes adjectives look like verbs: The depressing movie made me cry all night long. Be careful of falling rocks in this area! There were so many crying babies on the flight to Toronto. verb + "ing" These adjectives describe what the nouns are doing. We need to get our broken window fixed quickly. The forgotten package was picked up by the cleaners. The talented piano player performed at the concert hall. V3 form of verb These adjectives describe the state ( )מצבof the nouns. Exercise - Note the difference between each pair of words, and translate to Hebrew. 1. a confusing teacher _________________________ a confused teacher _________________________ 2. a frightening monster ________________________ a frightened monster _________________________ 52 3. a shocked psychologist _______________________ a shocking psychologist _______________________ Noun Modifiers Nouns can be modified by adjectives, or by other nouns. When two or more nouns are next to each other in a sentence, the first one(s) act(s) as an adjective and describe the last noun of the sequence. Example: A horse race is a race where horses compete with each other. A race horse is a horse trained for racing. Exercise 1: Read the following sentences. Underline noun modifiers and circle the nouns they describe. 1. A mystery story keeps you in suspense until the end. 2. My second-floor neighbor is a sleep-walker. I saw him walk around at night. 3. The blood-stained murder weapon was forgotten at the scene of the crime. 4. A new book review was highly recommended by our teacher. 5. The prison officials allowed prisoners to keep cats. 6. I wrote a letter to the central government office. 7. O’Henry’s short stories have become world famous for their witty, sparkling humor. 8. Who do you think will be the next world chess champion? 9. We decided to meet at Hyde Park corner at eight o’clock. 10. The shabbily dressed woman walked down the street with a shopping cart full of old clothes. 11. The article describes the traditional medical practices that are passed from generation to generation. 12. The Royal Ballet Company dancers are well-known for their excellent performing skills. 13. Thousands of first time voters will take part in the coming elections. 14. Eilat is a popular tourist attraction in Israel. 15. Joseph Rotbolt, a Nobel Peace Prize winner, gave the $1 million prize money to the French Peace Organization. 53 Exercise 2 Read the sentences and answer the questions by circling the correct answer: 1. You should visit the Shakespeare Memorial Theatre in Stratford-on-Avon. What should you visit? a) Shakespeare’s memorial. b) the theatre c) the memorial in Stratford-on-Avon 2. The course in English Language History, which I took at university, was very interesting. Which course was very interesting? a) in English language b) in the history of English c)in the history of England 3. My little sister is afraid of ghost stories. What is my sister afraid of? a) ghosts b) stories about ghosts c) stories told by ghosts 4. Prado is Spain’s biggest picture gallery. What is Prado? a) the biggest city in Spain b) a very big picture c) an art gallery 5. His travel company offers an unforgettable wine-tasting tour of the Chianti country. What does the travel company offer? a) a tour to taste wines b) unforgettable wines c) unforgettable Chianti country 6. The audience warmly greeted the world-famous opera singers. Who or what was warmly greeted by the audience? a) the well-known singers b)the famous opera c) the singers from all over the world 7. Their lavish wedding was followed by a fairy-tale honeymoon cruise along the Chao Phya river. What followed the wedding? a) a fairy tale about a honeymoon b) reading fairy tales c) a cruise along the river Complex sentences: A complex sentence is the main clause and the subordinate clause/s together. In order to simplify a complex sentence, we should be able to recognize the parts it is made of, namely, the main clause and the subordinate clause/s. A subordinate clause may appear in the following forms: 1. Adjective clauses 2. Reduced adjective clauses 3. Dependent clauses 54 The adjective clauses and the reduced adjective clauses usually separate between the subject and the verb. It is, therefore, essential to recognize them to understand the idea of the sentence. Adjective clauses: My aunt Linda, whose son is working with refugees in Africa, now lives in Israel. The girl who was riding a bicycle said hello to me. The town where I lived in my childhood had a population of only 5,000 people. Pay attention to the following words, which may indicate an adjective clause: who (refers to person), which (refers to an object or an animal), that (replaces who and which), whose (shows possession), where (refers to place), when (refers to time) Exercise 1: Underline the adjective clause in each sentence. Then circle the word the clause modifies. Put a box around the main verb. EXAMPLE: The book that was missing had turned up at last. 1. Only people who have experience with lions and tigers need apply. 2. The carton that contained the dishes was undamaged. 3. A trapper who knew the woods well led the rescue party. 4. Grandpa still has the first dollar that he ever earned. 5. The author dedicated the book to his uncle, who had been kind to him. 6. The beggar whom the poor farmer helped was really the king. 7. We need a treasurer who can add and subtract. 8. The judges awarded the prize to the girl who made the dragon kite. 9. The page that has the brownie recipe on it is too smudged to read. 10. Alicia finally met the woman whom she had admired for so long. 55 Reduced adjective clauses: The man responsible for the administration of the hospital refused to consider the request. = The man who is responsible for the administration of the hospital refused to consider the request. How can we identify reduced adjective clauses? There are some patterns to look for: 1. noun + adjective noun adjective The neighbor (who is) responsible for my children is not at home. 2. noun + V+ing noun V+ing The movie (which is) playing at the mall is sold out. 3. noun + V3 noun V3 The equipment (that was) broken yesterday cost a thousand dollars Exercise 2: Underline the adjective clause in each sentence. Then circle the word the clause modifies. Put a box around the main verb. EXAMPLE: Factories polluting the environment must be closed or controlled. 1. In some countries, people producing trash are punished. 2. Follow the instructions given in the user’s guide to use your cassette player wisely. 3. The scientists researching the causes of climate change are making progress. 4. The photographs taken of the Earth were wonderful. 5. The strategy planned to control pollution in Tehran is effective. 6. Acid rain created by burning of gas, oil, and coal destroys forests. 7. Factories burning coal and oil help increase pollution. 8. Farming produces another greenhouse gas called methane. 9. Global warming caused by human activities has serious effects on people’s health. 10. Trash believed to be useless can be burned to produce energy. 56 Note: Sometimes the information provided in the clauses is essential, while at other times it may be ignored. Consider the following examples: Monotheism is the belief that [there is only one God]. In this sentence the subordinate clause marked by [ ] provides essential information. Steinberg, who [is an expert on proper dietary practices] has found that [the Rambam had very specific guidelines on how we should maintain our health through proper diet and exercise]. While the information in the first clause is completely minor, the second clause provides the message of the sentence, from which we learn about the Rambam. Sometimes commas are very important to the meaning of the sentence. Consider this example: The bananas, which are green, are not ready to be eaten. The bananas which are green are not ready to be eaten. In the first sentence, the information between the commas is minor, but in the second sentence the same words provide an important condition about which bananas can be eaten, and which cannot. Exercise: 1. a. My brother, who is a tour guide, has shown me all around Israel. b. My brother who is a tour guide has shown me all around Israel. Which sentence implies that I have more than one brother? _____ 2. a. The children, who ran in the house, wanted to eat ice cream. b. The children who ran in the house wanted to eat ice cream. Which sentence implies that all the children wanted to eat ice cream? _____ Dependent clauses: A dependent clause is a group of words that has a subject and a verb of its own, but is NOT the main part of the sentence; it explains or expands the main clause. Dependent clauses start with connectors. As [inflation rises], people spend less money because [the price of everyday items goes up]. "People spend less money" is the main clause of the sentence. 57 Exercise: In the following sentences underline the main clause once and the subordinate clause twice. Then answer the comprehension questions that follow. 1. If children do not have words to use, their minds are, inevitably, a jumble of responses to which they can react only emotionally, often with frustration. a. Under what conditions do children’s minds become a jumble of responses? __________________________________________________________ b. What happens when the children’s minds become a jumble of responses? __________________________________________________________ 2. Women should achieve more status and power in the medical media, so that it reflects the real variety of women’s social roles. What is the purpose of the women’s aspiration to achieve more status and power in the medical media? __________________________________________________________ 3. Hunting was transformed from a means for survival into a leisure activity, which enabled men to gather together socially and satisfy their need for the excitement of hunting and killing animals. When hunting became a leisure activity, men could ______________ __________________________________________________________ 4. When Martin Luther King, Jr. and the movement he led guided mass demonstrations in Alabama in 1963, clashes between black demonstrators and police using police dogs and fire hoses were reported around the world. What information about the mass demonstrations in Alabama reached the media? __________________________________________________________ 6. Because of the success of the animal zealots in the general public, who do not necessarily understand the scientific implications, support for so called “animals rights” has become “politically correct”. a. The general public supports/doesn’t support animal activists. Why? ______________________________________________________ b. What is the result of this? ____________________________________ 7. In several countries, addicts can go to “injection rooms” where they can use drugs in a clean environment, without fear of catching diseases caused by sharing needles. Complete the sentence: Since sharing needles may lead to _________________ (one word), drug addicts in several countries can use _______________________. 58 What is Passive Voice? Verbs are said to be either active voice (The committee approved the new policy) or passive voice (The new policy was approved by the committee). In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward: the subject is a be-er or a do-er and the verb moves the sentence along. In the passive voice, the subject of the sentence is neither a do-er nor a be-er, but is acted upon by some other agent or by something unnamed (The new policy was approved). Why are some sentences written in the Passive Voice? 1. We don't know who did the action in the sentence. My wallet was stolen last night. (We don’t know who stole the wallet.) 2. When the agent ("doer") is unimportant: The new students’ centre was completed last week. (We don't need to know who built the centre in order to understand the meaning of the sentence.) 3. When the agent ("doer") of the action is obvious from the context: I was born in March of '55. (Everyone knows that my mother bore me) 4. To emphasize (put importance on) the recipient (receiver) of the action: a. Only Jane was injured in the accident; everyone else was unhurt.(we want Jane to be the subject of the sentence and at the beginning to emphasize her importance) b. Erina was chosen as best student. (The teacher who chose Erina is not what we want to emphasize.) 5. To make general statements, announcements, and explanations: a. Something should be done about the traffic jams in this town. b. Customers are asked not to smoke. c. The computer is turned on, then the disk is inserted into the drive. 59 Formation of the Passive Voice The Passive is formed like this: Passive Subject + To Be + V3 If the agent ("doer") is important, use "by": Example (Active Voice): Tim Wilson wrote "The Flight to Brunnswick" in 1987. Changes to: "The Flight to Brunnswick" was written in 1987 by Tim Wilson. Only verbs that take an object can be used in the passive. The following chart includes sentences changed from the active to the passive in the main tenses. Active Passive Time Reference David cleans the house. The house is cleaned by David. David is cleaning the house. The house is being cleaned by Present Continuous David. David cleaned the house. The house was cleaned by David. Present Simple Past Simple David was cleaning the house The house was being cleaned when I arrived. when I arrived. Past Continuous David has cleaned the house every week since he got married. The house has been cleaned by David every week since he got married. Present Perfect David is going to clean the house tomorrow. The house is going to be cleaned by David tomorrow. Future Intention with Going to David will clean the house tomorrow. The house will be cleaned by David tomorrow. Future Simple Note that the tense (time reference) is now identified by the form of the addition of the "to be" verb. Identifying the Passive Voice Read the following article. Circle all verbs in the Passive Voice. 60 Travel Chaos This Weekend A £100m engineering programme means that sections of three of the busiest railway lines will be closed over the August bank holiday weekend. All trains between Reading and London have been cancelled until 0500 BST on Tuesday. Extra trains have been scheduled from Waterloo. Services between London and Stansted airport will be disrupted on Sunday, while trains from London to Birmingham New Street will be diverted around Coventry and Birmingham International on Saturday and Sunday. The head of the railway company said, ‘The choice has to be made when to do the work, and I recognise that some people are going to be inconvenienced this weekend.’ ‘The bank holidays are three-day weekends, and, when major works are being done, it gives us the opportunity to do these efficiently and at a reduced cost.’ A representative of the Rail Passengers Council said that passengers had not been informed of the plans. He told our reporter that increased disruption could be accepted if people thought that it was being planned efficiently. Read these sentences. Are they in the Active or Passive Voice? 1. The instructions have been changed. A ___ P ___ 2. People must not leave bicycles in the driveway. A ___ P ___ 3. She will have to be taught how to swim. A ___ P ___ 4. This car was manufactured in Japan by Toyota. A ___ P ___ 5. They were cooking dinner when I arrived. A ___ P ___ 6. Why aren't the exercises being finished on time? A ___ P ___ 7. Last year 2,000 new units had been produced by the time we introduced the new design. 8. A ___ P ___ They are going to perform Beethoven's Fifth Symphony next weekend. A ___ P ___ 9. Casual clothes must not be worn. A ___ P ___ 10. 044,444$in profit has been reported this year. A ___ P ___ 11. The test will be given at five o'clock this afternoon. A ___ P ___ 12. Students are required to wear uniforms at all times. A ___ P ___ 13. They have finished the new product design. A ___ P ___ 14. This rumor must have been started by our competitors. A ___ P ___ 15. The students will finish the course by July. A ___ P ___ 16. They are repairing the streets this month. A ___ P ___ 17. All work will have been completed by five o'clock this evening. A ___ P ___ 18. We were told to wait here. A ___ P ___ 19. You should take care when working on electrical equipment. A ___ P ___ 20. A ___ P ___ Lunch was being served when we arrived. 61 MAIN IDEAS: The following paragraphs have main ideas that may appear at various places within the paragraph. Identify the main idea of each paragraph by filling in the correct sentence number in the space provided. Fill in two numbers in the one case where the main idea appears twice. 1. 1 People's ideals of beauty often change over time. 2 During part of the sixteenth century, for example, very high foreheads were considered beautiful. 3 Women sometimes plucked their eyebrows and shaved off part of their hair in order to make their foreheads look higher. 4 A little later, Queen Elizabeth I of England wore a solid inch of make-up on her face. 5 Standards of beauty in former times were thus sometimes very different from our standards today. Main idea(s): _________ 2. 1 The entertainment world has a history of discrimination against black performers. 2 For many years, for instance, radio listeners tuned in to Amos 'n' Andy, a popular situation comedy about two black men. 3 But the actors who played Amos and Andy were both white. 4 In those same years, before the start of the civil-rights movement, talented black singers were hired to dub in movie songs for white actresses who couldn't sing. 5 The singers' names, however, could never appear in the movie credits. Main idea(s): _________ 3. 1 About 20,000 robots are already working in American factories, with General Motors being the largest user. 2 Including all fringe benefits, it costs GM about twenty-five dollars an hour per autoworker. 3 However, a robot does the same work -- with no days off, no complaining, and no mistakes -- at a cost of five to six dollars an hour. 4 In addition, international competition will force us to use more and more of the money-saving robots. 5 Japan is already using over four times the number of robots in the workplace as America 62 does. 6 Economic reasons in and out of our country make the rapid growth of robot labor in America likely. Main idea(s): _________ 4. 1 In 1967, the Age Discrimination Act made it a federal policy to prohibit the firing of employees because of their age before they reached the required retirement age. 2 In 1978, Congress extended the mandatory retirement age from 65 to 70 in business, industry, and the federal government. 3 In 1986, Congress voted to ban mandatory retirement for all but a few occupations, such as police officers, firefighters, and airline pilots, where safety is an issue. 4 Federal laws now prohibit employers from firing older workers, who have seniority and higher salaries, just to save money. 5 The rights of older workers in our society, then, continue to strengthen. Main idea(s): _________ 5. 1 For a year or so in the 1950s, the Hula Hoop (a hoop twirled around the body) became a popular fad. 2 Millions were sold, and Hula Hoop makers who got in on the fad became rich. 3 The ones who got in too late, though, were stuck with thousands of Hula Hoops that no one wanted. 4 The same thing happened in the 1970s and 80s with mood rings and pet rocks. 5 In promoting a fad, timing and imagination are everything. 6 For example, the Walt Disney Company once found itself stuck with warehouses of unwanted coonskin caps after a fad for Daniel Boone caps died down. 7 But the company solved its problem by making a TV show about Davy Crockett, who also wore a coonskin cap. 8 The show became popular and Disney was able to sell the rest of its coonskin caps as Davy Crockett caps. Main idea(s): _________ 6. 1 When Chevrolet began to sell its Nova cars in Latin America, hardly anyone would buy them.2 The company finally learned that Spanish speakers read the car’s name as the Spanish phrase “no va," meaning "doesn't go"! 3 Like Chevrolet, many American companies have learned the hard way that they need to know their customers’ language. 4 When Pepsi-Cola ran its "Pepsi gives you life" ads in China, the consumers laughed. 5 The company had not translated its slogan quiet right. 6 In Chinese, it came out as "Pepsi brings your ancestors back from the dead.” Main idea(s): _________ 7. 1 Profound changes have reshaped American family life in recent years. 2 In a decade, divorce rates doubled. 3The number of divorces today is twice as high as in 1966 and three times higher than in 1950. 4 The rapid upsurge in the divorce rates contributed to a dramatic increase in the number of single-parent households -- or what used to be known as broken homes. 5 The number of 63 households consisting of a single woman and her children has tripled since 1960. 6 A sharp increase in female-headed homes has been accompanied by a startling increase in the number of couples cohabitating outside of marriage. 7 The number of unmarried couples living together has quadrupled since 1970. Main idea(s): _________ 8. 1 Usually we think of best as a stronger claim than merely better. 2 But in advertising, best and better don't mean what they do in everyday life. 3 In advertising law, you can call a product better only if it really is better than competing products. 4 But to call a product best you only have to show that it is as good as the others. 5 If all the products are equally good, then according the law, they are all the best. 6 If a headache pill is said to contain the best pain reliever, this just means that it is as good as the pain reliever in other pills. Main idea(s): _________ PATTERNS OF ORGANIZATION: The following textbook passages use a combination of patterns of organization (as is often the case in all types of writing). Circle the letters of your answers to the questions about the passages. A. 1 Japanese children go to school year-round, including half-days of classes on Saturdays. 2 Admission to Japanese universities is based entirely on competitive examinations. 3 Test scores literally make or break the college aspirations of young people, whether they are rich or poor. 4 Students prepare frantically for these all-important examinations, and parents often see that their children are well prepared by enlisting the services of tutors to supplement regular classroom study. 5 Despite placing enormous pressure on adolescents, the Japanese educational system produces impressive results. 6 In a number of academic areas – most notably mathematics and science – Japanese students outdistance students of all other industrial societies, including the United States. 1. The main idea of the passage is a. sentence 1 b. sentence 2 c. sentence 3 4. sentence 5 2. The results of the Japanese educational system are explained in a. sentence 1 b. sentence 2 c. sentence 4 d. sentence 6 B. It’s been a long time since Johann Sebastian Bach, the eighteenth-century German composer, last wrote any music. But listeners can be forgiven if they briefly mistake music created by Kemal Ebcioglu for Bach’s work. Ebcioglu devised a computer program that writes harmonies remarkably similar to Bach’s. Ebcioglu analyzed Bach’s music and came up with 350 rules that govern harmonization. The resulting program displays what is known as artificial intelligence. 64 Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to computer programs capable of doing things that require intelligence when done by people. Artificial intelligence is based on the fact that many tasks – from harmonizing music to medical diagnosis – can be reduced to a set of rules applied to a body of information. AI is valuable in situations where speed, memory and persistence are required. In fact, AI programs are better at some tasks than humans. 1. Overall, this passage a. lists a series of steps in the process of creating artificial intelligence b. discussed the causes and effects of the rules governing harmonization c. illustrates, defines and explains artificial intelligence d. lists events in the history of artificial intelligence 2. The first paragraph a. illustrates “artificial intelligence” b. compares the music of Ebcioglu’s program with Bach’s music c. briefly describes the process Ebcioglu used in creating his program d. does all of the above D. 1 Although some evidence exists that women experience more minor illness than men, women outlive men by an average of more than seven years. 2 Sociologists and others have proposed various explanations for why women outlive men. 3 Some of the explanations take into account differences in lifestyle, diet, activity level and social circumstances between men and women. 4 Some analysts, for example, point to the fact that more men smoke cigarettes and engage in risky behavior (drinking too much, participating in dangerous sports, driving too fast and until recently men experienced more of the stresses and strains of the workplace and of the breadwinner role. 5 Other analysts maintain that certain genetic factors make women, in a sense, psychologically or medically superior to men. 6 Female hormones, for example, seem to play a role in protecting premenopausal women from heart disease and women seem less prone to high blood pressure than men. 8. The main idea of the paragraph is a. sentence 1 b. sentence 2 c. sentence 3 d. sentence 4 9. According to this paragraph, genetic factors are possible causes/effects. 10. Which outline best represents the organization of the paragraph? a. Possible reasons for why women outlive men b. Differences in lifestyle and social circumstances c. Genetic differences 65 References Reference Words: Words that refer to other words in the text are called Reference Words. They can be used individually or as groups of words, sentences or groups of sentences. The reference word usually points to something/someone mentioned earlier (before) in the text, however, it can sometimes refer to something that comes later (after) it Examples: The party was to take place on Saturday, however it was cancelled because of the storm. The word ‘it’ refers back to the party. Here are the people I want you to meet. ‘They’ will be able to help you in your work. The word ‘they’ refers back to people. In order to see if you have understood the reference word, substitute the reference word with the word you think it points to and see if the meaning is clear in the sentence in context. A reference word can also continue an idea. Example: Yesterday it rained very heavily all day. This caused flooding in the Southern part of the country. Here is a list of the more common reference words: 1. he/she, it, they Miriam is an English teacher; she teaches in Ashkelon College. 2. one (ones) Many books are uninteresting, but the one about the Rambam is fascinating. Chocolates are very delicious, but the ones with cherry liqueur are the most delicious. 3. this (these) that (those) There are people who are always prepared to denigrate other people’s opinions. This does not seem to be very fair. 66 4. so I think that to learn a language, you have to spend many hours reading, writing and speaking. Some students don’t think so. Millions of people all over the world know that smoking is harmful, but they do so anyway. 5. such(+noun) Almost everybody watches television, however, to watch television for hours is such a waste of time. 6. there, then My schooldays were some of my happiest days; there I learnt some valuable lessons in cooperation. When someone in the family dies, then one’s friends are very supportive. 7. the former, the latter Mr. Cohen and Mr. Levi are computer programmers. The latter has won many prizes. Exercise 1 Find the reference of the underlined words. 1. When we visited Luxembourg, we were surprised to see how beautiful it is. Everywhere its streets are wide and clean. it ______________________ its ________________________ 2. Recent research shows that Israel has one of the lowest scores in mathematics. This presents a serious problem in our schools. The students there are not getting to their potential. this_____________________ there ______________________ 3. Cigarettes are obviously bad for your health, so why do so many people get addicted to them? Many young people die of drug overdose, but it doesn’t stop them from experimenting. them ___________ it _____________ them______________ 4. Walking is good for you. Walkers are usually healthier and thinner than people who just sit and watch television. According to the latest research, they are also happier. they _________________________ 5. Many people are renovating their homes. They are putting in new bathrooms, kitchens and floors. Such renovations are very expensive. Such ___________________________________ 6. Politicians earn very large salaries. They are representatives of the people and should be examples to them. However, they do not always do the job expected of them. They ______________ them _________________ 7. In London, in the Underground the stations and trains are often old and dilapidated. In the Metro in France, the stations and trains are modern and clean. The former is also quite a fire hazard according to the newspapers. former ______________________ 67 8. Malnutrition is rife in Third World countries. Many African countries are known by this term. this term ______________________________ 9. My parents told me that it is important to save money from my salary. I also think so. so ____________________________________ 10. Charles Darwin was a brilliant naturalist who changed the way people think about life on earth. One reason why he was able to do this was because he was always passionate about science and nature. this ____________________________________ 11. Last year Canada's inflation rate was half that of the United States. that ___________________________________ Exercise 2 Answer the questions. Circle the reference word(s). 1. The approach taken by Bernstein is unacceptable because it ignores the psychological problems that the child is facing at that time. What doesn't take certain problems into account? __________________________ 2. The study with children was problematic, but the researchers conducted another study involving university students. This study was more successful. Which study was more successful? ____________________________________ 3. John criticized the new book very strongly. He did so because he had evidence supporting exactly the opposite theory. What did the evidence lead John to do? ________________________________ 4. Children must learn to listen carefully when teachers explain new concepts. In this way they will always keep up with the rest of the class. a. Who will keep up with the rest of the class? _________________________ b. How will they do this? ____________________________________ 5. Teenagers who disobey their parents' rules often get into trouble at school as well as at home. Such teenagers need very clear guidelines. What kind of teenagers need clear guidelines? _________________________________ 68 RECOGNIZING QUESTION TYPES 1. Looking for the Main Idea Sample Questions: a. What do the examples in paragraph 2 illustrate/show/demonstrate? b. Why was X mentioned/discussed? ("x" is an example of a main point) c. According to this paragraph, x, y and z are examples of ___________. d. What is the main idea of this paragraph? e. What is the writer's purpose in writing this article? Helpful phrases to find answers: for example, for instance, demonstrate, show, point out, illustrate Exercises: Text A: The study confirmed what is already known: Drug use among travelers in the Far East is significantly higher than among the same age group in Israel. Some 62.1 percent of the young people said that they used cannabis (hashish and marijuana), as opposed to 5.6 percent in Israel; some 33.8 percent said they used so-called “hard” drugs (including LSD, ecstasy, speed, opium, cocaine, and heroin), as opposed to 1.2 percent in Israel. Question A: What idea do the statistics in the above paragraph support? _____________________________________________________________ Text B: Every culture has developed preferences for certain kinds of food and drink, and equally strong negative attitudes towards others. It is interesting to note that much of this ethnocentrism is in our heads and not in our tongues, for something can taste delicious until we are told what it is. We have all heard stories about people being fed a meal of snake or horse meat or something equally repugnant in American culture and commenting on how tasty it was--until they were told what they had just eaten; as a result, they turned green and hurriedly asked to be excused from the table. Question B: What point is illustrated by the examples of meals of snake and horse meat? __________________________________________________________ Text C: Some doctors and social critics cannot help noticing that so many of the childhood syndromes now being diagnosed in record numbers affect far more boys than girls. Attention deficit disorder, said to afflict 5 percent of all children, is thought to be about three to four times more common in boys than girls. Dyslexia is thought to be about four times more prevalent in boys than girls; and boys practically have the patent on conduct disorders. Question C: The information in the above paragraph illustrates the idea that _______________________________________________________________ Text D: Meanwhile, the bureaucracy that accompanies a lot of aid is just as crippling. The African country of Tanzania is reportedly burdened with preparing 2,400 reports each quarter and hosting 1,000 meetings with donors annually -- no doubt at great cost. … Robert Calderisi cites a US$300million malaria project in which one cent of each dollar spent went to medicine, one cent to insecticides, six cents to mosquito nets, and 92 cents to training, research, administration and evaluation, most of which returned to Western donor countries in the pockets of consultants. 69 Question D: What do the Tanzania and malaria project examples illustrate? ______________________________________________________________ Text E: Most coffee drinkers think of their morning cup of coffee as containing little more than hot water, caffeine and coffee flavor. It's true that caffeine is responsible for many of coffee's health effects, both good and ill. But that's hardly the whole story; there are other beneficial ingredients in coffee. In 2005, for example, newspaper headlines promoted the finding that coffee is the number-one source of antioxidants in the US diet. Less publicized was the more recent finding that for most US adults, coffee is the main dietary source of many minerals, including the trace element boron. An essential nutrient for plants, boron may also prove beneficial to humans. Question E: Why does the author mention antioxidants and minerals? _____________________________________________________________ 2. Finding References A reference word usually refers to information that was mentioned earlier in the text. Therefore, in order to find the word or words that can replace the reference word(s), go back to sentences you have already read. Sample Questions: a. What does x refer to? b. What word can you use instead of x? c. Quote from text: "Such ideas are interesting." Which ideas are interesting? Common Reference Words: this, that, these, those, it, he, she, they, them, its, his, her, their, such, one, ones, there, then, which, who, whom, whose Exercises: Text A: In one group of monkeys, disputes over females were responsible for the deaths of thirty out of thirty-three of them. Two points are of particular interest in these fights for possession. First, they are often carried to such an extreme that they end in the complete destruction of the objects of common desire. Question A: What are “often carried to such an extreme…”? ________________________________________________________________ Text B: The notion of equal opportunity is central to the American ideal. For that goal to have any meaning, it must be rooted in an education system that gives every child a chance to succeed. But for decades, a gulf has been widening between the quality of public schooling for children of privilege and that for those born into poverty. Question B: In the above paragraph: "For that goal to have any meaning…" What goal is he referring to? _____________________________________________________________ 70 Text C: Our body movements always convey something about us to other people. The body "speaks" whether we are sitting or standing, talking or just listening. On a blind date, how the two individuals position themselves tells a great deal about how the evening will unfold: Is she leaning in to him or away? Is his smile genuine or forced? The same is true of gestures. Almost always involuntary, they tip us off to love, hate, humility and deceit. Yet for years, scientists spent surprisingly little time studying them, because the researchers presumed that hand and arm movements were mere by-products of verbal communication. Question C: “The same is true of gestures.” What is true of gestures? _____________________________________________________________ Text D: Lifestyle factors had long been implicated in the incidence of heart disease, but Ornish found that diet, exercise and stress reduction were being tried on a piecemeal basis only. No researcher had put them all together in a single experiment and measured the effect on the heart. Ornish decided to do just that, on the theory that if people could benefit from one major change in their lives, they could benefit even more by making several. Question D: “Ornish decided to do just that”. What is the author referring to? _____________________________________________________ 3. Identifying Questions of Cause and Effect Cause tells "why" something happened. Words identifying causes of an event: cause(s), why, the reasons (for), because, since. Sample questions: a. Why did x take place/happen? b. What was the cause of x? c. What were the reasons for x? Effect tells "what happened", what was the result or outcome of the issue. Words identifying effect (that is, the event itself) are: the result is, the outcome is, the effects are, as a result, leads to, Sample questions: a. What did x and y cause? b. Complete the following sentence: Because of x and y, _____________ happened. Draw an arrow between A and B, according to the instructions: A causes B A -------- B A results from B A -------- B A leads to B A -------- B A follows B A -------- B A results in B A -------- B A is a result of B A -------- B Since A, B A -------- B 71 Exercises: Text A: Common stereotypes and previous research suggest that sports participation may have a significant effect on the attitudes of peers and others, and vice versa. … Our society maintains gender stereotypes pertaining to participation in some sports, at least for dedicated athletes. This stereotyping of athletes may have an important impact on the willingness of athletes to participate in certain sports. Likewise, these stereotypes may tend to filter out certain types of potential participants-e.g., macho males, individuals with a high need for social approval or those high in self-monitoring --in athletic activities which are "inappropriate" for one's gender. Question A: What are the two possible results of athlete stereotyping? i. ____________________________________________________________ ii. ____________________________________________________________ Text B: No one seems to know where all the money went. Its disappearance has led to the current skepticism over aid's effectiveness. The old idea that something will eventually trickle down to the truly needy the moment local elites have lined their pockets no longer does the trick. . Question B: What is the reason for the current skepticism over aid's effectiveness? ________________________________________________________________ Text C: Last year “eco warriors” (environmental activists) began sounding the cry that Costa Rica's most coveted beach front and third most popular tourist destination spot had dangerous fecal concentrations. This announcement resulted in widespread shock and panic. Swimmers and surfers fled the sea, visitors panicked and packed up, and even banks re-evaluated construction loans, spelling disaster and a potential market crash. Question C: What caused “widespread shock and panic”? The fact that ___________________________________________________________________ 4. Identifying Listing Questions Questions that ask for numbers of elements/factors/reasons usually rely on words of sequence: first, second, third, further, another, in addition, moreover, next, then, later, afterwards, finally, and, also Sample questions: a. Name 3 factors/characteristics that are mentioned in paragraph 5. b. How many conclusions are listed/made/drawn? Text A: The causes of female infanticide are primarily economic. In India a daughter is often described as a "guest in her parents' house." Once she marries, a woman is expected to live with her husband's family, performing household chores and caring for her in-laws. Not only do her parents lose her services, but they are also expected to bear the full cost of the wedding. In addition, they must provide a dowry of cash and other gifts. A son, on the other hand, brings wealth – and another worker – into the family when he weds, and he continues the family name and business. Question A: What are the disadvantages for parents of a daughter when she gets married? 72 i) ___________________________________________________ ii) ___________________________________________________ iii) ___________________________________________________ 5. Identifying Contrast Questions These questions ask you to identify contrast in the text. You will likely see contrast connectors: but, however, while, on the other hand, yet, although, in spite of, instead of, unlike, even though, whereas, etc. Sample questions: a. While boys like to ________________, girls prefer to ____________. b. What is the relationship between paragraph 5 and paragraph 6? -- contrast, exemplification, addition or comparison Text A: It seems that most people are not making much of an effort. They are becoming aware of energy use of home appliances, shopping fair trade, and recycling but don't know much about the perils of the meat industry or commercial fishing, hidden costs of alternative energy or bio-piracy and seed modification. So, on the one hand, there is greater awareness within the general public about the overall state of affairs of the environment. But on the other hand, there isn't much awareness at all about causes and effects of specific issues. Question A: Complete the following sentence, showing the contrast presented in this paragraph. Whereas the public seems to be aware of the environmental issues in general, ______________________________________________________ 6. Identifying Comparison Questions These questions ask you to identify comparisons found in the text. You will likely see comparison connectors: similarly, like, likewise, just as …so, as…as, both, in the same way, etc. Sample Questions: a. X and y are similar in that both ________________________. b. What is x compared to in paragraph 3? Text A: In a recent study at the Baker Medical Research Institute in Prahran, Australia, 5741 people attending a heart disease risk clinic were questioned about their lifestyle, and whether they had any pets. Researchers found that the average cholesterol level of the 874 patients who owned pets was 2 percent lower than those who did not own pets. Epidemiologists estimate this might lower the risk of heart attack by four percent. Pet owners also had lower levels of fats in their blood and lower blood pressure, which indicated that owning a pet was as efficient in reducing blood pressure as eating a low salt diet or cutting down on alcohol. Question A: What are the TWO things owning a pet is compared to in paragraph 6? a.___________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________ 73