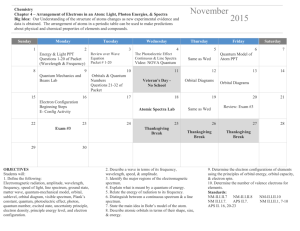
rev hwk cp u4
advertisement
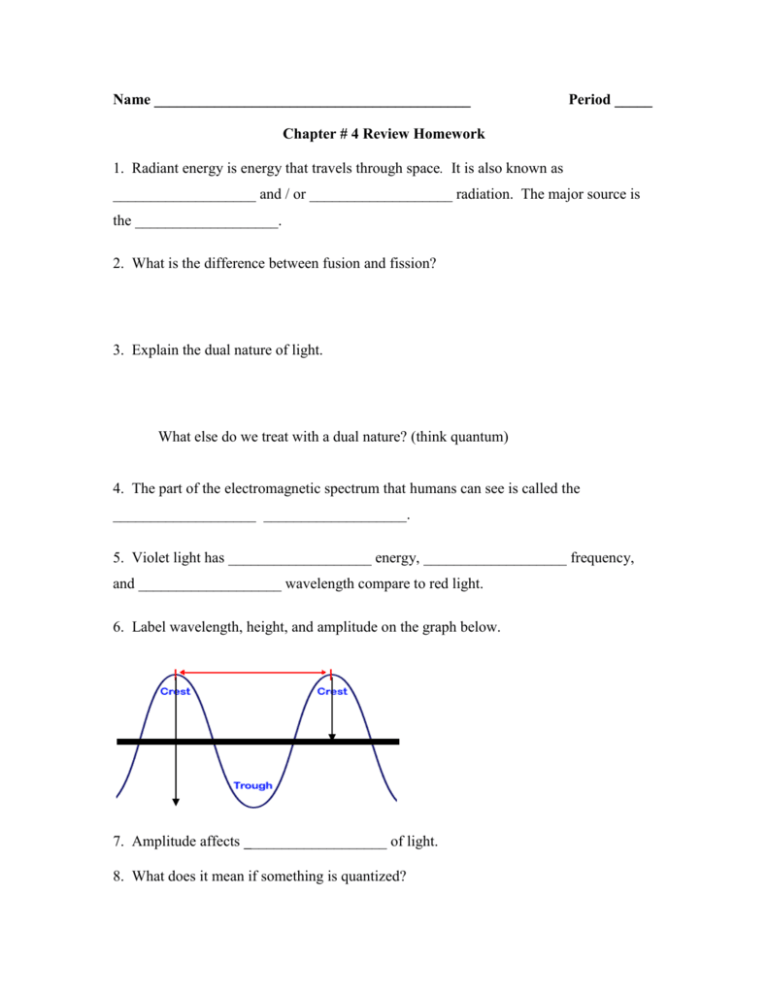
Name __________________________________________ Period _____ Chapter # 4 Review Homework 1. Radiant energy is energy that travels through space. It is also known as ___________________ and / or ___________________ radiation. The major source is the ___________________. 2. What is the difference between fusion and fission? 3. Explain the dual nature of light. What else do we treat with a dual nature? (think quantum) 4. The part of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see is called the ___________________ ___________________. 5. Violet light has ___________________ energy, ___________________ frequency, and ___________________ wavelength compare to red light. 6. Label wavelength, height, and amplitude on the graph below. a h 7. Amplitude affects ___________________ of light. 8. What does it mean if something is quantized? 9. A piece of light is called a ___________________ or a ___________________. 10. How is energy related to frequency? Frequency to wavelength? And so energy to wavelength? 12. The properties of an element are primarily a result of its ELECTRONS! know it! 13. How did the Gaviscon lab demonstrate the importance of valence electrons? 14. Write electron configurations for B, Ga, C, Be. 15. Look at the configurations in # 14, which element would you expect to react similarly to B? WHY? 16. If a light wave has a wavelength (λ) of 3.0 * 106 m, what is its frequency? 17. In problem #16, use the frequency (ν) to calculate the energy. (Plank’s constant = 6.626e-34 Js) (Show ALL work!) 18. If a wave has an energy of 10.0 J, what is its frequency? What is its wavelength? (Plank’s constant = 6.626e-34 Js) (Show ALL work AND answer both questions!) 19. Light with an energy of 300. mJ has a frequency of ______? 20. Light with a frequency of 6.0 * 1017 Hz, has a wavelength of how many nanometers? 21. Ant Arthur Compton was named after a famous scientist, who demonstrated that light can act as a particle. How did he demonstrate this? 22. Draw what happens as an electron becomes excited and falls back down to the ground state (YOU MUST SHOW AND/OR EXPLAIN ALL ENERGY CHANGES!) 23. Circle the correct option for each of the three choices below: Atoms prefer to be STABLE OR UNSTABLE, have LOW OR HIGH ENERGY, be in the GROUND OR EXCITED STATE. 24. How is an excited state different from the ground state of an atom? 25. Explain the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. 26. Explain how the current model of an atom is similar to the electron cloud, but also similar to Bohr’s model. 27. Pauli exclusion principle - 28. How do we define the “address” of the electron within the atom? 29. How many electrons in an orbital? _____ How many orbitals in each sublevel? s = _____ p = _____ d = _____ f = _____ How many sublevels in each energy level? 1 = _____ 2 = _____ 3 = _____ 4 = _____ 30. Energy increases _________________________ the nucleus. 31. Is the orbital pictured below an s, p, or d orbital? ______ 32. Is the orbital pictured below an s, p, or d orbital? ______ 33. Is the orbital pictured below an s, p, or d orbital? ______ 34. Why does the ring model for energy levels work even though individual orbitals can have complex 3d shapes? 35. For the following elements construct the complete electron configuration and answer the questions. a. Fluorine Electron configuration = ___________________________________ What is the highest filled energy level? _____ What is the highest filled sublevel? _____ What is the highest filled orbital? _____ b. Calcium Electron configuration = ___________________________________ What is the highest filled energy level? _____ What is the highest filled sublevel? _____ What is the highest filled orbital? _____ 36. Element Noble Gas Notation Orbital Diagram # of Valence Elecs. F Ca 37. If an electron moves from a 3s orbital to a 3p orbital has it gained or lost energy? 38. If an electron moves from a 2p to a 3s orbital has it released or absorbed energy?