Mesopotamia - TeacherWeb
advertisement
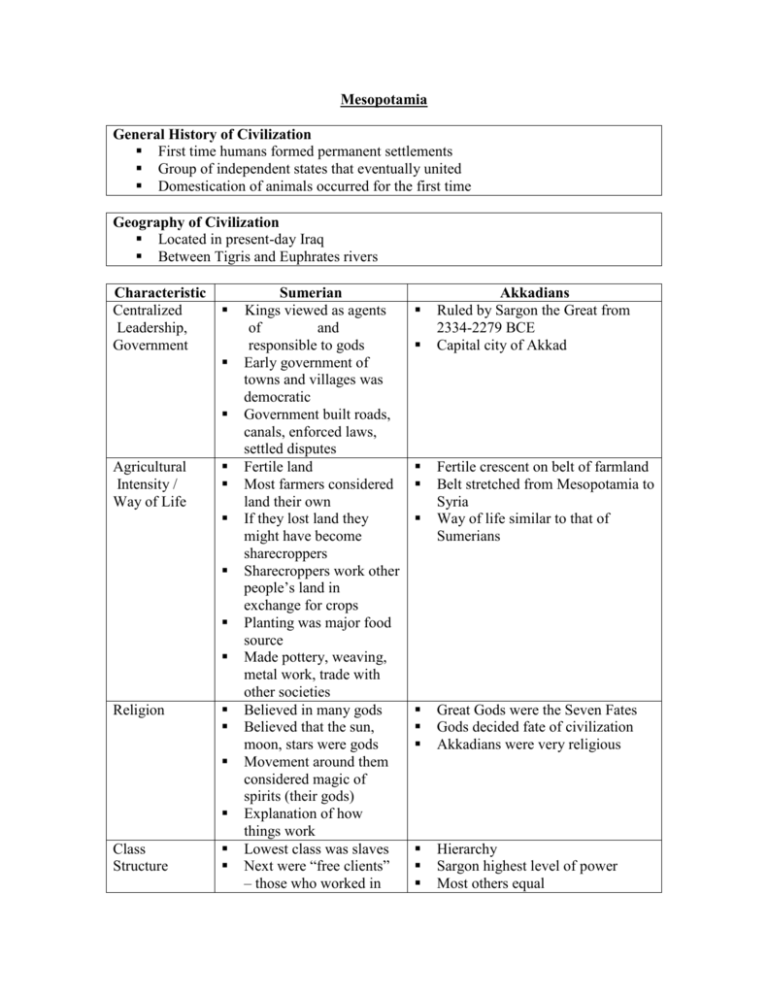
Mesopotamia General History of Civilization First time humans formed permanent settlements Group of independent states that eventually united Domestication of animals occurred for the first time Geography of Civilization Located in present-day Iraq Between Tigris and Euphrates rivers Characteristic Centralized Leadership, Government Agricultural Intensity / Way of Life Religion Class Structure Sumerian Kings viewed as agents of and responsible to gods Early government of towns and villages was democratic Government built roads, canals, enforced laws, settled disputes Fertile land Most farmers considered land their own If they lost land they might have become sharecroppers Sharecroppers work other people’s land in exchange for crops Planting was major food source Made pottery, weaving, metal work, trade with other societies Believed in many gods Believed that the sun, moon, stars were gods Movement around them considered magic of spirits (their gods) Explanation of how things work Lowest class was slaves Next were “free clients” – those who worked in Akkadians Ruled by Sargon the Great from 2334-2279 BCE Capital city of Akkad Fertile crescent on belt of farmland Belt stretched from Mesopotamia to Syria Way of life similar to that of Sumerians Great Gods were the Seven Fates Gods decided fate of civilization Akkadians were very religious Hierarchy Sargon highest level of power Most others equal Science, Technology, Arts Merchant and Trade Occupation Specialization, Gender Roles Impact on History/Society Characteristic Centralized Leadership, Government Agricultural exchange for land Next were people who owned their own land Next were nobles Highest were kings, priests Oldest full-fledged writing ever found (cuneiform) Math Kept records of supplies Created pottery Created first wheeled vehicle Farmers traded their goods for other goods First people to use form of money Most were farmers Men dominant over women, which was put into law If husband died, widow was put under control of his brother or father No protection for women under the law Woman’s only power was influence of her personality within her family Start to basic way of life that lived on for hundreds of years Many aspects of their society are still seen in societies today Babylonians King Hammurabi Established control of Mesopotamia because of centralized location Government structure similar to Sumerian Agriculture same as Some positions appointed by King Social, economic, intellectual growth Created pottery Continued to develop writing Traded merchandise such as copper, silver, black stone Traded these items in present-day Turkey Similar to Sumerians Females were believed to have been serving males Legend of Sargon left a huge mark on society Affected archaeological inquiry Way of life continued to evolve government, civilization, communications and technology Assyrians Same as Sumerian Leader was Assurnasirpal II Same as Sumerians Intensity / Way of Life Assyrians were ruthless people Large part of life was war 8600 gods and demigods All shared same religion Oldest recorded religion Same as Sumerian Gold work, ceramic bowls, board games Continued development of writing System of keeping time developed Religion Sumerian Similar jobs as Sumerians Life followed newly developed laws Same as Sumerian Laws based on religion Class Structure Science, Technology, Arts Same as Sumerian Developed first set of written laws – Code of Hammurabi Laws divinely inspired Continued development of writing Same as Sumerian Same as Sumerian Same as Sumerian Same as Sumerian Code of Hammurabi influenced civilizations and societies that followed to keep written record of laws Many of laws and ideologies developed by Hammurabi still followed today Merchant and Trade Occupation Specialization, Gender Roles Impact on History/Society Developed system of keeping track of time to organize life 60 second minute still used Continued development of civilization and government which became dominant forces in the successfulness of civilizations to follow