LATIN_PRONUNCIATION_REVISED
advertisement

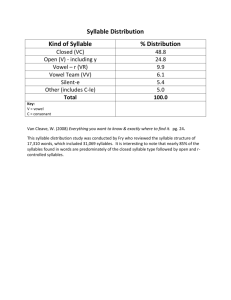
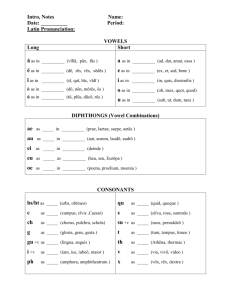
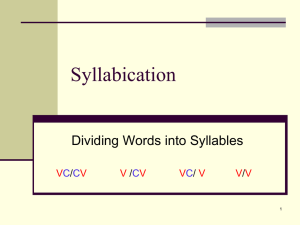
LATIN PRONUNCIATION Alphabet The Latin alphabet is very similar to the English alphabet. In Latin there is no j or w. Latin uses i for both i and j, and v for both w and v. K, y and z are rarely used. Vowels Latin & English have the same vowels: a, e, i, o, u. Each vowel has 2 sounds: long & short. Long vowels are marked with a macron above the vowel and take longer to say than a short vowel. Long Short a= a in father (ah as in blah) e = e in they (ay as in day) i, y = i in machine (ee as in see) o = o in note (oh as in oh) u = u in rude (oo as in zoo) a = a in adrift e = e in bet i = i in sit o = o in omit u = u as oo in look or put Diphthongs A diphthong is a blending of two vowels in order to form a single sound. ae = aye, or i in like au = ow in now oe = oy in joy ei = ei in vein eu = eu in feud (ay-oo, as one syllable) ui = uee in queen Consonants The following will sound as they do in English: B, D, F, H, K, L, M, N, P, Z These are the exceptions: c and ch = k (hard) g = g in go (hard) i = y in yes s = s in sill (soft) t = t in ton v=w x = ks th = thick ph = philosophy bs = ps bt = pt Syllables A Latin word contains as many syllables as it has vowels & diphthongs. (Exceptions: Consonant i is not counted as a vowel, nor u when it sounds like an English w after g, q, or sometimes s). When dividing a word into syllables: 1. A single consonant (t) is placed with the following vowel. pater = pa / ter 2. Double consonants (tt) are separated: dimitte = di / mit / te 3. If there are 2 or more consonants, the first is generally placed with the preceeding vowel: nostrum = nos / trum 4. Exceptions: iu /be /o lin /gua per / sua / de / o Accent The last syllable of a Latin word is called the ultima, the next to last the penult, the one before that the antepenult. Syllables are classified as long or short (depending on how long it took to say them). A syllable is long by nature if: it has a vowel marked with a macron or is a diphthong. A syllable is long by position if: it has a short vowel followed by 2 consonants or X. Otherwise the syllable is considered short. Latin words of three or more syllables are accented as follows: 1. On the next-to-last syllable (penult) if it is long: di / mit / te 2. On the third-to-last syllable (antepenult), if the penult is short: ad / ve / ni / at On a 2 syllable word:. on the first syllable: nos / ter N.B. (Nota Bene = note well): The final syllable (ultima) is never accented except in 1 syllable words: rem