ch3.3
advertisement

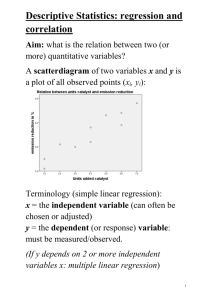
ST 361: Ch3.3 Simple Linear Regression Topics: a) Definition b) Finding the regression line: methods of least squares c) Deviation between regression line and data d) Statistical inference ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(a) Simple Linear Regression: ___________________________________________________ Ex1. Speed of cars and the distances taken to stop. X (________________ variable; explanatory variable) = speed (mph) Y (________________ variable; response variable) = distance (feet) obs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Speed 4 4 7 7 8 9 10 10 10 11 11 12 12 12 12 13 13 xi Dist 2 10 4 22 16 10 18 26 34 17 28 14 20 24 28 26 34 yi obs 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Speed 13 13 14 14 14 14 15 15 15 16 16 17 17 17 18 18 18 xi dist obs 34 46 26 36 60 80 20 26 54 32 40 32 40 50 42 56 76 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Speed 18 19 19 19 20 20 20 20 20 22 23 24 24 24 24 25 xi dist 84 36 46 68 32 48 52 56 64 66 54 70 92 93 120 85 1 A (sample) regression line has the form of ____________________________ that best describes the ______________ relationship between Y and X as displayed in the scatter plot. a : ____________ Usually not of interests b : _____________ slope = 0 implies __________________________________________ Ex1. The sample regression line is as show below: Y = 17.1 3.9 X The (sample) regression line Y = a bX can be used to (1) Describe the (linear) relationship between X and Y How? To report that when X increases by 1 unit, Y increases/decreases _____ units. E.g., in the speed-distance example (Ex1), (2) Predict Y using X How? If we know someone with X = x * , then we can predict the corresponding Y by Yˆ = a bx * E.g., in the speed-distance example (Ex1), for a car with speed X = 15 mph, we can predict the required stopping distance using 2 Interpolation: if x * is inside the range of the observed xi values E.g., predict Y for x * within ___ to ___ mph in the speed-distance example Extrapolation: if x * is outside the range of the observed xi values. Extrapolation too far could be dangerous, as we have no idea how the relationship may be. Population regression line vs. sample regression line The true underlying relationship between X and Y is Y = X …………………….. population regression line From sample data and obtain the estimates of and , and get Y = a bX………………………..sample regression line (b) Finding the regression line: Methods of Least Squares Thoughts: Each sample point in the scatter plot can be presented as ( xi , yi ) yi Residual (denoted by _____) = The difference between real yi and the predicted ŷi The best regression line Y = a + bX is the line that makes ei ’s as small as possible. That is, we find the line by finding a and b that minimizes n n i 1 i 1 ei2 yi a bxi 2 3 The solutions of the least square method: Comments: Swapping labels of X and Y will/will not (choose one) changes the value of b Regression line always goes through point x, y Regression coefficient b vs. correlation coefficient r (1) b and r have _____________ sign (2) the values of b and r are _______________ b measures the level of change in Y when X increase 1 unit r measures how far away the dots to the line (see (c) below) (3) Labels of variables X and Y b is/isnot sensitive to the labels of X variable and Y variable, while r is/is not (4) Change of units on X or Y b is/is not sensitive to the unit change (on either X or Y), while r is/is not 4 Ex1 (continue). In the speed-distance example, x i i 770, yi 2149, s x 5.3, s y 25.8, xi yi 38482 . i i Find (1) the regression line Y=a+bx, and (2) correlation coefficient r . 5 Ex2. Tips Y vs. Bill X (in dollars) X 20 40 60 80 Y 2.4 8 10 22 (a) Draw a scatterplot. Is the relationship between X and Y linear? (b) Determine the regression line using least square method. 4 x 50, y 10.6, s x 25.8, s y 8.3, xi y i 2728 i 1 (c) Calculate the sample correlation coefficient r. (d) What is the expected tip when the bill is 36 dollars? Is it a reasonable prediction? (e) What is the expected tip when the bill is 6 dollars? Is it a reasonable predication? 6