WODSS SCIENCE
advertisement

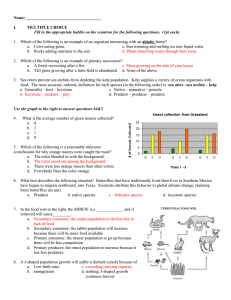
ECOLOGY UNIT REVIEW Topics: 1. Levels of biological organization 2. Feeding Relationships 3. Biotic relationships – Predation, symbiosis (mutualism, commensalism, parasitism) and competition 4. Energy movements through the ecosystem – Trophic levels, pyramid of energy and calculating transfer of energy through the pyramid. 5. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification 6. Nutrient cycles: Carbon and nitrogen cycles – various processes involved (how the nutrient moves between living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem) The reactions for photosynthesis and cellular respiration Role of decomposers in recycling nutrients. Human impacts on nutrient cycles 7. Human impacts on sustainability of biodiversity 8. Carrying capacity and limiting factors 9. Species at risk Part A: Write the word(s) needed to complete each of the following sentences. 1. The solid part of the Earth’s surface is called the _____________________________. 2. Oxygen is required by almost all organisms for the process ______________________________ and is a by-product of ______________________________. 3. The _______________________ refers to all water on the Earth in solid, liquid and gas states. 4. An ecosystem is __________________ if it can continue to function over very long periods of time. 5. A(n) __________________ describes a community of living things and their surrounding physical environment. 6. Because of its warm, moist climate, a tropical biome is home to many different plants and animals, and so it is said to have high _____________________________. 7. When non-native species are able to outcompete native species, they may become ____________. 8. Some pesticides and other environmental toxins build up or _______________________ in the __________ tissue of living organisms. 9. A(n) ____________________________ is a single species growing in one area. 10. The population that an ecosystem can support continuously is called its __________________. Part B: Matching the terms on the left with descriptors or appropriate example on the right Term Letter Descriptor or appropriate example Match the terms on the left with appropriate example on the right Mutualism A. Burrowing owls nest in abandoned ground squirrel tunnels Parasitism B. Robins feed heavily on earthworms Commensalism C. Fruit eating bats feed on figs and spread their seeds Competition D. The winter tick lives on moose and feeds on its blood Predation E. Overcrowding can lead to food shortages and starvation Match the terms on the left with appropriate example on the right Species A. Herd of elephants Population B. Tropical rain forest Community C. A raccoon Ecosystem D. Deer, grass, trees, wolves, rabbits of Algonquin park Biome E. Puslinch Lake Match the terms on the left with appropriate definitions on the right Extinct A. A species that may become threatened or endangered Extirpated B. A species facing imminent extinction or extirpation Endangered C. A species that no longer exists Threatened D. A species that no longer lives in a particular region Special concern E. A species likely to become endangered if factors do not change. Part C: Short answers 1. Describe two abiotic factors and two biotic factors that could affect a population of squirrels. 2. Snapping turtles eat frogs, frogs eat grasshoppers, and grasshoppers eat grass. (a) Construct a food chain using the above organisms. (b) What happens to these organisms when they die? (c) What is the source of energy for the producers? (d) If the grass was sprayed with a pesticide, in which organism would you find the highest concentration of pesticide? 3. List four impacts that humans have on biodiversity and sustainability. 4. In what ways might individuals of the same species compete with each other if they are (a) Carnivores (b) Producers. 5. Give an example of an invasive species and describe how it has affected an ecosystem. 6. You drive past a pond that is covered in a layer of green algae. Why might this have happened? 7. Use a T chart to compare photosynthesis and cellular respiration using the following criteria: (a) What raw materials are needed? (b) What are the products? (c) Which occurs in plants? (d) Which occurs in animals? (e) Is light needed? (f) Is energy released? (g) Is energy needed? (h) Is chlorophyll needed? 8. Describe how nitrogen from the atmosphere is converted to nitrates that plants can use. 9. Differentiate between the processes nitrogen fixation and denitrification. 10. Examine the two simplified food webs and answer the questions below. Prior to European settlement throughout southern Ontario Cougar White-tailed deer Grasses Wolf Elk Shrubs Moose Aquatic plants Southern Ontario after 200 years after European settlement White-tailed deer Beaver Grasses Shrubs Elk Moose Aquatic plants Beaver Aspen trees Aspen trees (a) List differences in the two food webs. Give a possible explanation for your observation. (b) What impacts do you think these changes had on the remaining species? (c) Is it surprising that some regions of Ontario are experiencing overpopulation problems with white-tailed deer and beaver? Explain. (d) Lyme disease is spread by wood ticks that feed on white-tailed deer. Predict how these changes might influence the spread of Lyme disease. 11. Examine the graph below. The Population of Mink from 1730 to 1743 Number of Mink 1500 1000 500 0 1725 1730 1735 Year 1740 1745 (a) During which years is this population of minks growing the fastest? (b) What is the carrying capacity of the population? (c) What factors cause the population to level off rather than continue to increase? (d) What may have contributed to the sudden increase in minks?