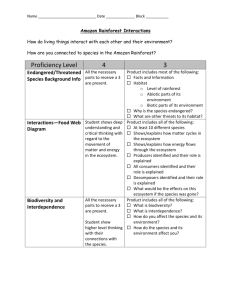
Ecosystems
advertisement
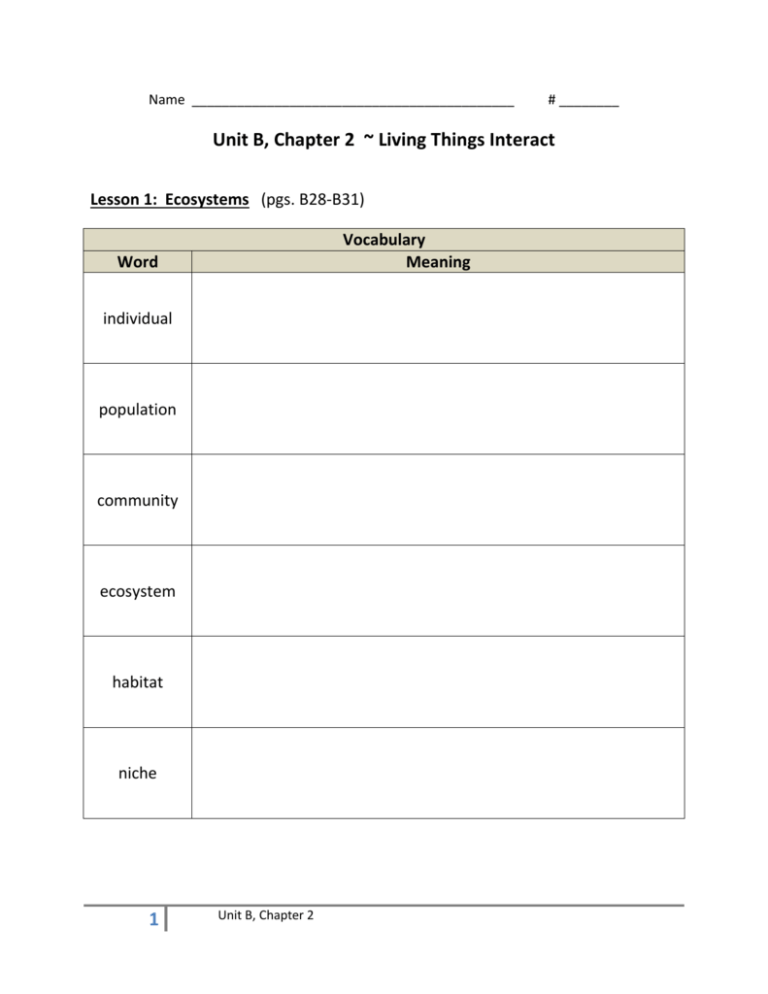
Name ___________________________________________ # ________ Unit B, Chapter 2 ~ Living Things Interact Lesson 1: Ecosystems (pgs. B28-B31) Vocabulary Meaning Word individual population community ecosystem habitat niche 1 Unit B, Chapter 2 Organisms and Their Environment (B28) Habitats and Niches (B29) Limiting Factors (B30) 2 Unit B, Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Review Questions (B31) 1. What is the relationship of a population to a community? 2. What is an ecosystem? 3. Use the data on page B30. How much warmer is it in June in the southern Arizona desert ecosystem than it is in the forest ecosystem of southern Vermont? 4. The environment determines the ecosystem of an area. What things in the environment where you live determine your local ecosystem? 5. Nonliving things that affect the organisms living in an ecosystem include weather, landforms, and _____. a. habitat b. niche c. soil d. population 3 Unit B, Chapter 2 Lesson 2 : How Energy Is Transferred in an Ecosystem (pgs. B34-B39) Vocabulary Meaning Word producer consumer food chain decomposer food web energy pyramid 4 Unit B, Chapter 2 Living Things Need Energy (B34) Food Chains (B35) A Prairie Food Web (pg. B36-B37) Energy Pyramids (B38) 5 Unit B, Chapter 2 Lesson 2 Review Questions (B39) 1. In most ecosystems, what kinds of organisms are producers? 2. What benefit do decomposers provide for an ecosystem? 3. What is an organism that eats another organism called? 4. Think of three things you like to eat. What level consumer are you for each of the foods you chose? 5. Organisms at the bottom of an energy pyramid are always ___. a. plant eaters b. producers c. hunters d. scavengers 6 Unit B, Chapter 2 Lesson 3: Ways in Which Organisms Compete (B42-B47) Vocabulary Meaning Word competition symbiosis instinct learned behavior Competition for Limited Resources (B42-B43) 7 Unit B, Chapter 2 Sharing Resources (B43-B44) Symbiosis (B45) Instincts and Learned Behaviors (B46) 8 Unit B, Chapter 2 Lesson 3 Review Questions (pg. B47) 1. Why does a female sea turtle lay more than a thousand eggs at a time? 2. How might the number of oak trees in a park affect the number of squirrels that can live there? 3. What resources are sometimes shared by squirrels and certain birds? 4. Think of an animal that lives in your area. What behaviors does it have for survival? 5. Which of the following is NOT a survival instinct for birds? a. building nests b. migrating c. eating insects d. learning to talk 9 Unit B, Chapter 2 Lesson 4: Extinction and Its Causes (pgs. B50-B53) Vocabulary Meaning Word exotic extinct endangered threatened Population Decline (B50) 10 Unit B, Chapter 2 Extinction Is Forever (B51) Success Stories (B52) Lesson 4 Review Questions (B53) 1. Name a natural cause of decline in a population. 2. How is a threatened organism different from an endangered one? 3. How many living individuals are there in a population that is extinct? 11 Unit B, Chapter 2 4. Think of an animal or plant in your state. What changes in the environment could cause it to become threatened or endangered? Give specific examples. 5. It is impossible for an endangered organism to recover if ___. a. its habitat is restored b. its population is too small c. hunting is stopped d. it is bred in captivity 12 Unit B, Chapter 2