Pspice WORKSHOP 2000
advertisement

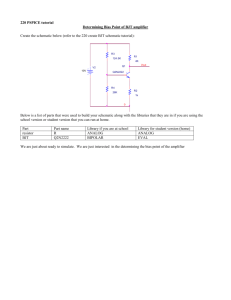
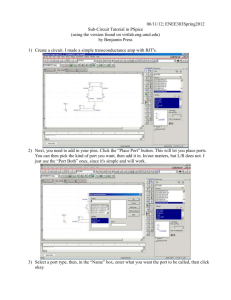
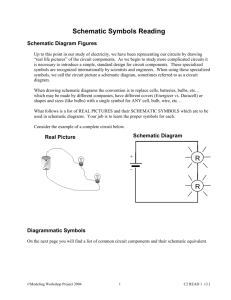
Getting Started With Pspice ECST Computer Link College of Engineering, Computer Science, and Technology. California State University, Los Angeles Update: 2/17/2016 Author: CG Introduction Pspice is a powerful circuit simulation program. Through the schematic capture option of Pspice, users could create circuits, run analyses, plot graphs, and obtain results. Typical Analysis available from MicroSim PSpice: AC Sweep and Noise DC Sweep Transient Digital Monte Carlo Standard Schematic Annotation Graphics Standard Schematic Simulation Drawing Main Schematic Window Creating and Editing a Schematic After opening the main schematic window, users can place components by accessing the Part Browser. You can access the browser in three ways: Press Ctrl + G. Press Alt + D or select: Draw ► Get New Part. Select: Note: Press “Advanced” in the part browser to expand the window and be able view the part symbol. In the part browser, under Part Name, enter the following parts and place them in the main schematic window by pressing Place” or “Place & Close”. Part Name R VDC AGND Description Resistor Independent DC voltage source Analog ground Number 2 1 1 Reference R1, R2 V1 New attributes Same 12 2 IPROBE VIEWPOINT Current Probe Voltage viewpoint 1 1 Using the main schematic window as your breadboard, connect all the components as shown in figure 1. Notes: Add wire or bus to the parts by selecting “Draw” in the menu bar. Alternatively, you can select: Add grid and other options to the schematic by selecting: Options ► Display Options… Rotate, flip, and align any part, just like R2 in figure 1, by selecting: Edit Zoom in, out, to fit, or in an area by selecting: View. Alternatively, you perform these tasks by selecting: “V1”, “R1”, and “R2” are references or labels while “DC=”, and “1k” are attributes. Use “Esc” key to cancel current task. Figure 1. Simple DC Circuit We are now ready to edit the attributes and references. If the reference of your parts does not match the one in figure 1, you can double click on them and directly change them in the “Edit Reference Designator” window, however it is not necessary to change them as long as there is no duplication. As for the attributes, some of them already have default values such 1k, 1u, 1n, and so on. These default values denote kilo, micro, nano, and so on. It is not necessary to include the units. We basically enter attributes the same way as references (with the exception of the window). Alternatively, we can hi-light a part and select: Edit ► Attributes … Save Attribute Attribute Changeable Attribute Reference We can also change the display properties of any part by hi-lighting any “System-defined Attributes” and selecting “Change Display.” Notes: Since this is a simple circuit, and we already have some probes in it, we can easily run a simulation by pressing “ the simulation tool bar or select: Analysis ► Simulate. ” icon in Quick Exercise: Create and edit the schematic in figure 2. Figure 2. Current Gain of a BJT Part Name Q2N3904 VDC AGND Description Small Signal NPN BJT DC voltage source Analog ground Number 2 1 1 Reference R1, R2 V1 New attributes Same 5 3 IDC DC Current Source 1 Running Analysis and the Probe You can run any of the typical analysis stated in the previous page. For specific analysis, user needs to setup the configuration since the default analysis for new schematics is only bias point details. We shall use the schematic in figure 2 to show how to configure an analysis. From the main schematic window of fig. 2, select: Analysis ► Setup…. Our objective is to observe the DC current gain of the BJT. To accomplish this, select DC Sweep… and configure the DC sweep window for following values: Sweep Var. Type Sweep Type Name Start Value End Value Pts/Decade Current Source Decade I1 1u 1m 20 Run the simulation and the probe window should appear ►► From the Probe Window: To trace a plot, select: To change axis settings: To label plot, select: Trace Plot Tools ► Add… Insert ► X Axis Setting… ► Label Figure 3. Probe Quick Exercise: Create and edit the schematic in figure 4. Setup and simulate the circuit with following parameters (Digital Setup) Plot, in the probe window, the following parameters: Q5, Q6, Q7, Q8 Analysis Configurations 4 Part Name 7400 7402 7404 7408 7432 7486 7493A AGND Bubble Digital_Clock Description 2-input positive-nand gate 2-input positive-nor gate inverter 2-input positive-and gate 2-input positive-or gate 2-input xor gate 4-bit binary counter Analog ground Connection bubble Digital Clock 50% Duty Cycle Number 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 1 Reference New attributes As Specified Frequency 1k Figure 4. Logic Gates 5