Outline Patanan Vongsuvan 5080413 Thitinun Danromyen 5080404
advertisement

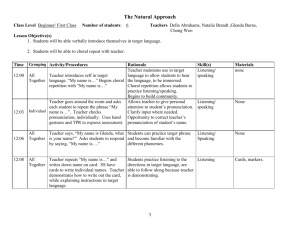
Outline Patanan Vongsuvan 5080413 Thitinun Danromyen 5080404 Tuangtip Chawiskul 5080470 Natural Approach Background (history): A. "Language acquisition does not require extensive use of conscious grammatical rules, and does not require tedious drill."-Stephen Krashen (Stephen Krashen's, 2007). B. The Natural Approach was developed by Stephen Krashen together with Tracy Terrell in the early eighties (The Natural Approach, n.d.). Theory: A. Krashen’s theory of second language acquisition consists of five main hypotheses: a. The Acquisition-Learning Hypothesis b. The Monitor Hypothesis c. The Natural Order Hypothesis d. The Input Hypothesis e. The Affective Filter Hypothesis (Krashen and Terrell’s, n.d.) Objectives: A. Natural Approach is designed to help beginners become intermediates, not the same level of a native speaker, in communicative skills. B. There is no need of grammatical details. C. It depends on learner needs (SIL International, 1999). Learner roles: A. Learners should not try to learn a language in the usual sense; however, they must try to lose themselves in activities (The Natural Approach, n.d.). B. There are three basic stages identified in the approach: a. Pre-Production b. Early-Production c. Extending-Production (The Natural, n.d.) Teacher Roles: A. Natural Approach teachers will mainly focus on the three essential roles. a. Teachers are the core source of comprehensible input. b. Teachers must create a classroom atmosphere that is interesting for learning. c. It is important for the teacher to choose a variety of classroom activities (The Natural Approach, n.d.) Outline Patanan Vongsuvan 5080413 Thitinun Danromyen 5080404 Tuangtip Chawiskul 5080470 Activity Types: A. These are the techniques that are used in the Natural Approach theory a. Total Physical Response (TPR) i. It can be used with props into commands, “Use your right hand to pick up a pencil and put it under the book.” b. Mime i. We point an object to ensure comprehension, “Look at Alice. She has long black hair. Her hair is not short. It is long and black.” c. Gesture i. It can be used in a form of questions such as “What is the name of the woman with glasses?” B. Visual aids such as magazine pictures can be handed to students with different ones, and instruct them to assign the names of those pictures (The Natural Approach, n.d.). C. The “Acquisition activities” (communication form) a. Learners will be formed in pairs, then in groups, and finally work together with the whole class (similar to Communicative Language Teaching) (The Natural Approach, n.d.). Evaluation: A. The Natural Approach is the method focusing on providing comprehensible input and classroom environment B. It can minimize learner anxiety and maximize learner self-confidence. C. Also, learners should be able to survive in a simple situation as they have been through the real situations and experiences. D. All in all, the Natural Approach has nothing to do with the perfect production of grammatical structures, but we would emphasize on practical activities of the second foreign language instead. Outline Patanan Vongsuvan 5080413 Thitinun Danromyen 5080404 Tuangtip Chawiskul 5080470 Bibliography Krashen and Terrell’s (n.d.). Krashen and Terrell’s “Natural Approach.” Retrieved July 3, 2010 from http://www.stanford.edu/~kenro/LAU/ICLangLit/NaturalApproach.htm Stephen Krashen's (2007). Stephen Krashen's Theory of Second Language Acquisition. Retrieved July 3, 2010 from http://www.sk.com.br/sk-krash.html The Natural (n.d.). The Natural Approach. Retrieved July 3, 2010 from http://www.englishraven.com/method_natural.html The Natural Approach. (n.d.). The Natural Approach. Retrieved 3th July 2010 From http://www2.vobs.at/ludescher/alternative%20methods/natural_approach.htm SIL International (1999). The Natural Approach. Retrieved July 3, 2010 from http://www.sil.org/lingualinks/languagelearning/waystoapproachlanguagelearning/ thenaturalapproach.htm