Review for China Test
advertisement

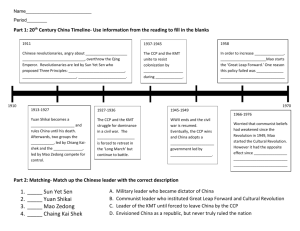
Review for China Test Philosophies Confucianism o Confucius during Zhou dynasty o Mencius- Built upon Confucius principles o All people are good—Education cultivates goodness o Based on 5 relationships Ruler-Ruled Parent-child Older sibling-younger sibling Friend-Friend Husband-Wife o Analects (and other literature) o Benevolance (kindness is key) o Filial Piety- Respect for parents Ancestral worship o Importance of education in leadership Civil Service Examinations Memorizing texts 3 day test Only Boys Daoism (Taoism) o Laozi (other spellings) during the Zhou o Upset by turmoil of the Zhou dynasty and leaves o May be a fictional character o Daodejing outlines Dao (The way) o Nature takes its course Wu-Wei (not acting against nature) o Opposes hierarchy of Confucianism o More a spiritual philosophy o Developed into a religion o Yin-Yang o Qi (energy) o Arts (acupuncture acupressure feng shui) Legalism o Han Feizi o All people are bad o Severe consequences o Harsh government to keep people in line o Shi Huangdi First Chinese emperor Implemented legalism Short-lived dynasty People revolted Dynasties Xia 2100-1800 BCE o Not a dynasty but a early civilization o Bronze and stone tools o Not know until 1959 Shang 1650-1027 o 1st Dynasty o Polytheism o Oracle Bones (messages read by oracle on bones) o Irrigation and farming o Developed writing 3000 symbols Only upper class could write o Proficient with bronze Zhou 1027-221BCE o Beginning of Mandate of Heaven o Much the same as Shang without sacrifices o Daoism, legalism and Confucianism developed during this time Qin 221BCE-207BCE o Shi Huangdi o Established Legalist Principles o Established Uniform weights and measure o Beginning of great wall (forced peasant labor) o Network of roads (forced peasant labor) Han 202BCE-220CE o More trade along silk road o Confucianism o Buddhism spreads to China o Universities built o Civil Service exam- merit-based leadership o Innovations: Better calendar, seismograph, paper, sundial, water clock, ag methods, medical methods (blood circulation) Tang and Sung (Golden Ages) 618-1279 o More trade o Seagoing trade o Arts and Literature o Invention of Printing allowing more access to books and education Yuan (Mongol rule) 1279-1368 CE o Kublai Khan o Marco Polo- European explorer who reported the magnificence of China to Europe and contributed greatly to history o Roads to rule o Got rid of Confucianism o Grand canal Ming 1368-1644CE o Zhu Yuanzang is a peasant who revolts and expels the Mongols o Confucianism revival o Building of forbidden city and great wall (As we know it today) o Naval expeditions and more contact with Europeans o Sudden isolation o China begins to lose ground to the advancement of the west Qing 1644-1911CE o Manchus take over o (Think about the movie of Kang Xi and the forbidden city) o Beginning of trade with Europeans (see below) Relations with the west Early trade with Portuguese o China restricts o China belief of superiority Long-nose barbarian Kowtow o East India Company Wants silk, porcelain and tea Trades Begins going broke Opium to China Opium Wars Treaty of Nanjing Extraterritoriality Hong Kong Free trade Compensation for opium o Other European Powers Japan, France, Russia, Germany, Britain Spheres of influence America Open Door Policy McKinley and Hay ask for free trade (open door notes) Boxer Rebellion (1901) Want to expel foreigners US and Europe put down revolt US keep presence in China and gain trade rights Leading up to Communism 1911 Ci Xi dies and China becomes a republic o End of dynasties Some transitional governments Chiang Kai Shek—Nationalist Party o Backed by West and Elites in China Mao Zedong o Backed by Peasants (majority of Chinas population) Chiang Kai Shek, with the help of West drive Mao and peasants into mountains o Long March- 6000 miles and majority dead 1931 Japanese take Manchuria o Need raw materials from Manchuria, rich with resources, to help drive the war machine 1937 Japanese invade and take China o Chinas surrender leads to many atrocities committed by the Japanese against civilians 1945, After WWII ends, Mao and Kai-Shek join to expel the Japanese Mao, on October 1, 1949, establishes the Peoples Republic of China o Peoples Republic of China Gives land to peasants Soviets support Mao Communist but declared “republic” Eventually Soviets withdraw support Mao starts “Great Leap Forward” o Modernization to catch up with world Backyard furnaces to melt steel Close planting of crops Removal of peasants from land All land taken by state Communes of 20-40 families set up Roads, bridges, etc built by peasants Famine, starvation due to crop failure Not enough farmers Insects due to killing of sparrows Close planting takes all nutrients from soil After failure of Great Leap Forward Mao starts “Cultural Revolution” o All old ideas gotten rid of o Red Guard (youth groups) denounce old, artists, teachers, parents and anyone who opposes Mao’s ideology o Propaganda Posters Little Red Book --- “Quotes from Chairman Mao” o Many persecuted, imprisoned and killed o Helped to end the old feudal systems (over past thousands of years) to make way for new o Helped to unite the country 1976—Mao Dies Deng Xiaoping becomes new leader Reforms o 4 Modernizations Modernizing Agriculture Building China’s defenses Expansion of Industry Focus of Science and Technology o Increase foreign trade o o o Issues Focused more on “light industry” Training overseas Responsibility System- Crops farmed for household use (subsistence) and surplus sold to Government at a set price Tiananmen Square Massacre o People upset Not enough reforms by Deng Xiaoping—Students and intellectuals Too many reforms by Xiaoping—Industry workers o Military is called in to stop protests o 100,000+ protestors Hunger strikes Calls for reform Calls for talks with government o Eventually military is called in Blocked by students Military dragging and beating students Shooting 100s up to 7000 dead One-Child Policy o Reasons for this policy Mao pushing for more births and Xiaoping trying to slow them Overpopulation, not enough good land to support the people o Results Infanticide Child black market Cruel policies of forced abortions Lack of help on the rural farms Lack of equality Demographic Problems Too many men Too many old people Pollution, Taiwan Question and Media restrictions