Integrated Science Name Seasons Interactive Lab Go to Seasons
advertisement

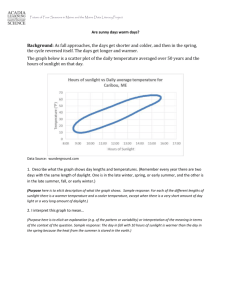
Integrated Science Seasons Interactive Lab Name __________________________________________ Go to Seasons Interactive SEPUP, p. 9 of my Links This may take a bit to load, be patient! (http://www.sepuplhs.org/students/iaes/simulations/SEPUP_Seasons_Interactive.swf) READ ME: The opening page shows the world with key latitudes and cities indicated. Answer the following using this graphic. 1. What is the definition of “latitude?” 2. At what latitude is Anchorage, Alaska: _______; Quito, Ecuador: __________ 3. Which latitude is the Tropic of Cancer: ________; North Pole: ___________ Open the Interactive 4. Fill in the table below by selecting the indicated City and Month at 23.5o Earth’s Tilt. CITY/ Anchorage, AK Daylight Hours Temperature Range Chicago, IL Daylight Hours Temperature Range Quito, Equador Daylight Hours Temperature Range Melbourne, Australia Daylight Hours Temperature Range March June September December 5. Use the “EARTH TOP VIEW” box and use the “Distance between the Earth and Sun” information to answer the following: a. In which month is the Earth closest to Sun? _________, Dist= __________________km b. In which month is the Earth farthest? _________, Dist= __________________km 6. Click on “TROPICS/EQUATOR” to turn this feature ON. a. In which month(s) is the Sun hitting the Equator? _________________________________ b. In which month(s) is the Sun hitting directly the Tropic of Cancer? ______________ c. In which month(s) is the Sun hitting directly the Tropic of Capricorn? ___________ 7. Click on 0o in the EARTH’S TILT box. a. Where is the Sun hitting directly in ANY month? ________________________ b. Observe the temperature ranges for the four cities. Describe their pattern as you click through January through December. c. Suggest a reason for these observations. Go to Seasons Interactive 2, p. 9 of my Links (http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::800::600::/sites/dl/free/0072482621/78778/Seas ons_Nav.swf::Seasons%20Interactive) READ ME FIRST: The interactive starts with the axial tilt (“Inclination Angle”) at 0 o . The white “X” indicates a position about 45o N latitude. You can observe the Sunlight Angle and control the Speed of the planet’s revolution. You can also click on and hold the planet to move it along in its orbit. 8. If the inclination angle (tilt) is zero, how does the path of the Sun in the sky change in one revolution (year)? a. How does the temperature change from Summer to Winter? b. How does the angle of sunlight striking the ground change? c. How do the hours of daylight change from Summer to Winter? 9. Change the inclination angle to 23o or select Earth in lower right. Go through a complete revolution (year). a. How does the temperature change from Summer to Winter? b. How does the angle of sunlight striking the ground change? c. How do the hours of daylight change from Summer to Winter? 10. Change the inclination angle to 60o. a. How does the temperature change from Summer to Winter? b. How does the angle of sunlight striking the ground change? c. How do the hours of daylight change from Summer to Winter? 11. Change the inclination angle to 86o or select Uranus. If you lived at the “X” latitude, estimate number of months that you would be in total darkness. (Assume a 12-month year.) 12. What is the smallest inclination angle which leads to a 24-hour period (day) without sunlight? Name ___________________________________________ If time permits (BONUS Work ahead….) Go to Seasons Interactive 3, p. 9 of my Links (http://www.learner.org/jnorth/tm/ReasonsBack.html) 13. Tilt and Revolution What exactly causes the seasons? 14. Common Misconceptions about the Seasons If Earth is closer to the Sun in winter (January), WHY is it so cold in our Northern hemisphere in January? 15. What is the difference between solstice and equinox? Relate your answer to the WHERE the Sun’s rays are strongest. Hint: Look at the maps provided. Click on Season Simulator to open the animation. 16. Drag the person icon on globe to approximately 60 N latitude. Advance the calendar (along bottom) to March 21. Change the left diagram to Celestial Sphere. Under top right globe box, click on “View from Sun” a. Over which latitude is the Sun centered? ________________________________ b. What is the Sun’s altitude (see lower box depicting angle of sunlight)? ____________ c. In the left celestial sphere diagram, which TWO lines intersect on this date? Hint: click on labels. 17. Advance the calendar to June 21. a. Over which latitude is the Sun centered? ________________________________ b. What is the Sun’s altitude (see lower box depicting angle of sunlight)? ____________ 18. Advance the calendar to September 21. a. Over which latitude is the Sun centered? ________________________________ b. What is the Sun’s altitude (see lower box depicting angle of sunlight)? ____________ c. In the left celestial sphere diagram, which TWO lines intersect on this date? 19. Advance the calendar to December 21. a. Over which latitude is the Sun centered? ________________________________ b. What is the Sun’s altitude (see lower box depicting angle of sunlight)? ____________ c. Which season is starting in the Northern Hemisphere? 20. Name the DATES for start of each season: Spring: ______________; Summer: _______________ Fall: ___________________; Winter: _________________ Go back to p 9 of my Links and check out the other Seasons Links. Tell me something!