Plant Nutrients – Substances that are primary (macro) and
advertisement

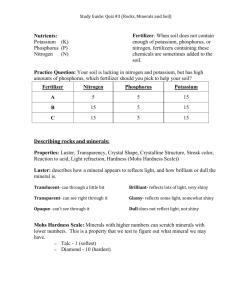
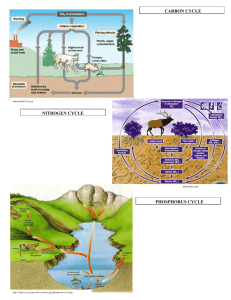
Plant Nutrients – Substances that are primary (macro) and secondary requirements for growth and development of plants. Macronutrient plants get from air and water: ____carbon____, ______oxygen, ______Hydrogen Macronutrients plants get from the soil: Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Potassium (K) Secondary nutrients found in the soil: _____calcium_______magnesium______sulfur Nitrogen (N) - most important nutrient - required for proper growth and _green color of stems and leaves - determines _____fruit size - comes from organic matter (__humus___) (nitrogen cycle) - lack of nitrogen results in _slow growth and yellow leaves - too much nitrogen creates __weak stems and plants are more susceptible to ____disease___________ - too much nitrogen in food can cause nitrogen _____poisoning_______ in animals (cattle) Phosphorus (P) - necessary for _root__, _flower_ and ____seed_ development - found only in certain rocks and may become _limited_ - lack of phosphorus causes slow growth and purple leaves Potassium (K) - necessary of the development of ___strong stems____ and resistance to disease - needed for the development and ripening of ruit_ - found in many _rocks_ so the supply is less limited than phosphorus - lack of potassium causes __browning of leave edges__ pH - the measure of _acidity_ and alkalinity_ of a soil – extremely important - if the ph is too acidic or basic for a plant, nutrients will not be _absorbed_ by the roots - most plants prefer 6.0 – 7.0 Fertilizer – any substance added to the soil to supply plants with nutrients. Two types – _synthetic__(man-made) or _organic_ (found naturally) – (see fertilizer lab.) Each has their advantages (pages 244 – 247 Environmental text) List advantages of each _______Synthetic___________________Organic_____