Nitrogen
advertisement

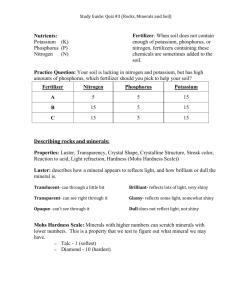
Primary Nutrients (N-P-K) Macronutrients: nutrients needed in large amounts Nitrogen (N) Nitrogen is the element, which stimulates aboveground growth and produces the rich, green color characteristic of a healthy plant. Excess will cause delaying maturity or ripening of the crop, lowering its quality, lodging, and decreased resistance to disease. Nitrogen is an important element that must be used in a balanced ration with the other plant foods. The most common source of Nitrogen is from organic matter (ex. Manure) and commercial fertilizers. Soils are generally 0.1% Nitrogen, so if not replenished, the soil will be depleted by continual cropping. Nitrogen leaches and adds to the depletion. Nitrogen from organic matter is not available until the organic matter is eaten by bacteria and converted into nitrite. Nitrogen deficiency shows signs of yellowing on the leaf tips and along the midrib of the leaf. Nitrogen is mobile in the plant, moving from the older portion of the plant to the newer growth when in short supply. If all the leaves are green, this means too much Nitrogen was used. If more leaves are brown, this means not enough Nitrogen was applied. Phosphorus (P) Phosphorus is necessary for the hardy growth of the plant and activity of the cells. It encourages root development, and by hastening the maturity of the plant, making the plant more disease resistant. It plays an important part in increasing the palatability of plants and stimulates the formation of fats, convertible starches and healthy seeds. In low pH soils Phosphorus is bound in a form unavailable to plants. Phosphorus moves very little in the soil. Inert. Potassium (K) Potassium (Potash) has much to do with the tone and vigor of plants, encouraging development of healthy root systems. It is essential for starch formation in the plant and the development of chlorophyll by encouraging photosynthesis. pH is important for growing plants to take up potassium and if the soil is very acid there will be a lack of Calcium, which is important for uptake of Potassium. Potassium moves very little in the soil.