Soil Nutrients & Fertilizers
advertisement

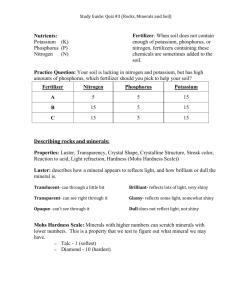
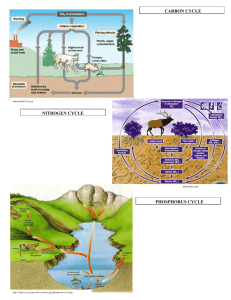
Soil Nutrients & Fertilizers Plant Nutrients Substances that are primary (macro) and secondary requirements for growth and development of plants. Macronutrient plants get from air and water: carbon, oxygen, hydrogen Macronutrients plants get from the soil: Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Potassium (K) Secondary Nutrients found in soil Calcium, Magnesium, Sulfur Nitrogen (N) Most important nutrient Required for proper growth and green color of stems and leaves Determines fruit size Comes from organic matter humus (nitrogen cycle) Lack of nitrogen results in slow growth and yellow leaves Too much nitrogen creates weak stems and plants are more susceptible to disease Too much nitrogen in food can cause nitrogen poisoning in animals (cattle) Leaf Lacking Nitrogen Phosphorus (P) Necessary for root, flower and seed development Found only in certain rocks and may become limited Lack of phosphorus causes slow growth and purple leaves Potassium (K) necessary for the development of strong stems and resistance to disease needed for the development and ripening of fruit found in many rocks so the supply is less limited than phosphorus lack of potassium causes browning of leaf edges pH The measure of acidity and alkalinity of a soil > extremely important! If the pH is too acidic or basic for a plant, nutrients will not be absorbed by the roots Most plants prefer 6.0 – 7.0 Fertilizer Any substance added to the soil to supply plants with nutrients. Two types: Synthetic (man-made) Organic (found naturally) So now you’re a farmer… How do you use N-P-K values to fertilize your crops? Look up fertilizers and how you might “pick” the right fertilizer based on NPK of the bag…what do the NPK values mean? On your farms, you notice you have slightly purple leaves on your corn, VERY small sized fruit and it takes a VERY long time for your fruit to ripen. Find me a fertilizer that will work for your farm to maybe solve your problems. Each has their advantages List Advantages and Disadvantages of each from page 244-247 (worksheet table)