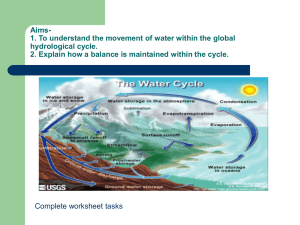
Surface Hydrology
advertisement

Surface Hydrology 1. Course Name: Surface Hydrology 2. Course Code: GRM 1102 3. Course Description This course introduces students to the basic components of surface hydrology including the components of the hydrological cycle. These are further discussed in detail including evapotranspiration, precipitation, interception, run off and stream flow. Attention is paid to techniques for the measurement and collection of data on the different components. The course also covers hydrographs and their applications in hydraulic engineering for river structures and planning and management of water resources. Water balance is discussed and at the end an overview of the hydrological conditions in Africa is given. The course is divided into the following major topics: The hydrological cycle Evapotranspiration Precipitation Runoff and hydrographs Streams and stream flow Water balance Hydrological conditions in Africa 4. Course objectives The objectives of the course are to: Introduce the basic components of the hydrological cycle. Give a detailed account of the different components (evapotranspiration, precipitation, interception, run off and stream flow including techniques for their measurements. Introduce hydrographs and highlight how they can be applied to hydraulic engineering and water resource management. Discuss the water balance model. Give an overview of the hydrological conditions in Africa. 5. Teaching and Assessment Pattern Duration of the Course The content of the course will be covered in one 15-week semester with three hours of instruction per week.. Mode of Instruction Most of the instruction will classroom based and students will be encouraged to ask questions during the lecture. Whenever possible, demonstrations will be made in the field during field excursions. Students will be free to seek help outside the Lecture room from the instructor. There will monthly be assignments. There will at least be two major tests Assessment Pattern The following instruments will be used to assess the extent of growth in skills, abilities and understanding acquired: Requirements a) Tests b) Assignments c) Final examination a&b c Total No. of units 2 4 1 Contribution 40% 60% 100% 7. Reading List The reading list will include but not limited to the following texts: Todd, D.K. (1980): Groundwater Hydrology, J. Wiley Hamill, L. & Bell, F.G. (1986): Groundwater Resources Development Fetter, C. W. (1994): Applied Hydrogeology, Prentice Hall Richard, J.C. (1969): Introduction to Physical Hydrology Balek, J. (1983): Development in Water Sciences 18: Hydrology and Water Resources in Tropical Regions, Elsevier UNESCO (1978): Studies and Reports in Hydrology 25: World Water Balance and Water Resources of the Earth Lecture Notes by A. Muwanga 7.Course Outline The hydrological cycle Definitions, the hydrological cycle, components, reservoirs Evapotranspiration Evaporation, transpiration, evapotranspiration , factors affecting evapotranspiration ; movement of water during evapotranspiration, measurement of evaporation/evapotranspiration, estimation of evaporation/evapotranspiration by calculation Precipitation Overview, forms of precipitation, formation of precipitation, types of precipitation , measurement precipitation - areal precipitation, areal analysis of precipitation data; rainfall Intensity, interception of Runoff and hydrographs Channel precipitation, depression storage, infiltration, overland flow, shallow subsurface storm flow, groundwater flow ; Hydrographs , hydrograph shape, the Unit Hydrograph, duration curves and their practical applications. Streams and stream flow Stream gauging, discharge measurement, rating curve Water balance The water balance equation, discussion of components Hydrological conditions in Africa Precipitation, evapotranspiration, runoff and river discharges – discharges in the different river basins 8. Suggested Teaching Programme I. The hydrological cycle Definitions The hydrological cycle Components Reservoirs II. Evapotranspiration (1 week) (3 weeks) Assignment 1 Evaporation Transpiration Evapotranspiration o Factors affecting evapotranspiration o Movement of water during evapotranspiration o Measurement of evaporation/evapotranspiration o Estimation of evaporation/evapotranspiration by calculation TEST 1 III. Precipitation (3 weeks) Assignment 3 Channel precipitation Depression storage Infiltration Overland flow Shallow subsurface storm flow, Groundwater flow o Hydrographs o Hydrograph shape o The Unit Hydrograph, o Duration curves and their practical applications. V. Streams and stream flow Assignment 2 Overview Forms of precipitation Formation of precipitation, Types of precipitation Measurement of precipitation o Areal precipitation o Areal analysis of precipitation data o Rainfall Intensity, interception IV. Runoff and hydrographs ( 2 weeks) Stream gauging Discharge measurement (2 weeks) Rating curve VI. Water balance (1 week) The water balance equation Discussion of components TEST 2 VII. Hydrological conditions in Africa (3 weeks) Assignment 4 Precipitation Evapotranspiration Runoff and river discharges Discharges in the different river basins o The Nile basin o The Congo basin o The Niger basin o The Zambezi basin 9. Responsibility of the Student Regular attendance, do all assignments and tests 10. Responsibility of the Lecturer Regular and punctual teaching, accurate and prompt grading of assignments, tests and examinations and available to students for consultation outside teaching hours.