Plant Cell Structure & Function
advertisement

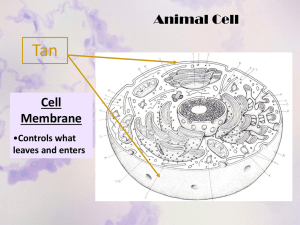
Plant Cell Structure & Function. From http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plantcell.html A plant cell is made up of a cell wall, a cytoplasm, and lots of different organelles. Each of these organelles has a different function and they all play a vital role in the structure of the cell. Nucleus The nucleus is the part of the cell where it’s genetic material (DNA) is stored. The nucleus also co-ordinates the main functions of the cell, including protein synthesis and cell division. Without the nucleus, a plant cell (or any other cell for that matter) wouldn’t be able to grow, acquire nutrients or reproduce. Only Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/nucleus/nucleus.html Nucleolus The nucleolus is an organelle that is contained within the cell nucleus, surrounded by a layer of chromatin. It is essential in the cell due to the fact that it assembles and produces ribosomes (whose main function is to translate RNA into protein), and without these ribosomes, the cell would simply not function, because there wouldn’t be any proteins or amino acids. Golgi Apparatus The Gogli apparatus is the part of the cell that stores, modifies, processes and “tags” proteins and lipids that are made within the cell. The “tagging” makes sure that the chemical goes to its correct destination (stored inside or distributed to outside the cell). If the golgi apparatus did not exist, the cell wouldn’t function because it wouldn’t be able to store the important chemicals or get rid of the unwanted ones. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/golgi/golgiapparatus.html Ribosomes Ribosomes are the protein synthesizers of the cell. The proteins that are made can be used as enzymes or to help other functions within the cell. Ribosomes are much smaller than the other organelles and are usually found floating around in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribsomes are made up of approximately 60% RNA and 40% protein. Without ribosomes, the cell would not be able work, due to the lack of proteins and amino acids. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/ribosomes/ribosomes.html Lysosomes Lysosomes are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. They are small capsules full of digestive enzymes which help to break down anything that is un-needed, even the cell itself. They also help by breaking down food when the cell absorbs it. If the lysosomes didn’t exist, the cell wouldn’t function because it wouldn’t be able to get rid of anything it didn’t need and it also wouldn’t be able to gain nutrients. Endoplasmic Reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum works very closely with the golgi apparatus and the ribosomes. It acts as a packaging system, like the golgi apparatus. Rough Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes scattered all over it. The chains of amino acid or protein that the ribosomes make get pushed into the rough endoplasmic reticulum which then sends them out in vesicles, to the inside or outside of the cell. Smooth Smooth endoplasmic reticulum acts as a storage organelle, storing steroids and ions. The cell would not be able to function without the endoplasmic reticulum simply because it wouldn’t get the chemicals it needs for the rest of the organelles to function. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicreticulum/endoplasmicreticulum.html Mitochondria Mitochondria is the part of the cell that breaks down nutrients and creates energy for the cell. The internal matrix of the mitochondria is filled with water and enzymes. The enzymes then take molecules of food and turn them into oxygen for energy. One cell can have any number of mitochondria, depending on what it needs to do. A cell wouldn’t be able to exist without a mitochondria, as there would be no other way to get energy. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/mitochondria/mitochondria.html Cytoplasm The cytoplasm is like a liquid “soup” made of enzymes, fatty acids, sugars and amino acids. It suspends the organelles in the cell and also uses enzymes to dissolve waste products and other such things. If the cytoplasm didn’t exist, the cell would fall apart because there would be nothing filling the gaps. Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane is present in all living cells. It acts as a semi-permeable membrane and makes sure the organelles in the cell don’t seep out. It also acts as a barrier against unwanted substances. The membrane is made up of proteins and phospholipids. The proteins help move molecules around the cell. If a cell didn’t have a plasma membrane, nothing would stay inside it, and it would cease to function. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plasmamembrane/plasmamembrane.html Plastids Plastids are the part of the cell that are responsible for photosynthesis and the storage of starch products. Plastids also help to synthesise fatty acids, among other things. If a plant cell didn’t have plastids, it would be unable to gain nutrition from photosynthesis, and therefore wouldn’t survive. Vacuole Vacuoles are responsible for removing unwanted substances from within the cell, isolating substances that may be a threat to the cell, containing waste product, maintaining a healthy pH level, exporting unwanted substances from the cell and enabling the cell to change its shape. The cell wouldn’t be able to function without the vacuole because none of these things would happen. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plants/vacuole.html Chloroplasts Chloroplasts conduct photosynthesis and are a specific kind of plastid. They absorb light energy and turn it into glucose which helps the plan cell function. Without the chloroplasts, a plant cell wouldn’t be able to use photosynthesis, and would therefore be unable to produce any nutrients to help itself function. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/chloroplasts/chloroplasts.html All of these organelles are vital in retaining the health and structure of the cell. Without any of them, the cell would simply cease to function.