Prof
advertisement

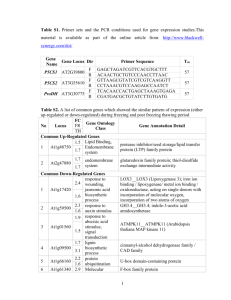
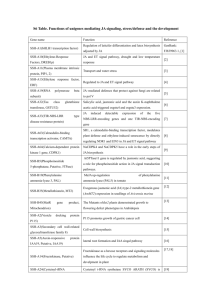
Prof. Dr. Venkatesan Sundaresan Section of Plant Biology and Dept. of Plant Sciences Life Sciences Bldg. One Shields Ave. University of California Davis Davis, CA 95616 Lab phone 530-754-9852 e-mail: sundar@ucdavis.edu website: http://www-plb.ucdavis.edu/Labs/sundar/ Degrees 1982 PhD Biophysics Harvard University B.Sc. - University of Poona M.Sc. - Indian Institute of Technology M.S. - Carnegie Mellon University Research Contribution Biotechnology applied to agriculture will help farmers and people living in developing countries. Research Interests Genetics and molecular biology of plant reproduction. Functional genomics in model plants- Arabidopsis and rice. Bioinformatics of small RNAs. Microbiomes and metagenomics. For details please see the lab website at http://www-plb.ucdavis.edu/Labs/sundar/ An overview of current projects & foci in lab Genomics of the Zygotic Transition in Rice The fusion of two highly differentiated cells, the egg cell and the sperm cell, results in a totipotent zygote: a single cell with the capacity to develop into an entirely new organism. In this respect, the zygote can be considered to be the ultimate stem cell. In both plants and animals, early embryo development is dependent on maternal transcripts deposited in the egg cell before fertilization. The degradation of these maternal transcripts and the initiation of zygotic transcription take place during the Maternal to Zygotic Transition (MZT). Regulation of the MZT in plants and animals is critical to successful reproduction. Read more... The Rice Microbiome Plants, much like humans and other animals, harbor rich communities of potentially beneficial bacteria. The collective genomes of this complex microbial network, termed the metagenome, encode diverse metabolic capabilities unfounded within plants, essentially offering a functional extension to the host plant's genome. Soil microbes in close proximity to plant roots (termed the rhizosphere) have been shown to promote plant disease suppression and nutrient acquisition. Using rice (Oryza sativa) as a model, we are answering questions based around how plants recruit and moderate their associated root microbiomes. Unraveling the composition and maintenance of the rice microbiome is not only important for bolstering our basic understanding of host-microbe interactions: it is of great agronomic and ecological importance as well. Read more... Patterning of Arabidopsis Embryo Sac Development of the gametophyte, the haploid generation of the plant life-cycle, is important for plant reproduction and seed formation. In flowering plants, the female gametophyte is called the embryo sac. It consists of only four cell types, including two gametes, which are the result of a precise developmental program. Until recently, relatively little was known about the molecular mechanisms that establish developmental pattern in the embryo sac, in part due to the relative inaccessibility of the gametophyte and the limited availability of informative mutants. Read more... Publications Anderson, S., Johnson, C., Jones, D., Conrad, L., Gou, X., Russell, S., Sundaresan, V., 2013. Transcriptomes of isolated rice gametes characterized by deep sequencing: Evidence for distinct sex-dependent chromatin and epigenetic states before fertilization. The Plant Journal, 76: 729-741 Martin, M., Fiol, D., Sundaresan, V., Zabaleta, Pagnussat, G., 2013. oiwa, a Female Gametophytic Mutant Impaired in a Mitochondrial Manganese-Superoxide Dismutase, Reveals Crucial Roles for Reactive Oxygen Species during Embryo Sac Development and Fertilization in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 25: 1573-1591 Spence, C., Alff, E., Johnson, C., Ramos, C., Donofrio, N., Sundaresan,V., Bais, H., 2014. Natural rice rhizospheric microbes suppress rice blast infections. BMC Plant Biology, 14:130. Leshem Y., Johnson C., Sundaresan V. 2013. Pollen tube entry into the synergid cell of Arabidopsis is observed at a site distinct from the filiform apparatus. Plant Reproduction, 10.1007/s00497-013-0211-1 Tsai H., Missirian V., Ngo K., Tran R.K., Chan S., Sundaresan V., Comai L. 2013. Production of a high efficiency TILLING population through polyploidization. Plant Physiology, doi:10.1104/pp.112.213256 Yang S-Y, Gronlund M, Jakobsen I, Grotemeyer MS, Rentsch D, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Kumar CS, Sundaresan V, Salamin N, Catausan S, Mattes N, Heuer S, Paszkowski U. 2013. Nonredundant Regulation of Rice Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis by Two Members of the PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 Gene Family. The Plant Cell, 24:4236-4251 Ngo QA, Baroux C, Guthörl D, Mozerov P, Collinge MA, Sundaresan V, Grossniklaus U. 2012. The Armadillo Repeat Gene ZAK IXIK Promotes Arabidopsis Early Embryo and Endosperm Development through a Distinctive Gametophytic Maternal Effect. The Plant Cell, 24:4026-4043 Leshem Y., Johnson C.A., Wuest S.E., Song X., Ngo Q.A., Grossniklaus U., Sundaresan V. 2012. Molecular Characterization of the glauce Mutant: a Central Cell-Specific Function Is Required for Double Fertilization in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 24:3264-3277 Gutjahr C, Radovanovic D, Geoffroy J, Zhang Q, Siegler H, Chiapello M, Casieri L, An K, An G, Guiderdoni E, Kumar CS, Sundaresan V, Harrison MJ, Paszkowski U. 2011. The half-size ABC transporters STR1 and STR2 are indispensable for mycorrhizal arbuscule formation in rice. The Plant Journal, 69:906-920 Ravi M., Kwong P.N., Menorca R.M., Valencia J.T., Ramahi J.S., Stewart J.L., Tran R.K., Sundaresan V., Comai L., Chan S.W. 2010. The rapidly evolving centromere-specific histone has stringent functional requirements in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics, 186:461-471 Ma H., Sundaresan V. 2010. Development of flowering plant gametophytes. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol., 91:379-412 Sundaresan V., Alandete-Saez, M. 2010. Pattern formation in miniature: The female gametophyte of flowering plants. Development, 137:179-189 Li N., Yuan L., Liu N., Shi D., Li X., Tang Z., Liu J., Sundaresan V., Yang W.-C. 2009. SLOW WALKER2, a NOC1/Mak21 Homologue, Is Essential for Coordinated Cell Cycle Progression during Female Gametophyte Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology , 151:1486-1497 Johnson, C., Kasprzewska, A., Tennessen, K., Fernandes, J., Nan, G-L., Walbot, V., Sundaresan, V., Vance, V., and Bowman, L.H. 2009. Clusters and superclusters of phased small RNAs in the developing inflorescence of rice. Genome Research, 19:1429-1440 Pagnussat, G.C., Alandete-Saez, M., Bowman, J.L., Sundaresan, V. 2009. Auxin-Dependent Patterning and Gamete Specification in the Arabidopsis Female Gametophyte. Science, 324:1684-1689 Krishnan A, Guiderdoni E, An G, Hsing YI, Han CD, Lee MC, Yu SM, Upadhyaya N, Ramachandran S, Zhang Q, Sundaresan V, Hirochika H, Leung H, Pereira A. 2009. Mutant resources in rice for functional genomics of the grasses. Plant Physiology, 149:165-70. Boavida LC, Shuai B, Yu HJ, Pagnussat GC, Sundaresan V, McCormick S. 2009. A Collection of Ds Insertional Mutants Associated With Defects in Male Gametophyte Development and Function in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics, 181:1369-85. Capron, A., Gourgues, M., Neiva, L.S., Faure, J.E., Berger, F., Pagnussat, G., Krishnan, A., Alvarez-Meija, C., Vielle-Calzada, J.-P., Lee, Y.-R., Liu, B., Sundaresan, V. 2008. Maternal control of male-gamete delivery in Arabidopsis involves a putative GPI-anchored protein encoded by the LORELEI gene. The Plant Cell, 20: 3038Â3049. Meyers BC, Matzke M, Sundaresan V. 2008. The RNA world is alive and well. Trends in Plant Sciences, 13:311-3. Qu, S., Desai, A., Wing, R.A., Sundaresan, V. 2008. A Versatile Transposon-Based Activation Tag Vector System for Functional Genomics in Cereals and Other Monocot Plants. Plant Physiology, 146:189-99. Chen, Z., Tan, J., Inguoff, M., Sundaresan, V. , Berger, F. 2008. The Chromatin Assembly Factor 1 regulates the cell cycle but not the cell fate during male gametogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development, 135:65-73. Pagnussat, G., Yu, H.-J., Sundaresan, V. 2007. Cell-fate switch of synergid to egg cell in Arabidopsis eostre mutant embryo sacs arises from mis-expression of the BEL1-Like Homeodomain gene BLH1. The Plant Cell, 19:3578-92 Ngo, Q.A., Moore, J.M., Baskar R., Grossniklaus, U., and Sundaresan, V. 2007. The Arabidopsis glauce mutant reveals a novel regulatory function of the female gametophyte in autonomous endosperm development and expression of paternal alleles during early embryogenesis. Development, 134: 4107-4117. Dewitte, W., Scofield, S., Alcasabas, A.A., Maughan, S.C., Menges, M., Braun, N., Collins, C., Nieuwland, J., Prinsen, E., Sundaresan, V., Murray, J.A.H. 2007. Arabidopsis CYCD3 D-type cyclins link cell proliferation and endocycles and are rate-limiting for cytokinin responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA , 104:14537-14542. Griffith, M.E., Mayer, U., Capron, A., Ngo, Q., Surendrarao A., McClinton, R., Jurgens, G., Sundaresan, V. 2007. The TORMOZ gene encodes a nucleolar protein required for regulated division planes and embryo development in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell , 19: 2246-2263 Johnson, C., Sundaresan, V. 2007. Regulatory small RNAs in plants. In Plant Systems Biology Birkhauser, Springer-Verlag, Switzerland. pp. 99-113. Johnson, C., Bowman, L., Adai, A., Vance, V., Sundaresan, V. 2006. CSRDB: a small RNA integrated database and browser resource for cereals. Nucleic Acids Res., 35:D829-D833. Sundaresan, V. 2005. Control of seed size in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA , 50:1788717888. Kumar, C.S., Wing, R.A., Sundaresan, V. 2005. Efficient insertional mutagenesis in rice using the maize En/Spm elements. The Plant Journal 44: 879-897. Yu, H.-J., Hogan, P.S., Sundaresan, V. 2005. Analysis of the female gametophyte transcriptome of Arabidopsis by comparative expression profiling.Plant Physiology 139: 1853-1869. Pagnussat, G., Yu, H.-J., Ngo, Q., Rajani, S., Mayalagu, S., Johnson, C., Capron, A., Xie, L.-F., Ye, D., Sundaresan, V., 2005. Genetic and molecular identification of genes required for female gametophyte development and function in Arabidopsis. Development 132:603-614 Nishal, B., Tantikanjana, T., Sundaresan, V., 2005. An Inducible Targeted Tagging System for Localized Saturation Mutagenesis in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiology 137:3-12. Adai A., Johnson, C., Mlotshwa, S., Archer-Evans, S., Manocha, V., Vance, V., Sundaresan, V., 2005 Computational prediction of miRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana.Genome Research 15:78-91 Tantikanjana T, Mikkelsen M.D, Hussain M, Halkier B.A, Sundaresan V, 2004. Functional analysis of the tandem-duplicated P450 genes SPS/BUS/CYP79F1 and CYP79F2 in glucosinolate biosynthesis and plant development by Ds transposition-generated double mutants. Plant Physiol. 135:840-848. Hirochika H, Guiderdoni E, An G, Hsing YI, Eun MY, Han C.D, Upadhyaya N, Ramachandran S, Zhang Q, Pereira A, Sundaresan V, Leung H, 2004. Rice mutant resources for gene discovery. Plant Mol Biol. 54:325-334. Kolesnik, T., Szeverenyi, I., Bachmann , D., Kumar, C.S., Jiang, S., Rengasamy, R., Cai, M., Ma, Z., Sundaresan, V., Ramachandran, S. , 2004. Establishing an Efficient Ac/Ds Tagging System in Rice: Large-Scale Analysis of Ds Flanking Sequences. The Plant Journal 37 :301-314. Reddy, T.V., Agashe, B., Kaur, J., Sundaresan , V. and Siddiqi, I. , 2003. The DUET Gene is Necessary for Chromosome Organization and Progression During Male Meiosis in Arabidopsis and Encodes a PHD Finger Protein. Development 130:5975-87. Yang, S.L., Xie, L.F., Mao,H.-Z., Puah, C.S., Yang, W.C., Jiang, L., Sundaresan,V., and Ye,D., 2003. The TAPETUM DETERMINANT 1 Gene Is Required for Cell Specialization in The Arabidopsis Anther. The Plant Cell 15 :2792-804. Kwee, H.S., and Sundaresan, V. , 2003. The NOMEGA gene required for female gametophyte development encodes the putative APC6/CDC16 component of the Anaphase Promoting Complex in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal 36 :853-866. Buell, C.R., and Sundaresan, V., 2003. A workshop on establishing a rice resource center in the United States. Plant Physiology 132 :1137. Kumaran M., Bowman, J.L., and Sundaresan, V., 2002. YABBY Polarity Genes Mediate Repression of KNOX Homeobox Genes in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 14:2761-2770. Selected Older Publications Rajani, S. and Sundaresan, V., 2001. The Arabidopsis myc/bHLH gene ALCATRAZ enables cell separation in fruit dehiscence. Current Biology 11:1914-1922. Tantikanjana, T., Yong J.W.H., Letham, D.S., Griffith, M., Hussain, M., Ljung, K., Sandberg, G., and Sundaresan, V., 2001. Control of Axillary Bud Initiation and Shoot Architecture in Arabidopsis through the SUPERSHOOT gene. Genes and Development 15:1577-1588. Ramachandran, S. and Sundaresan, V., 2001. Transposons as Tools for Functional Genomics. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 39:243-252. Parinov, S. and Sundaresan, V., 2000. Functional genomics in Arabidopsis: Large scale insertional mutagenesis complements the genome sequencing project. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 11:157-161. Yang, W.C. and Sundaresan, V., 2000. Genetics of gametophyte biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 3:53-57. Parinov, S., Mayalagu, S., Ye, D., Yang, W.C., Kumaran, M., and Sundaresan,V., 1999. Analysis of flanking sequences from Ds insertion lines: A database for reverse genetics in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 11:2263-2270. Yang, W.C., Ye, D., Xu, J., and Sundaresan, V., 1999. The SPOROCYTELESS gene of Arabidopsis is required for initiation of sporogenesis and encodes a novel nuclear protein. Genes and Development 13 :2108-2117. Kumaran, M.K., Ye, D., Yang, W.C., Griffith, M.E., Chaudhury, A.M., and Sundaresan, V., 1999. Molecular cloning of Abnormal Floral Organs: A gene required for flower development in Arabidopsis. Sexual Plant Reproduction 12:118-122. Colasanti, J., Zhuang, Y., and Sundaresan, V., 1998. The indeterminate gene encodes a zinc-finger protein and regulates a leaf-generated signal required for the transition to flowering in maize. Cell 93:593-603. Sundaresan, V., 1996. Horizontal spread of transposon mutagenesis: Old elements find new uses. Trends in Plant Sciences 1:184-190. Springer, P., McCombie, R., Sundaresan, V., and Martienssen, R., 1995. Gene trap tagging of Prolifera, an MCM2/3/5 homolog in Arabidopsis. Science 268: 877-880. Sundaresan, V., Springer, P., Volpe, T., Haward, S., Jones, J.D.G., Dean, C., Ma, H., and Martienssen, R.,1995. Patterns of gene action in plant development revealed by enhancer trap and gene trap transposable elements. Genes and Development 9:1797-1810.