Topographic Maps
advertisement

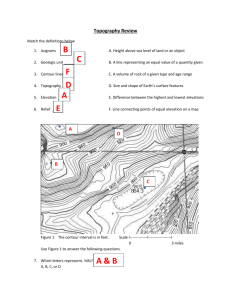
Topographic Maps Topography: The surface features of the Earth; the rises and falls of the land Topographic Maps Show 3-D surface on a 2-D plane Made on Quadrangles (7.5 minute or 15 minute squares of latitude and longitude) Made by the USGS for military, scientific, and commercial use Features Name and Date o Shown in the lower right o Usually named after nearby towns North Arrows o Located just left of center in the bottom margin o MN – Magnetic north (where a compass points) o GN – Grid north (north for the US grid system – townships and ranges) o N↑ – True north (points to the north pole) Latitude and Longitude o Listed at the map sides and corners in degrees minutes and seconds Scale o o o o Located at the bottom center Verbal - A statement (one inch equals one mile) Graphic - Shows actual distances Fractional States a ratio or fraction of measurements Example: 1:24000 => one unit on the map = 24000 units on the earth Smaller scales show more area, but less detail (things on the map appear smaller) Larger scales show less area, but more detail (things on the map appear larger) Symbols o Buildings, Schools, Railroads, Churches o Colors Red and Black - roads and man-made features Purple - revised features Blue - water features (lakes, streams, marshes) Brown - contour lines Contour Lines Represent elevation above sea level and shape of the land Connect and mark points of elevation Contour interval - difference in elevation between 2 contour lines Benchmarks o Show points of exact elevation o Examples: BM 106; VABM 1212; X 5487; BM X 236 Relief - difference in elevation between 2 points Slope = relief / distance Contour Line Rules Contour lines may never cross. Hills - Contour lines form closed concentric circles Depressions - Contour lines form closed concentric circles with hachure marks pointing inward Steep slopes - contour lines are close together Gentle slopes - contour lines are widely spaced Rule of V's - In streams and stream valleys, the contour lines bend and make a 'V' pointing upstream.