chapt25
advertisement

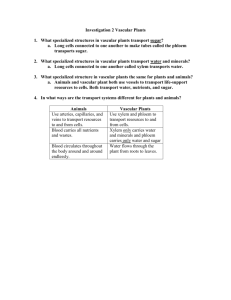
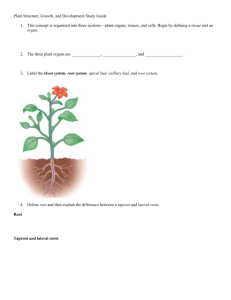
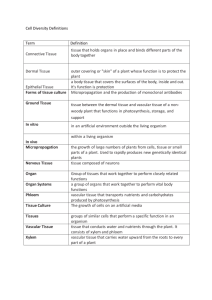
Chapter 25 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. The cortex found in the center of a dicot stem or a monocot root is made of what type of tissue? A. ground tissue B. epithelial tissue C. vascular tissue D. dermal tissue 2. We are very familiar with two things found in large woody plants, wood and bark. The wood is essentially made of ________ and the bark is essentially made of _________. A. xylem; phloem B. vascular tissue; epidermal tissue C. the cortex; the epidermis D. pith; cork 3. Which two of the following foods are by definition stems? A. potato B. celery C. onion D. carrots E. potato and onions are stems 4. Which function is NOT shared by both the root system and the shoot system of a plant? A. absorb water B. transport water C. transport inorganic nutrients D. transport organic nutrients 5. Which of the following tissue types in the plant gives rise to the other three types? A. epidermal tissue B. ground tissue C. meristem D. vascular tissue 6. Which of the following tissues makes up the majority of the interior of the plant? A. epidermal tissue B. ground tissue C. meristem D. vascular tissue 7. Which of the following tissues forms the outer protective covering of the plant? A. epidermal tissue B. ground tissue C. meristem D. vascular tissue 8. Which of the following tissues transports water and nutrients within the plant? A. epidermal tissue B. ground tissue C. meristem D. vascular tissue 9. The Greek root word meaning "cup-shaped cavity" is the basis for the term A. pistil. B. stamen. C. cotyledon. D. petal. E. carpal 10. Which of the following tissues is an embryonic tissue type found at the apex of roots and shoots? A. epidermal tissue B. ground tissue C. meristem D. vascular tissue 11. The Greek root words meaning "over" and "skin" are the basis for the term A. stomate. B. sclerenchyma. C. cotyledon. D. parenchyma. E. epidermis. 12. Which statement is NOT true of the epidermis of a plant? A. The epidermis covers the entire body of a herbaceous plant. B. Guard cells are specialized epidermal cells found on root surfaces. C. The epidermis is impervious to gas exchange. D. Root hairs increase the surface area of epidermal cells on roots. E. Cork cells replace epidermal cells on older woody plants. 13. Which of these plant tissue types most closely corresponds to the "typical" unspecialized plant cell? A. xylem B. phloem C. collenchyma D. sclerenchyma E. parenchyma 14. Which of these plant tissue types has cells with thick secondary cell walls, and is made up of fibers and sclereids? A. xylem B. phloem C. collenchyma D. sclerenchyma E. parenchyma 15. The Greek root words meaning "beside" and "infusion" are the basis for the term A. stomate. B. schlerenchyma. C. cotyledon. D. parenchyma. E. epidermis. 16. Which of these plant tissue types is composed of hollow nonliving tracheids and vessel elements that transport water from the roots to the leaves? A. xylem B. phloem C. collenchyma D. sclerenchyma E. parenchyma 17. Which of these plant tissue types is composed of cells with primary walls thickened at the corners that provide support for immature parts of the cell body? A. xylem B. phloem C. collenchyma D. sclerenchyma E. parenchyma 18. Which of these plant tissue types is composed of sieve-tube cells and companion cells, and transports organic nutrients made in the leaves? A. xylem B. phloem C. collenchyma D. sclerenchyma E. parenchyma 19. Which of these vascular tissue cells is alive but lacks a nucleus? A. tracheid B. sieve-tube cell C. vessel element D. companion cell 20. Which statement is NOT true about vascular tissue in plants? A. In leaves, the vascular tissue is found in the leaf veins. B. In stems, the vascular tissue is found in the vascular bundles. C. In roots, the vascular tissue is found in the central vascular cylinder. D. Xylem cells are hollow and nonliving, and they form a continuous pipeline that transports water and minerals. E. Phloem cells are hollow and nonliving, and they form a continuous pipeline that transports sugars. 21. Which statement is NOT true about primary plant growth? A. Only woody plants show primary growth. B. Primary growth increases the length of the plant. C. The ground meristem is a primary meristem that produces ground tissue. D. The procambium is a primary meristem that produces primary vascular tissue. E. The protoderm is a primary meristem that produces the more mature dermal tissue. 22. You need to identify a plant, but it is winter and the leaves have fallen to the ground mixed with others, and the parts of flowers, fruits, and seed leaves of germinating seeds are not available either. Your best clue to whether it is a monocot or a dicot is to A. inspect the stem for woody bark (only dicots have woody tissue). B. determine if there are parallel xylem tubes in the stem (if so, it is a monocot). C. determine if the roots lack phloem and xylem (if so, it is a monocot). D. cut the stem (if the vascular bundles are in a distinct ring, it is a monocot). E. cut the stem (if the vascular bundles are scattered in the stem, it is a monocot). 23. To prepare a microscope slide of mitosis, where could you most likely find examples of cell division in a plant? A. near the root tip B. in a tree trunk, near the center C. anywhere in the mesophyll of a leaf D. at the center of a root, back from the tip 24. Which of the following statements is NOT correct about the arrangement of tissues in the dicot root? A. The specialized root tissues are seen at the zone of maturation. B. The epidermis of the root has no cuticle on its outer surface, unlike other epidermal tissues. C. The pericycle is the outer layer of cells in the vascular cylinder, with the ability to form secondary or branch roots. D. The Casparian strip is a waxy lining on four sides of the cells of the endodermis, which forces water into the endodermal cells. E. The star-shaped phloem is located in the center of the vascular cylinder, with xylem arranged between the arms of phloem. 25. Which type of root is important in dicot food storage in plants such as carrots and radishes? A. adventitious root B. prop root C. fibrous root D. taproot 26. The Greek root words meaning "within" and "skin" are the basis for the term A. endodermis. B. schlerenchyma. C. cotyledon. D. parenchyma. E. epidermis. 27. Consider the possibility that we discover a gene that regulates both the amount of root hairs and where root hairs grow on a root tip. Since the surface area provided by root hairs is so critical to their uptake of water and nutrients, expanding their growth area seems a great advantage. However, which of these might be a problem? A. Growth of root hairs in the zone of cell division would interfere with root cell proliferation. B. Growth of root hairs in the root cap would cause them to be shredded off since this area takes substantial abrasion. C. Growth of root hairs in the zone of elongation would cause them to be shredded off as they anchored in soil and the root lengthened. D. All of these choices pose a problem. 28. The fibers that get stuck between your teeth when eating celery are A. pith. B. mesophyll. C. Casparian strips. D. rhizomes and stolons. E. vascular bundles of xylem and phloem. 29. Which type of root develops from an underground stem? A. adventitious root B. prop root C. fibrous root D. taproot 30. The Latin root words meaning "vessel" and "exchange" are the basis for the term A. apical meristem. B. vascular cambium. C. dicotyledon. D. herbaceous stem. E. primary xylem. 31. The Latin root word meaning "vegetation" or "plant" is the basis for the term A. vascular. B. xylem. C. cotyledon. D. herbaceous. E. cambium. 32. A fifteen-foot tree growing in a fencerow is used as a fencepost, to which barbed wire is stapled at a height of five feet. Years later, the tree is thirty feet high. The fence is A. still five feet up since the trunk only grows outward. B. split because the trunk grew up but the bottom stayed at ground level. C. fifteen feet up because the tree doubled in height. D. twenty feet up, still ten feet from the top of the tree. E. twenty feet up because it added fifteen feet to the original five-foot height. 33. Which of the following structures is an aboveground horizontal stem? A. bulb B. rhizome C. corm D. stolon 34. Which statement is NOT true about woody stems? A. Woody stems contain secondary growth. B. Secondary phloem accumulates to form the wood. C. The stem is organized into a central pith, wood, and outer bark. D. Cork cambium produces waterproof cork cells that become bark. E. The vascular cambium is located between the xylem and phloem of the vascular bundles in a woody stem. 35. Mechanisms by which plants protect themselves against invading bacteria and fungi include A. producing strong preservative chemicals. B. maintaining a waxy nonliving cuticle surface. C. building up and replacing an outer layer of dead cork (bark). D. having guard cells open to expose the soft juicy mesophyll of a leaf only when gas exchange is needed. E. All of the choices are correct. 36. Consider the seasonal transfer of sugars in a tree in the temperate zone where leaves are regularly shed before freezing winters. For lumber to be lightweight and dry so that it doesn't warp, it is best to cut timber A. in the summer while leaves are still on. B. in the early fall when leaves are about to fall. C. in the early winter when sap is in the roots. D. in the spring after sap is rising. E. anytime, since there would be no differences in how wet the wood would be. 37. The Latin root word meaning "shoot" is the basis for the term A. xylem. B. stolon. C. cotyledon. D. phloem. E. rhizome. 38. The Greek root word meaning "root" is the basis for the term A. xylem. B. stolon. C. cotyledon. D. phloem. E. rhizome. 39. Considering that leaf stomates have the conflicting functions of allowing gaseous carbon dioxide into the leaf, yet preserving the plant's supply of water, which of the following is/are reasonable? A. A submerged-water plant would have no stomates. B. Tree leaves that orient flat and present the top side to the sun would have most of their stomates on the bottom of the leaf. C. Corn, oats, rice, and wheat–all monocots–have relative upright blades with sunlight hitting both sides and would have stomates distributed fairly evenly on both sides. D. All of the choices are reasonable. E. None of the choices is reasonable, since stomates are found uniformly on all type of leaves. 40. The Greek root words meaning "middle" and "leaf" are the basis for the term A. palisade. B. mesophyll. C. cambium. D. phloem. E. rhizome. 41. Which statement about leaves is NOT correct? A. The epidermis is covered by a waxy layer of cuticle that reduces water loss. B. Gas exchange occurs through tiny openings in the leaf surface called stomates. C. Regulation of gas exchange through the leaf is the responsibility of the guard cells. D. Vascular tissue is arranged in a net pattern in dicots and a parallel pattern in monocots. E. The photosynthetic mesophyll is made up of an upper spongy layer and a lower palisade layer. 42. Plant roots function to A. anchor the plant. B. store the products of photosynthesis. C. produce hormones that stimulate stem growth. D. All of the choices are plant root functions. 43. Leaves often are specialized to A. carry on photosynthesis. B. protect buds. C. store food. D. capture insects. E. All of the choices are specializations of leaves. 44. The fate of an axillary bud is to produce A. nothing–it is shed with the leaf. B. a branch or a flower. C. wood. D. inhibitors of growth. 45. Of the following, which is not characteristic of a monocotyledon plant? A. vascular tissue in a ring in the root B. vascular bundles scattered in the stem C. netted venation of leaf vascular bundles D. parallel venation of leaf vascular bundles 46. Which of the following are monocots? A. potatoes B. rice C. beans D. beets 47. Vascular tissue that transports organic nutrients from the leaves to the roots is A. xylem. B. phloem. C. cambium. D. meristem. 48. The root endodermis A. forms a boundary between the cortex and inner vascular cylinder of the root. B. contains impermeable lignin and suberin called a Casparian strip that controls water and nutrient movement between adjacent cell walls. C. is a single layer of rectangular cells. D. All of the choices are true of root endodermis. 49. A stolon is a horizontal stem that can function in asexual reproduction of a plant. True False 50. Bacteria associated with the roots of plants are called mycorrhizae. True False 51. The shoot system of the plant is the aboveground portion that holds leaves up for capturing the energy of sunlight. True False 52. Vascular tissue extends throughout the plant, in both the root system and the shoot system. True False 53. Root hairs are first seen in the epidermal cells in the zone of elongation in the dicot root. True False 54. The root cap is located between the zone of cell division and the zone of elongation in the dicot root. True False 55. Monocot roots have centrally located ground tissue called pith, surrounded by a ring of xylem and phloem bundles. True False 56. The pericycle is the most important root tissue for regulating mineral and water movement into the vascular cylinder. True False 57. Primary growth of stems occurs in the tip of each growing stem, as the shoot apical meristem. True False 58. The section of a stem where a leaf is attached is called the internode. True False 59. Monocot stems have vascular bundles scattered throughout the stem, whereas dicots have vascular bundles in a ring between the pith and cortex. True False 60. The spines of cacti and the traps of the Venus's-flytrap are modified leaves. True False 61. Wood is dead xylem. True False 62. Ground tissue forms the bulk of plant tissues. Ground tissue contains parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. True False 63. An internode is the point of leaf attachment. True False 64. List and describe the activities of the various kinds of plant tissues. 65. Describe the specializations and functions of the root and shoot systems in plants. 66. Define the differences between monocots and dicots, including leaves, stems, and roots. 67. Describe the areas of differentiation in the development of the dicot root. 68. Explain the differences between primary and secondary growth in stems. 69. Describe the structure of a typical leaf. 70. Using the underwater plant Elodea, it is possible to conduct a simple experiment on the effect of increased light intensity on photosynthesis rate. The oxygen product of photosynthesis is readily given off by the Elodea, and the number of bubbles produced per minute gives an indication of the rate of photosynthesis. Draw a graph that would represent the logical production of gas bubbles as light was increased from the darkness of night to the average midday light. However, plants can suffer damage from too much light intensity. Draw a second graph that would represent your hypothesis for what would happen to the number of oxygen bubbles produced by Elodea if light intensity was increased to over ten times normal sunlight levels. What would happen to the submerged plant and photosynthesis if you continued to increase light intensity? Explain your answer. If we used a terrestrial plant, would the damaging effects occur sooner or later? Chapter 25 KEY 1. A 2. A 3. E 4. A 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. D 9. C 10. C 11. E 12. B 13. E 14. D 15. D 16. A 17. C 18. B 19. B 20. E 21. A 22. E 23. A 24. E 25. D 26. A 27. D 28. E 29. A 30. B 31. D 32. A 33. D 34. B 35. E 36. C 37. B 38. E 39. D 40. B 41. E 42. D 43. E 44. B 45. C 46. B 47. B 48. D 49. TRUE 50. FALSE 51. TRUE 52. TRUE 53. FALSE 54. FALSE 55. TRUE 56. FALSE 57. TRUE 58. FALSE 59. TRUE 60. TRUE 61. TRUE 62. TRUE 63. FALSE 64. Answers will vary. 65. Answers will vary. 66. Answers will vary. 67. Answers will vary. 68. Answers will vary. 69. Answers will vary. 70. Answers will vary.