MUSINGU HIGH SCHOOL DECEMBER 2013 HOLIDAY
advertisement
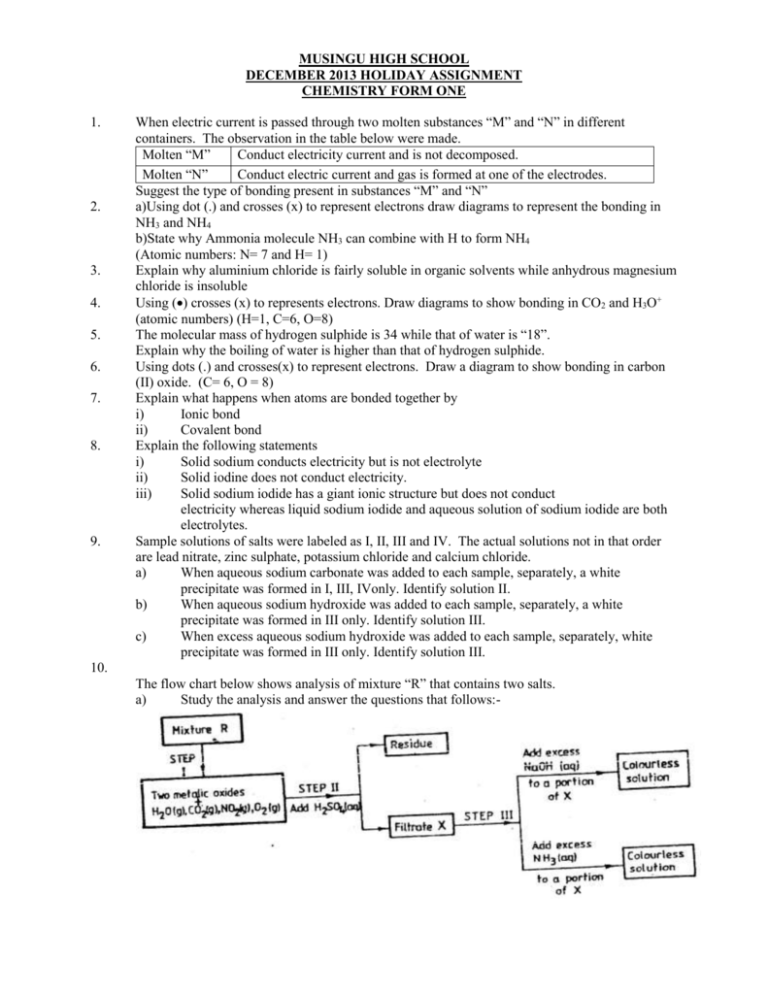
MUSINGU HIGH SCHOOL DECEMBER 2013 HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENT CHEMISTRY FORM ONE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. When electric current is passed through two molten substances “M” and “N” in different containers. The observation in the table below were made. Molten “M” Conduct electricity current and is not decomposed. Molten “N” Conduct electric current and gas is formed at one of the electrodes. Suggest the type of bonding present in substances “M” and “N” a)Using dot (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons draw diagrams to represent the bonding in NH3 and NH4 b)State why Ammonia molecule NH3 can combine with H to form NH4 (Atomic numbers: N= 7 and H= 1) Explain why aluminium chloride is fairly soluble in organic solvents while anhydrous magnesium chloride is insoluble Using () crosses (x) to represents electrons. Draw diagrams to show bonding in CO2 and H3O+ (atomic numbers) (H=1, C=6, O=8) The molecular mass of hydrogen sulphide is 34 while that of water is “18”. Explain why the boiling of water is higher than that of hydrogen sulphide. Using dots (.) and crosses(x) to represent electrons. Draw a diagram to show bonding in carbon (II) oxide. (C= 6, O = 8) Explain what happens when atoms are bonded together by i) Ionic bond ii) Covalent bond Explain the following statements i) Solid sodium conducts electricity but is not electrolyte ii) Solid iodine does not conduct electricity. iii) Solid sodium iodide has a giant ionic structure but does not conduct electricity whereas liquid sodium iodide and aqueous solution of sodium iodide are both electrolytes. Sample solutions of salts were labeled as I, II, III and IV. The actual solutions not in that order are lead nitrate, zinc sulphate, potassium chloride and calcium chloride. a) When aqueous sodium carbonate was added to each sample, separately, a white precipitate was formed in I, III, IVonly. Identify solution II. b) When aqueous sodium hydroxide was added to each sample, separately, a white precipitate was formed in III only. Identify solution III. c) When excess aqueous sodium hydroxide was added to each sample, separately, white precipitate was formed in III only. Identify solution III. 10. The flow chart below shows analysis of mixture “R” that contains two salts. a) Study the analysis and answer the questions that follows:- i) What conditions are necessary for the process in step I to take place? ii) Draw a labelled diagram to the set up that could be used to separate the mixture formed in step II. Write an ionic equation for the reaction between the cation in fitrate X and aqueous ammonia What observations would indicate the presence of NO2 (g) in step I. iii) iv) 11. 12. v) State how the water vapour in step I could be identified When dilute nitric acid was added to a sample of solid “C” a colourless gas that formed a white precipitate with lime water was produced. When another sample of solid “C” was heated strongly in a test tube, there was no observations changes. Write the formula of the ions in solid “C” When excess carbon (IV) oxide passed over heated lead (II) oxide in combustion tube, lead (II) oxide was reduced. a) Write an equation for the reaction which took place. b) What observations was made in the combustion tube when the reaction was complete? c) Name another gas which would be used to reduce lead (II) oxide. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19 20 21 22 When solid B1 was heated, a gas which formed a white precipitate when passed through lime water was produce. The residue was dissolved in dilute nitric (V) acid to form a precipitate which dissolved on warming was formed. a) Write the formula of the: I. Cation in solid B1 II. Anion in solid B1 b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction between the residue and dilute nitric (V) acid When extinguishing fire caused by petrol, carbon (IV) oxide is used in preference to water. Explain. Write an equation for the reaction that occurs when carbon (II) oxide is passed over heated Copper (II) oxide. a) Explain the following i) Temporary hardness in water ii) Permanent hardness in water. b) i) Draw a diagram and explain how ionic exchanger works. ii) Explain why hard water is recommended for healthy development of teeth. When a solid “T” is heated, a black solid is left and a colourless gas which form white precipitate with lime water is evaluated. Identify “T” and write an equation for the decomposition of “T”. State the confirmation test for the following gases:i) Carbon (II) oxide ii) Carbon (IV) oxide A gas occupies a volume of 400 cm3 at 500k and atmospheric pressure. What will be the temperature of the gas when the volume and pressure of the gas is 100 cm3 and 0.5 atmospheric pressure respectively? A sealed glass tube containing air at S.T.P was immersed in water at 1000C. Assuming there was no increase in volume of the glass tube due to expansion of the glass. Calculate the pressure of the air inside the tube. Standard pressure = 760mmHg: Standard temperature = 273 K. State Charles law The volume of a sample of hydrogen gas at temperature 291K and 1.0 x 105 pascals was 3.5 x 102 3 m . Calculate the temperature at which the volume of the gas would be 2.8 x 10-2 m3 at 1.0 x 105 pascals