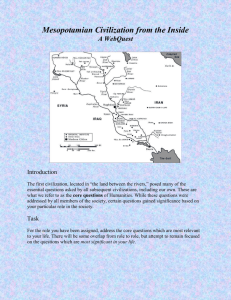
Theme Chart GRAPES Mesopotamia
advertisement
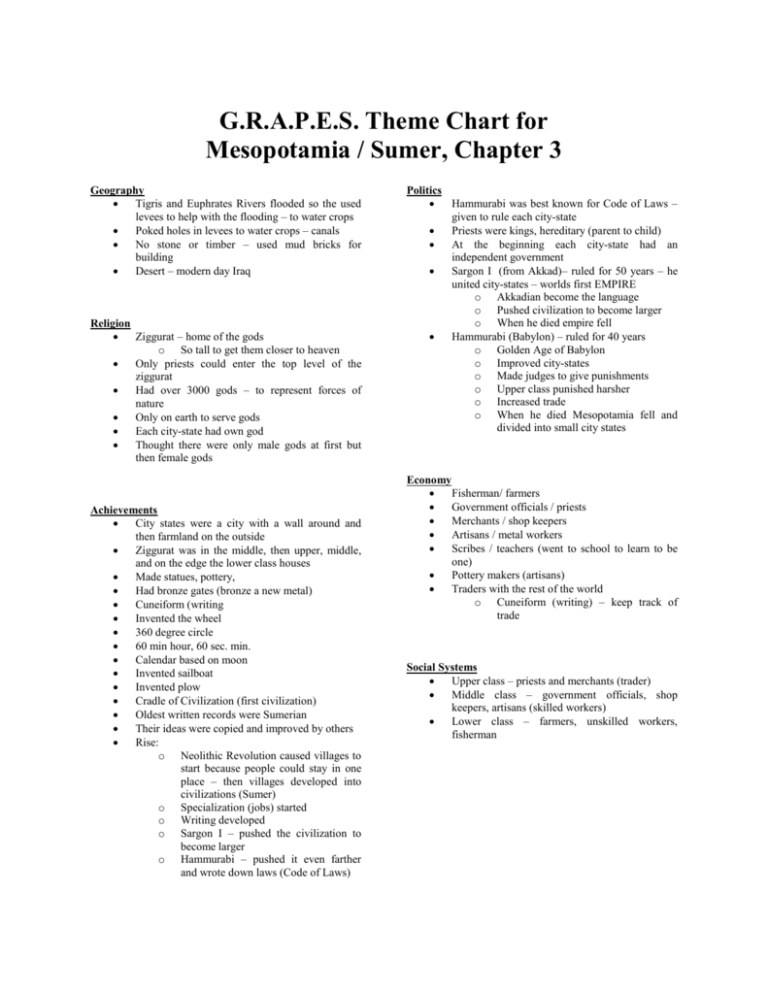
G.R.A.P.E.S. Theme Chart for Mesopotamia / Sumer, Chapter 3 Geography Tigris and Euphrates Rivers flooded so the used levees to help with the flooding – to water crops Poked holes in levees to water crops – canals No stone or timber – used mud bricks for building Desert – modern day Iraq Religion Ziggurat – home of the gods o So tall to get them closer to heaven Only priests could enter the top level of the ziggurat Had over 3000 gods – to represent forces of nature Only on earth to serve gods Each city-state had own god Thought there were only male gods at first but then female gods Achievements City states were a city with a wall around and then farmland on the outside Ziggurat was in the middle, then upper, middle, and on the edge the lower class houses Made statues, pottery, Had bronze gates (bronze a new metal) Cuneiform (writing Invented the wheel 360 degree circle 60 min hour, 60 sec. min. Calendar based on moon Invented sailboat Invented plow Cradle of Civilization (first civilization) Oldest written records were Sumerian Their ideas were copied and improved by others Rise: o Neolithic Revolution caused villages to start because people could stay in one place – then villages developed into civilizations (Sumer) o Specialization (jobs) started o Writing developed o Sargon I – pushed the civilization to become larger o Hammurabi – pushed it even farther and wrote down laws (Code of Laws) Politics Hammurabi was best known for Code of Laws – given to rule each city-state Priests were kings, hereditary (parent to child) At the beginning each city-state had an independent government Sargon I (from Akkad)– ruled for 50 years – he united city-states – worlds first EMPIRE o Akkadian become the language o Pushed civilization to become larger o When he died empire fell Hammurabi (Babylon) – ruled for 40 years o Golden Age of Babylon o Improved city-states o Made judges to give punishments o Upper class punished harsher o Increased trade o When he died Mesopotamia fell and divided into small city states Economy Fisherman/ farmers Government officials / priests Merchants / shop keepers Artisans / metal workers Scribes / teachers (went to school to learn to be one) Pottery makers (artisans) Traders with the rest of the world o Cuneiform (writing) – keep track of trade Social Systems Upper class – priests and merchants (trader) Middle class – government officials, shop keepers, artisans (skilled workers) Lower class – farmers, unskilled workers, fisherman