Distinguishing Powdery mildews by sequencing
advertisement

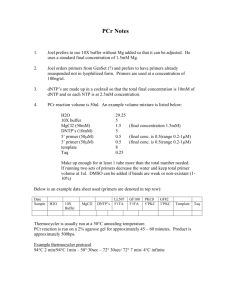
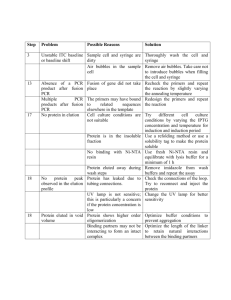
Identification Species of Powdery Mildew Pathogens by Direct Sequencing I. Amplification Using PMITS Primers A. Single-Round PCR Sample preparation Amplification using the PMITS1/2 primer pair works well on fresh tissue and has reportedly worked well on herbarium specimens (Cunnington et al, 2003). Remove 100 mg of fresh or dried plant tissue containing heavy mycelial growth and sporulation and extract genomic DNA using the DNEasy Plant Mini Kit. Add tissue to a sterile beadbeater tube containing two 5-mm diameter beads. Freeze in liquid nitrogen, beat tube twice for 30 sec at 2500 rpm, add Buffer AP1 and RNase A, incubate at 65°C as indicated in kit instructions, and follow remaining kit instructions. Elute in 100 µl Buffer AE. PCR Reaction Mixture (per 50 µl reaction) Nanopure water 5 µl MgCl2, 25 mM 2 µl Titanium Taq 10X buffer 5 µl dNTPs, 1.0 mM 10 µl Primer PMITS1, 0.8 µM 10 µl Primer PMITS1, 0.8 µM 10 µl Titanium Taq 1 µl Smart Cycler Additive Reagent 5 µl Sample 2.0µl of DNA extract (or controls as noted below) Primers Prepare to a concentration of 0.8 µM (0.8 pmol/µl) in Nanopure water: PMITS1 5’-TCGGACTGGCCYAGGGAGA-3’ PMITS2 5’-TCACTCGCCGTTACTGAGGT-3’ Controls Negative control: Positive control: 2 µl Nanopure water Genomic DNA from a known powdery mildew extract Cycling Protocol Name of protocol (on GeneAmp thermocycler): pmits.primers Ramp rate=MAX 1. 94ºC for 10 min 2. 35 cycles of: 94ºC for 1 min 63ºC for 1 min 72ºC for 2 min 3. 72ºC for 10 min Duration of protocol: not determined Expected Results Expected amplicon from PMITS primers is 700-800 bp in size (Cunnington et al, 2003). Sequencing Amplicon If a product of the correct size is amplified, gel-purifying may be necessary since fragments of other sizes may also amplify. Mix 42 µl of reaction mixture with 8 µl of loading buffer and dispense into three lanes joined together in a 1.5% agarose gel. Excise band and clean it using the QiaQuick gel extraction kit or equivalent, paying special attention to instructions in the kit which relate to direct sequencing. Elute in 30-50 µl Buffer EB. Sequence using PMITS1 and PMITS2. B. Nested PCR (for difficult targets) For targets that do not amplify well with the above reaction mix, a second, nested PCR is recommended (Cunnington et al, 2003), as follows. PCR Reaction Mixture (per 50 µl reaction) Nanopure water 7.3 µl MgCl2, 25 mM 2 µl Titanium Taq 10X buffer 5 µl dNTPs, 1.0 mM 10 µl Primer PMITS1, 0.8 µM 20 µl ITS4, 5 µM 3.2 µl Titanium Taq 1 µl Bovine serum albumin, 10 mg/ml* 1 µl *Sigma Cat. No. A-7030, filter-sterilized. Samples Run one tube with 0.5 µl of a 1:100 dilution of the reaction mixture from the SingleRound PCR Reaction (above), and run another with an undiluted 0.5 µl. Cycling Protocol Name of protocol (on GeneAmp thermocycler): pmits.nested Ramp rate=MAX 4. 94ºC for 10 min 5. 35 cycles of: 94ºC for 1 min 60ºC for 1 min 72ºC for 2 min 6. 72ºC for 10 min Sequencing Gel-purify product and sequence using PMITS1 and ITS4. II. Amplification Using Primers of Takamatsu et al. (2001) This protocol has not been evaluated in our laboratory, but the paper by Takamatsu et al (2001) suggests it also has promise. This may be useful for targets that fail to amplify with the primers of Cunnington et al (2003). For details, see paper. Primers ITS1 5’-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3’ PM5 5’-TTGCTTTGGCGGGCCGGG-3’ PM4 5’-CCGGCCCGCCAAAGCAAC-3’ PM6 5’-GYCRCYCTGTCGCGAG-3’ Controls Negative control: Positive control: 2 µl Nanopure water Use universal primer set ITS1/ITS4 References Cunnington, J. H., Takamatsu, S., Lawrie, A. D., and Pascoe, I. G. 2003. Molecular identification of anamorphic powdery mildews (Erysiphales). Australasian Plant Pathology 32:421-428. Takamatsu, S., and Kano, Y. 2001. PCR primers useful for sequencing of rDNA of the powdery mildew fungi. Mycoscience 42:135-139. Document Control: February 17, 2016