©EE, NCKU All rights reserved.
Laboratory #10 Pre-lab
Class:
Name:
Student ID:
1. Problem 1 (PSPICE simulation)
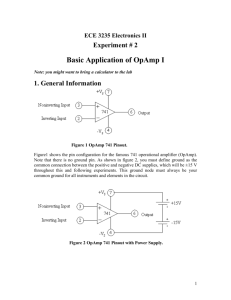
Assemble the circuit as shown in Fig. 10.9 using uA741 OPAMP.
The resistance values are R1=1kΩ, R2=10kΩ. Then, apply a sine
wave at input node with 1 Vpp amplitude and 1 kHz frequency. Plot the
waveforms at input and output terminals and explain the result.
2. Problem 2 (PSPICE simulation)
Assemble the circuit as shown in Fig. 10.10 using uA741 OPAMP.
The resistance values are R1=1kΩ, R2=10kΩ. Then apply a sine
wave at input node with 1 Vpp amplitude and 1 kHz frequency. Plot the
waveforms at input and output terminals and explain the result.
3. Problem 3 (PSPICE simulation)
Assemble the circuit as shown in Fig. 10.11 using uA741 OPAMP.
The resistance values are R=1kΩ, C=0.1μF. Then apply sine wave
at input node with 1 Vpp amplitude and 1 kHz frequency. Plot the
waveforms at input and output terminals and explain the result.
4. Problem 4 (PSPICE simulation)
Assemble the circuit as shown in Fig. 10.12 using uA741 OPAMP.
The resistance values are R=1kΩ, C=0.1μF. Then apply sine wave
at input node with 1 Vpp amplitude and 1 kHz frequency. Plot the
waveforms at input and output terminals and explain the result.
5. Problem 5 (Term explanation)
Explain the following terminologies:
(1) 3-dB bandwidth
(2) Gain margin
(3) Phase margin
(4) CMRR
(5) PSRR
電子學實驗(一) Electronics Laboratory (1), 2015
p. 10-1
成大電機 EE, NCKU, Tainan City, Taiwan
©EE, NCKU All rights reserved.
Laboratory #10 Report
Class:
Name:
Student ID:
1. Exploration 1
(1). Voltage measurements of pin 2, 3, 4, 6, 7,
Pin
Reference value
4
-15 V
7
+15 V
2, 3, 6
0V
Measured value
Table 10.2
(2). Voltage gain measurements of the inverting OPAMP
f
(Hz)
Vi(p-p)
(V)
Vo(p-p)
(V)
AV
(dB)
f
(Hz)
100
20k
500
50k
1k
100k
5k
200k
10k
500k
Vi(p-p)
(V)
Vo(p-p)
(V)
AV
(dB)
Table 10.3
2. Exploration 2
(1). Voltage measurements of pin 2, 3, 4, 6, 7,
Pin
Reference value
4
-15 V
7
+15 V
2, 3, 6
0V
Measured value
Table 10.4
(2). Voltage gain measurements of the non-inverting OPAMP
f
(Hz)
Vi(p-p)
(V)
Vo(p-p)
(V)
AV
(dB)
f
(Hz)
100
20k
500
50k
1k
100k
5k
200k
10k
500k
Vi(p-p)
(V)
Vo(p-p)
(V)
AV
(dB)
Table 10.5
電子學實驗(一) Electronics Laboratory (1), 2015
p. 10-2
成大電機 EE, NCKU, Tainan City, Taiwan
©EE, NCKU All rights reserved.
3. Exploration 3
(1). Voltage measurements of pin 2, 3, 4, 6, 7,
Pin
Reference value
4
-15 V
7
+15 V
2, 3, 6
0V
Measured value
Table 10.6
(2). Vi and VO graph with square wave input
(3). Voltage gain measurements of the OPAMP inverting integrator
f
(Hz)
Vi(p-p)
(V)
Vo(p-p)
(V)
AV
(dB)
f
(Hz)
100
600
200
700
300
800
400
900
500
1000
Vi(p-p)
(V)
Vo(p-p)
(V)
AV
(dB)
Table 10.7
4. Exploration 4
(1). Voltage measurements of pin 2, 3, 4, 6, 7,
Pin
Reference value
4
-15 V
7
+15 V
2, 3, 6
0V
Measured value
Table 10.8
(2). Vi and VO graph with ramp wave input
(3). Voltage gain measurements of the OPAMP differentiator
f
Vi(p-p)
Vo(p-p)
AV
f
Vi(p-p)
Vo(p-p)
AV
(Hz)
(V)
(V)
(dB)
(Hz)
(V)
(V)
(dB)
1k
6k
2k
7k
3k
8k
4k
9k
5k
10k
Table 10.9
電子學實驗(一) Electronics Laboratory (1), 2015
p. 10-3
成大電機 EE, NCKU, Tainan City, Taiwan
©EE, NCKU All rights reserved.
5. Problem 1
What’s the importance of CMRR in the amplifier circuits?
6. Problem 2
Use MATLAB or Excel to plot the frequency vs. gain figures
according to your measurement and explain the results.
7. Problem 3
The applied small signal input in exploration 1 and 2 is 1 Vpp. Is it
possible to apply a 5 Vpp signal? Why?
8. Conclusion
電子學實驗(一) Electronics Laboratory (1), 2015
p. 10-4
成大電機 EE, NCKU, Tainan City, Taiwan