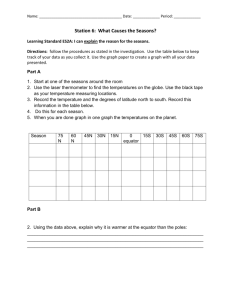
HSS_Interviews_10_28_07 - University of Massachusetts Boston
advertisement
HSS on Haiti Focus Meeting Info: Date: October 28, 2007 Time: 7:30-8:00 AM Place: WMBR Radio Attendees: Name Cornely, Pierre-Richard Brutus Leaderson Title HSS Public Relations Representative HSS Science Ak Progres Sponsored by HSS Segment 1: Introduction: Human beings have been observing the relationship between the sun and earth for many centuries and they generally agree to the following conclusions: 1. Sun rays reach the earth and they produce heat that can be used for many purposes including agriculture, electricity, and variations in the weather 2. The intensity of the sun rays vary with the time of day a. Typically, the intensity increases uniformly from sunset to Noon and decreases in much of the same manner from Noon to sunset b. The times for sunrise, noon and sunset vary with respect to geographical location c. Though there is a time called universal that is used around the world, each city has its own local time that is directly related to its geographical location 3. The amount of sun rays that will reach a specific city varies with its geographical location and the time of day a. Some countries will see more sun rays than other countries 4. There seems to be a relationship between the relative position of the sun to a country and the seasons in this country. For example, the United States has four seasons: Summer, Autumn, Winter and Spring while Haiti has only two seasons: dry and wet seasons. In this show, we would like to explore these observations, study the science behind them and develop a better understanding for the reasons behind the variations in these observations. 1 02/17/16 HSS on Haiti Focus When we come back, we will be joined in studio by a common guess, Dr. Cornely, who will help us answer these questions. Time permitting we will also take questions from the audience at the end of the show. Break Segment2: With us today on studio is Dr Cornely…..Welcome….. We have a number of big questions today for Dr. Cornely and we would like to start with the following: Q1: How do sunrays produce heat? Ultraviolet rays from the sun combine with and react on oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere to produce heat. The heat is what we observe on earth as the sun Q2: Why does the intensity of the sunrays vary with time of day? - The earth has two primary motions associated to it. - In the first motion, the earth turns around itself in 24 hours. - While the earth is turning around itself, since the sun is fixed, there are sections of the earth that are directly facing the sun while there are other section that face away from the sun. The locations on earth that are facing the sun at a particular time of day will be experiencing daylight while the other location are experiencing night light. - The amount of time and the specific time of the day that a particular location will see day light depends on its geographical location - Since the earth is rotating around itself in a counter clockwise direction, countries that are located in the East will see the sun first while countries in the west will see the sun later. For example in the United States of America, Massachusetts (say a city like Boston situated North East) will the sun before Upstate Washington (say a city like Seattle situated North West). - Also in general because the earth is rotating counterclockwise, the eastern part of any country around the globe will see the sun first, that is why we have a tendency to observe the sun rising from the east. - East and West are governed by the longitude position of a country and therefore there is also a connection between time of day and the longitude position of a country. - Longitude is counted in degrees and at the beginning when countries wanted to develop accurate maps of their location with respect to each other, it was decided by international treaty that 0 degree will be at a longitude line that crosses over Greenwich England. - Since there is a total of 360 degrees f longitude and the earth must rotate around itself in 24 hours, we can divide the total number of degrees the earth needs to rotate around itself with the total number of hours in which it does it to find the amount of degrees that the earth rotates per hours (360/24 = 15 degrees/hour) - We can also calculate the local time that a country will have with respect to another country by looking at the difference in the longitude locations. For example, the difference in time between Massachusetts (say a city like Boston) which is located 2 02/17/16 - - HSS on Haiti Focus approximately at 75 degrees of longitude West (i.e., 75 degrees behind the line of 0 degree longitude at Greenwich), and Kenya (say a city like Nairobi) which is located at 30 degrees East (i.e., 30 degrees to the right of o degree longitude at Greenwich) will have a difference in longitude of 75+30=105 degrees, 105degrees/15 degrees per hour = 7 hours. There will be approximately 7 hours difference between Nairobi and Boston, and since Boston is located behind Greenwich and Nairobi is located ahead of Greenwich, Boston will be behind Nairobi by 7 hours. Using the same reasoning we can look at the time difference between Massachusetts and Haiti and there are approximately at the same 75 degrees of longitude and therefore there will be not time differences between the two locations. Based on the above discussion, we can see why the amount of sun ray varies with time of day Also as shown below in Figure 1, the amount of sunrays a country will receive depends on its geographical location. In Figure 1 below, we see that countries that are near or at the equator will have 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of sunlight. On the other hand, the further North a country is, the amount of sun they receive vary from 6 hours of sunrays for countries located at 30 degrees of latitude like part of Mexico and Texas to 24 hours of sunrays for countries located at 70 degrees of latitude North like parts of northern Alaska Figure 1: Variation of the length of day with the seasons and the yearly rotation of the earth around the sun Break Q3: How does the amount of sunrays that a specific country receives vary with geographical location? 3 02/17/16 - - - - - HSS on Haiti Focus We have shown in the previous segment that the amount of sun varies a particular country will receive will with the time of day We have also seen that the time of day has a direct relationship with the longitude position of a country (i.e., countries that are positioned eastward will see the sun first, like Boston, Massachusetts will see the sun before Seattle Washington) There is yet another fundamental relationship between the geographical location of a country and the amount of sun ray that it will receive. Since the sun is fixed, it sends its rays directly to earth and depending on the geographical location of a country, it will receive the sun rays either directly (we mean that the sun rays will hit the country near to perpendicular) or indirectly (we mean that the sun rays will hit the country at an angle) Just like East and West positions are governed by 360 degrees of longitude, North and South are governed by 180 degrees of Latitude. The equator is at 0 degree of latitude and all countries above the equator are in the North while all countries below the equator are in the South. All countries near the equator (specifically the countries that are located within 20 degrees North and 20 degrees South of the equator receive the rays of sun in nearly perpendicular fashion. The countries include o Part of Central America: Southern Mexico like Mexico City, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. o Part of South America: Venezuela, Columbia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Equator, Peru, Brazil, Bolivia and part of Paraguay. All other countries located outside of –20 to +20 degrees of latitude will receive the ray of the sun at an angle The further away from the equator at 0 degree latitude a country is located the greater the angle at which they will receive the rays of the sun. The greater the angle at which a country receives the rays of the sun, the less intense is the sun in these locations Scientists have computed the percentage of sun intensity that will reach a location based on its location North and South of the equator (See table 1 below). The computation shows that countries near or at the equator will receive 90% of the sun intensity while countries very far away from the equator can receive as low as 10% of the sun’s energy. Table 1: the distribution of solar insulation based on geographical location SIN 80 = 0.98 or 98% SIN 70 = 0.94 or 94% SIN 60 = 0.87 or 87% SIN 50 = 0.77 or 77% SIN 40 = 0.64 or 64% SIN 30 = 0.50 or 50% SIN 20 = 0.34 or 34% SIN 10 = 0.17 or 17% 4 02/17/16 HSS on Haiti Focus SIN 0 = 0.00 or 0% - - Typically, regardless of its location a the southern part of a country will receive the most sun because it will receive the rays of sun that are at the largest angle, i.e., the rays of sun which provides the largest sun intensity. This is the reason why it is recommended to place solar panels facing South East for countries located above the equator (like Massachusetts, and countries in central America like Mexico) and North East for counties located below the Equator (like countries in South America like Bolivia, Paraguay, Argentina) Figure 2: Variation of solar flux and intensity with yearly earth’s rotation around the sun Q4: Is there any relationship between the sun and the seasons? And why do some countries like the Unites States have 4 seasons and other like Haiti have only two? We said before in a previous segment that the earth has two main motions. 1. The earth rotate around itself in 24 hours 2. The earth also rotates around the sun in 3641/4 - With this rotation around the sun, earth is in different positions at different times during the year - For a country like the United States for example, around June 21-22, the earth is West of the sun, this corresponds to summer. - Around September 22-23, the earth is South of the sun, this corresponds to Autumn - Around December 21-22, the earth is East of the sun, this corresponds to winter. - Around March 21-22, the earth is North of the sun, this corresponds to spring. - While the earth countries in the United States are going through the various seasons, other countries depending on their location may be going through other seasons. For example, when Massachusetts is in its winter season, countries in South America like 5 02/17/16 HSS on Haiti Focus Paraguay or Bolivia will be in their summer season. It is because while Massachusetts is facing the away from the sun in the winter, some countries in South America are facing toward the sun as illustrated in Figure 3 and figure 5. Figure 3: Earth’s rotation around the sun and the seasons Figure 4: Earth’s rotation around the sun and the soltices Break Q5: Is there any relationship between the geographical location of a country and its seasons? 6 02/17/16 HSS on Haiti Focus The difference in locations around the earth facing either towards the sun or away from the sun is due to the double motion of the earth around the earth. - While the earth is rotating around the sun in 3651/4 days, it is also rotating around itself in 24 hours. - This combination of motion manifest likes the earth is tumbling around itself which makes the Northern part of the earth face the sun at some times of the year while the southern part of the earth is facing the sun at other times of the year. - Locations on earth like the United States will experience all for seasons because as the earth rotates around the sun during the year, cities in the United States will be facing the sun or facing away from the sun and facing in between. - When the cities are facing the sun we will have the summer and Spring - When the cities are facing away from the sun we will have Winter and Autumn - This relationship will vary for other locations around the earth. For example, some countries do not have winter. This includes all of the countries that are located close to the equator. They have days and nights that are equal in time (and therefore they need no daylight saving time) - Other countries in the central, south America and the Caribbean also do not have four seasons because they are located not too far from the equator and therefore they are receiving a good amount of sun rays throughout the year. Figure 5: relationship between the rotation of the earth around the sun, the seasons and geographical location - On the other hand countries that are located close to the North or South poles will have period of times during the year where the sun will never rise for months at a time, See Figure 1 (this includes earth locations like Alaska in the U.S and Greenland in Europe). It is because in these periods, these earth locations are facing away from the sun. 7 02/17/16 HSS on Haiti Focus Break Q6: Is there any relationship between wind direction, intensity and the sun? - - - - Because the sun does not evenly heat the earth’s surface, there will be locations on earth that will be hotter than others. This difference in heat will create differences in atmospheric pressure in different locations on earth. Wind develops as a result of spatial differences in atmospheric pressure. Generally, these differences occur because of the uneven absorption of solar radiation at the Earth's surface (See Figure 6). Winds blow because of differences in atmospheric pressure. Pressure gradients may develop on a local to a global scale because of differences in the heating and cooling of the Earth's surface. Wind is simply as air in motion. This motion can be in any direction, but in most cases the horizontal component of wind flow greatly exceeds the flow that occurs vertically. Figure 6: The creation of wind system due to variation in pressure due to uneven heating of the earth by the sun Q7: Is there any relationship between the sun and the tides? - An ocean tide refers to the cyclic rise and fall of seawater. Tides are caused by slight variations in gravitational attraction between the Earth and the moon and the Sun in 8 02/17/16 - - - HSS on Haiti Focus geometric relationship with locations on the Earth's surface. Tides are periodic primarily because of the cyclical influence of the earth’s rotation. The moon is the primary factor controlling the temporal rhythm and height of tides. The moon produces two tidal bulges somewhere on the Earth through the effects of gravitational attraction. The height of these tidal bulges is controlled by the moon's gravitational force and the Earth's gravity pulling the water back toward the Earth. At the location on the Earth closest to the moon, seawater is drawn toward the moon because of the greater strength of gravitational attraction. On the opposite side of the Earth, another tidal bulge is produced away from the moon. However, this bulge is due to the fact that at this point on the Earth the force of the moon's gravity is at its weakest. Therefore, any given point on the Earth's surface experiences two high tides and two low tides during each tidal period. Figure 7: the relationship between the moon, the sun and the earth and the formation of tides 9 02/17/16