File
advertisement

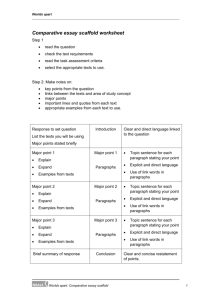
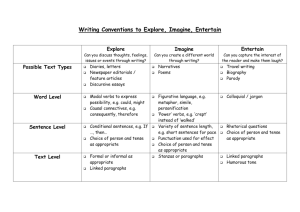
Autumn Term We Date ek Aims 1 STORIES WITH HISTORICAL SETTINGS 1 SEPT Possible Teaching Activities recognise a historical setting in stories recognise powerful verbs and say why they are important make class posters work out unknown meanings from the context hot seat characters role play write a character description Outcomes All children can: say what makes a setting historical identify likes and dislikes about a story ask questions about details they do not understanding Resources LITERACY WORLD FICTION 1 Some children can: begin to say how the author has made me think his way choose words to describe a character that will get the reader to react in a certain way 2 7 SEPT STORIES WITH HISTORICAL SETTINGS 3 14 SEPT recognise stages in a story and link events recognise powerful verbs and say why they are important STORIES WITH HISTORICAL SETTINGS to be able, using prior knowledge, to write own historically set story Identify the introduction, build-up, climax and resolution compare a TV drama and a paper based history story use time connectives write sentences with powerful verbs discuss characters, setting and main events for a class story All children can: discuss the features in TV dramas that are not in books map the stages in a story recognise the way events are linked in a story Some children can: understand the importance of using powerful verbs Tell own version of a class story write own story opening write build-up and climax of own story write own resolution add historical detail All children can: tell a story with an introduction, build-up, climax and a resolution add descriptive details use connecting words and phrases between paragraphs with support assess and evaluate peers' writing Some children can: 4 21 SEPT NON-CHRONOLOGICAL REPORTS to be able to identify content, structure, vocabulary and style of different types of texts Discuss purpose of headlines and paragraphs sort facts from opinions identify and use past tense discuss different points of view create headlines write a report use all five senses to describe a setting for a historical story LWF 1 movie and book: Lemony Snicket “Series of Unfortunate Events” LWF1 write a complete narrative story with paragraphs in place All children can: identify features of non-fiction texts (headings, lists, bullet points, captions..) generalise details delete unimportant details write a non-chronological report with support LITERACY WORLD NON FICTION 1 5 28 SEPT 6 5 OCT 7 8 12 OCT 19 OCT EVALUATING INTRUCTIONS to be able to identify features of instructional texts NEWSPAPER REPORTS to identify headlines, lead paragraphs, quotations and opinions in a newspaper report Sequence stages in a flow chart create a class checklist for flow charts investigate recipes turn a recipe into a flow chart follow directions to find a party on a map give directions for an imaginary route Compare features on newspapers' front pages plan a newspaper report for a known story write newspaper headlines, edit language practise alliteration identify powerful verbs All children can: - set out sequential stages use language of commands write clear instructions Some children can: CTD. improve the cohesion of written instructions through the use of link phrases and organisational devices All children can: identify powerful verbs in newspaper reports identify headlines, lead paragraphs, quotations and opinions LWNF 2 LWNF 3 CTD. write a newspaper report HALF-TERM BREAK 9 2 NOV STORIES SET IN IMAGINARY WORLDS to understand the devices authors use to create atmosphere in stories Discuss atmosphere and characters' reaction to the setting discuss techniques for establishing mood and atmosphere in stories hot seat characters mark parts of texts referring to mood All children can: describe the atmosphere in a story in own words find words relating to mood talk about their preferred settings identify adjectives and similes in texts LWF 2 Some children can: compare and contrast settings 10 11 STORIES SET IN IMAGINARY WORLDS (* 11 NOV BANK to be able to explain why an HOLIDAY) author used particular words and phrases to create different responses in readers 9 NOV 16 NOV STORIES SET IN IMAGINARY WORLDS - to be able to write story paragraphs which link together use body posture to reflect what a character is thinking Use storyboard sheets to tell a story use pictures to stimulate children to work on the setting and atmosphere of their stories discuss key features of fantasy stories make a class list of adverbs All children can: - say whether the image of a setting is effective use the four stages of a narrative with pictures of settings to tell a story recognise adverbs in sentences Some children can: use adverbs in different places in sentences LWF 2 Watch animations of scary places make a class list of connectives write own paragraph of the climax discuss individual paragraphs with the class All children can: use personification add visual images using five senses use connectives to join ideas between sentences with support Some children can: LWF 2 use connectives to join ideas between paragraphs 12 23 NOV STORIES SET IN IMAGINARY WORLDS - to be able to write story paragraphs which link together 13 30 NOV CREATING IMAGES to be able to identify similes and other ways of creating pictures with words create own similes Compare stories of similar themes word-process own stories add pictures review others' four paragraphs edit own work All children can: Discuss similes recognise a simile brainstorm similes for real and imaginary animals write own similes write similes around a colour use strategies to learn to spell key poetry words listen to music and create similes based on create a poem using similes Some children can: the atmosphere created read poems add extra details to make similes longer discuss cliches 14 7 DEC CREATING IMAGES 15 14 DEC to be able to use similes and other examples of vivid language when writing own poems POWERFUL VERBS to understand the function of verbs in sentences All children can: review own work edit own work word-process own writing add illustrations LWF 2 LWF 6 All children can: identify word pictures in a poem know hot to plan a poem in the same style as the one read write a poem modelled on a different one LWF 6 read poems explore images that create mood scan poems to find rhyming words with same spelling pattern talk about figurative language write own poem Change verb tenses discuss regular/irregular verbs write dialogues All children can: use irregular verbs 100 LITERACY HOURS p.50 use more exciting verbs in their daily writing XMAS BREAK Spring Term We Date ek Aims 1 STORIES FROM OTHER CULTURES to be able to read stories from other cultures, looking for differences between our world 4 JAN (* 6 JAN BANK HOLIDAY) Possible Teaching Activities Identify settings in stories find phrases in the text which give ideas about characters compare characters from different stories Outcomes Resources All children can: describe the setting of a story compare own life to a character's life use texts to support own ideas about characters LWF 3 2 11 JAN and the world of the characters brainstorm solutions to problems that story characters faced give reasons why one likes or dislikes the story STORIES FROM OTHER CULTURES to be able to read stories from other cultures, looking for differences between our world and the world of the characters Focus on speech verbs make a class list of the verbs to replace “said” writing own continuation of the story discuss how the setting and atmosphere affected characters' actions research information about South Africa All children can: say how e texts and events in the story make them feel find at least 3 ways the setting affected the characters list similarities and differences Some children can: 3 18 JAN STORIES FROM OTHER CULTURES 4 25 JAN 1 FEB 6 8 FEB to be able to scan information texts to find key words to be able to skim information texts to see how useful they are Make questions to ask the character role-play read about the author write two paragraphs about the author Predict contents of chapters from chapter titles identify topic sentences change statements into questions search the Internet for information make notes suggest solutions to problems based on what they have read about the character All children can: take part in a role-play based on a text state three facts about the author use paragraphs to structure own writing Some children can: NOTES AND INFORMATION 5 to identify descriptive and expressive language devise interview questions to ask a character to be able to take a role from the story read LWF 3 LWF 3 describe reasons why authors write All children can: prepare for factual research locate key words and phrases mark extracts by annotating make short notes collect information from a variety of sources LWNF 4 100 LH CTD. CTD. HALF-TERM BREAK 7 22 FEB STORIES WHICH RAISE ISSUES 8 29 FEB to be able to identify the issues and dilemmas a character in the story is facing STORIES WHICH RAISE ISSUES - to be able to identify the issues and dilemmas a character in the story is facing 9 7 MARCH STORIES WHICH RAISE ISSUES Summarise story issues identify the main character's dilemmas write own ending of the story write notes to retell the story punctuate direct speech identify compound words All children can: retell parts of the story using notes predict a plausible ending to the story discuss and compare different endings to the story summarise a story and identify key structural points LWF 4 Delete words in sentences to make notes watch a video clip and discuss how music and images contribute to stories role play characters' conversation discuss and list important issues relating to this particular dilemma All children can: identify key issues faced by a character identify the views of other characters LWF 4 Some children can: identify and explain in own words how music, images and words enhance a story All children can: Make notes about character's feelings identify how characters are feelings from their investigate shades of meaning in adjectives LWF 4 10 14 MARCH -to be able to identify different viewpoints in stories STORIES WHICH RAISE ISSUES - to be able to write a story based around a dilemma and adverbs write a letter to the main character from another character's point of view actions in the text use paragraphs in own writing Some children can: - suggest a suitable resolution for a dilemma Discuss ideas for a story based around a dilemma discuss good features of a story use speech marks in dialogues plan own story write and edit own story All children can: plan their stories effectively (with support) use paragraphs in writing develop characters in an interesting way (with support) resolve the main character's problem in own story Some children can: make changes to improve own writing LWF 4 Outcomes Resources EASTER BREAK Summer Term We Date ek Aims 1 POETRY 4 APRIL 2 11 APRIL Possible Teaching Activities to explore a range of poetic styles to understand how word endings change the classification and use of a word DICUSSION TEXTS to be able to read discussions and know how they are look at different types of poems, rhymes, rhythms compare poems categorising words by endings write limericks make nonsense words All children can: understand and identify the terms verse, chorus, couplet, stanza, rhyme, rhythm, alliteration Read and compare examples of arguments and discussions summarise a sentence or a paragraph All children can: explain how arguments are presented sequence points write own poem, with support 100 LH POETRY ANTHOLOGIES LWNF 7 structured assemble and sequence points in order to present a point of view summarise 3 18 APRIL DISCUSSION TEXTS - to be able to write a discussion using what I know about structure Use writing frames to back up points present a point of view in writing summarise key ideas in writing All children can: make a presentation use arguments clearly write a discussion 4 25 APRIL PLAYS discuss play features discuss scenes being built up apply adverbs to describe mood and volume discuss stage directions role play turn narratives into plays All children can: use adverbs to tell a character how to act choose suitable verbs to use stage directions identify the features of a playscript Some children can: continue writing a scene from a playscript using the correct layout LWF 5 Draw a portrait of a character to show their characteristics collectively improve stage directions write cast descriptions using adjectives practise improvising dialogue All children can: plan a play with scenes, supported write a cast list include stage directions in own script LWF 5 5 (* 2-3 MAY BANK HOLIDAY) to be able to read and perform playscripts use adverbs to give more information about actions PLAYS 4 MAY to be able to write a play (list the characters, describe how scenes start and finish, set out dialogues) Some children can: write informatively about characters when making a cast list 6 9 MAY PLAYS to perform own playscript and comment on own performance type and lay out playscript and amend text features watch a video of play performances and evaluate their success improvise how a character might speak following agreed rules All children can: write an ending for own playscript set out own playscript correctly using a wordprocessing package work in a group to rehearse and perform LWF 5 Some children can: comment how effects are achieved 7 16 MAY 8 23-25 MAY (*26-27 BANK HOLIDAY) 9 30 MAY EXPLANATION TEXTS - to identify how and why paragraphs are used to organise and sequence information PERSUASIVE WRITING Identify the purpose and audience of texts sequence chapter titles Investigate how style and vocabulary are All children can: read explanation texts to find out about structure and language write an explanation text explain a process clearly Some children can: - use time and cause and effect connectives independently LWNF 5 All children can: LWNF 7 CTD. - identify ad features and create one's own 10 6 JUNE PERSUASIVE WRITING - identify ad features and create one's own used in persuasive texts evaluate advertisements Design an advertisement talk about features of persuasive texts understand some of the techniques used in ads to persuade people All children can: use a range of presentational skills make their own ad LWNF 7 Some children can: use information to intrigue, tempt or persuade the customer 11 13 JUNE EXPLORING FORM 12 20 JUNE express own likes and dislikes about a poem to be able to work as part of the group and organise different roles so that everyone is involved EXPLORING FORM to be able to present own poem, using ICT, drama, sound and music, so that the audience enjoys and understands it read and compare haikus and cinquains explore alliteration focus on images evoked by poems discuss music, speech and dance that could be used to perform a poem All children can: identify the features of haikus and cinquains respond to a poem using art talk about the structure of simple poems take part in an effective presentation of a poem LWF 7 Some children can: structure a conversation poem investigate adding suffixes to root words write own haiku discuss how particular poems can be presented All children can: write a haiku with a correct number of syllables in each of the three lines write a poem based on a model Some children can: make positive comments to give further ideas to others SUMMER HOLIDAY LWF 7