here

CHAPTER SUMMARY – CHAPTER 14
Why Look at Individual Behavior?
Explain why the concept of an organization an iceberg is important to understanding organizational behavior.
Describe the focus and goals of organizational behavior.
Define the six important employee behaviors that managers want to explain, predict, and influence.
The idea of an iceberg reflects the fact that there are hidden aspects that affect how employees behave at work. (See Exhibit 14-1.)
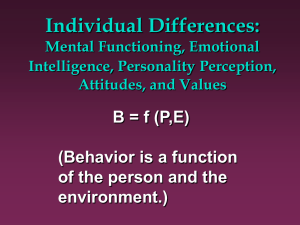
Organizational behavior focuses on two areas: individual behavior and group behavior. The goals of OB are to explain, predict, and influence employee behavior.
The six employee behaviors include: employee productivity – a performance measure of both efficiency and effectiveness; absenteeism – the failure to report to work; turnover – voluntary and involuntary permanent withdrawal from an organization; organizational citizenship behavior – discretionary behavior that’s not part of an employee’s formal job requirements; job satisfaction – an individual’s attitude towards his or her job; and workplace misbehavior – any intentional employee behavior that has negative consequences for the organization or individuals in the organization.
Attitudes
Describe the three components of an attitude.
Discuss the three job-related attitudes.
Describe the impact job satisfaction has on employee behavior.
Explain how individuals reconcile inconsistencies between attitudes and behavior.
Attitudes are evaluative statements concerning people, objects, or events. The three components of an attitude include the cognitive (beliefs, opinions, knowledge or information), the affective (the emotional or feeling part), and the behavioral (an intention to behave in a certain way).
Job satisfaction is an important attitude that can affect productivity (correlation is fairly strong); absenteeism (satisfied employees typically have lower levels); turnover
(satisfied have lower levels); customer satisfaction (satisfied employees increase customer satisfaction and loyalty); and workplace misbehavior (dissatisfied employee will respond somehow).
Individuals reconcile inconsistencies between attitudes and behaviors aligning their attitudes and behaviors so they appear rational and consistent or when there is an inconsistency by taking steps to make it consistent.
Personality
Contrast the MBTI and the big-five model of personality.
Describe the five personality traits that have proved to be the most powerful in explaining individual behavior in organizations.
Explain how emotions and emotional intelligence impact behavior.
The MBTI is a popular approach to classifying personality traits. It looks at social interaction (extrovert or introvert), preference for gathering data (sensing or intuitive), preference for decision making (feeling or thinking), and style of making decisions
(perceptive or judgmental). The Big Five model looks are five basic personality dimensions (extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness to experience) that underlie all others and encompass most of the signification variation in human personality.
The five personality traits that have proved to be the most powerful in explaining individual behavior in organizations include locus of control, Machiavellianism, selfesteem, self-monitoring, and risk-taking.
Emotions and emotional intelligence impact behavior because emotions, especially how we respond emotionally and how we deal with our emotions, can be functions of our personality.
Perception
Explain how an understanding of perception can help managers.
Describe the key elements of attribution theory.
Discuss how the fundamental attribution error and self-serving bias can distort attributions.
Name three shortcuts used in judging others.
Perception is a process by which individuals give meaning to their environment and managers need to understand how perception explains, predicts, and influences behavior.
The key elements of attribution theory (see Exhibit 14-6) are observation of behavior, interpretation of behavior (distinctiveness, consensus, consistency), and attribution of cause (external or internal).
The fundamental attribution error is the tendency to underestimate the influence of external factors and overestimate the influence of internal or personal factors. Selfserving bias describes how individuals attribute their own successes to internal factors while putting the blame for personal failure on external factors.
Three shortcuts used in judging others include assumed similarity (“like me” effect), stereotyping (judging someone on the basis of a group to which he or she belongs), and halo effect (letting a single characteristic form our general impression).
Learning
Explain how operant conditioning helps managers understand, predict, and influence behavior.
Describe the implications of social learning theory for managing people at work.
Discuss how managers can shape behavior.
Operant conditioning says that behavior is a function of its consequences and it helps managers understand, predict, and influence behavior.
Social learning theory says that people learn through observation and direct experience.
Managers can shape behavior by using positive reinforcement (administering something positive to get desired behavior), negative reinforcement (withdrawing something unpleasant to get desired behavior), punishment (penalizing undesirable behavior to eliminate it), and extinction (ignoring behavior to eliminate it).
Contemporary OB Issues
Describe the challenges managers face in managing Gen Y workers.
Explain what managers can do to deal with workplace misbehavior.
Managing Gen Y workers presents some unique challenges especially when it comes to appearance, technology, and management style. (See Exhibit 14-7.)
To manage workplace misbehavior, managers need to recognize that it exists and then try to prevent it. It can also be important to monitor employee attitudes because negative behavior can show up there as well.