Calcium and Integrin Binding protein 1a mediates protein kinase D2
advertisement

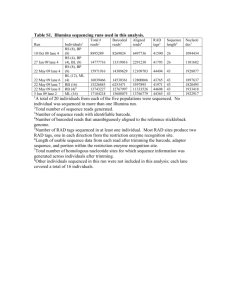
Supplementary Figure S1. Sequence analysis of CIB1a clone. cDNA sequence alignment of CIB1a (marked in black) with CIB1 (marked in green). Sequence analysis and alignment were done by MacMolly®Tetra, Version 3.9, 1999 (Soft Gene GmbH). Supplementary Figure S2. (A) Phospho-Serine118-specific antibody characterization by immunoblotting. Recombinant GST-CIB1a-WT was incubated with GFT-PKD2-WT or GFP-PKD2-DA or GFP-PKD2-3SE bound on Protein A Sepharose in kinase assay buffer with cold ATP. Phosphorylation of the recombinant GST-CIB1a was assessed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-Serine 118 (p-CIB1a). GFP-PKD2 mutants were isolated from HEK293-T cells incubated with or without PMA (400nM). Equal levels of proteins used in reactions were assessed by immunoblotting against anti-EGFP (for GFP-tagged PKD2), anti-CIB (for GST-CIB1a-WT). (B) Endogenous CIB1a is getting phosphorylated in response to PMA in a PKD2-dependent manner. PKD2 was silenced in Panc1 cells by shRNA directed against PKD2 NM_016457.x-294s1c1(sh13D5); (Sigma-Aldrich, NM_016457.x-1720s1c1(sh13D4); NM_016457.x-1767s1c1(sh13D6); NM_016457.x- 1335s1c1 (sh13D7)). Kinase knock-down was verified by Western blotting with anti-PKD2. CIB1a was immunoprecipitated from Panc1 cells (1mg of cell lysate) infected with control shRNA and shPKD2, stimulated with or without PMA (400nm), and IP was verified with anti-CIB (CIB1a). Phosphorylation of CIB1a in response to PMA was detected by immunoblotting with anti-phosphoSer118 (p-CIB1a). Graph represent quantification of integrated density done by ImageJ. Results shown represent the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (* p<0.05; **p<0.001;***p<0.0001). Supplementary Figure S3. (A) Phosphorylation of CIB1a at Serine 118 decreases its binding to PKD2. GFP (lane 1), GFP-CIB1a-WT (lane 2), GFP-CIB1a-S118A (lane 3) or GFP-CIB1a-S118E (lane 4) were co-expressed with Flag (lane 1) or Flag-PKD2-WT (lane 2, 3 1 and 4) in HEK293-T cells. The proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP (top left) or anti-Flag (bottom left) followed by anti-Flag or anti-CIB Western blotting, respectively. To verify that each tagged protein was expressed WCL were tested with anti-CIB (for GFP tagged CIB1a, top right) and anti-Flag, respectively (for Flag tagged PKD2, bottom right). Graphs represent quantification of integrated density done by ImageJ. Results shown represent the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (* p<0.05; **p<0.001;***p<0.0001). Supplementary Figure S4. Expression of phosphomimetic CIB1a mutant partially rescues tumour growth impaired by PKD2 knockdown. (A) HeLa cells were transduced with lenti-viruses expressing scramble control shRNA (Sigma-Aldrich scramble, shc002 (shCon)) and shRNA_PKD2 NM_016457.x-294s1c1(sh13D5); (Sigma-Aldrich, NM_016457.x-1720s1c1(sh13D4); NM_016457.x-1767s1c1(sh13D6); NM_016457.x- 1335s1c1 (sh13D7)). A PKD2 knockdown was probed using a specific anti-PKD2 antibody following selection. Blots were re-probed for Actin used as loading control. (B) Images of tumours developed on CAM. Semi-stable scramble control shRNA (shCon) and shPKD2 expressing HeLa cells were transfected with CIB1a-WT-IRES-GFP, CIB1a-S118A-IRES-GFP or CIB1a-S118E-IRES-GFP and applied in silicon rings on the CAM. Representative images of tumours are shown. (C) Graph represents quantification of the tumour areas within silicon rings. The dashed line indicates the quantified tumour area. Results shown represent the means ± S.E.M. of at least three tumours from three independent experiments (* p<0.05; **p<0.001;***p<0.0001). (D) Aliquots of cells used in the CAM assay were lysed and tested for equal expression of the CIB1a mutants and PKD2 knockdown. Membranes were reprobed with a β-actin antibody. (E) CIB1a does not significantly stimulate DNA synthesis of Hela cells. Hela cells were transfected with EGFP-vector, IRES-CIB1a-WT-GFP, IRES-CIB1aS118A-GFP or IRES-CIB1a-S118E-GFP plasmids and cultivated under normoxic or hypoxic 2 conditions. Subsequently the GFP-positive population was sorted, stained with propidium iodide and subjected to flow cytometric analysis as described in materials and methods. Bars are the means +/- SEM of the three independent experiments (T-test: *p<0.05; **p<0.001) Supplementary Figure S5. CIB1a interacts with FAK, but mutation within CIB1a does not affect significantly its binding capacity to the kinase. GFP-CIB1a-WT (lane 1), GFPCIB1a-S118A (lane 2), GFP-CIB1a-S118E (lane 3) or GFP (line 4) were co-expressed with Myc-FAK (lane 1, 2 and 3) or Myc (lane 4) in HEK293-T cells. The proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP (top left) or anti-Myc (bottom left) followed by anti-Myc or anti-CIB Western blotting, respectively. Proteins expression was verified in WCL by immunoblotting with anti-Myc (for FAK, top right) and anti-GFP, respectively (for CIB1a, bottom right). Graphs represent quantification of integrated density done by ImageJ. Results shown represent the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (* p<0.05; **p<0.001;***p<0.0001). (B) Immunoprecipitate kinase assay using mock- and HEK293-T cells co-transfected with CIB1a mutants and Myc-FAK. Although FAK expression levels are comparable (WB: Myc, for Myc-FAK), the amount of phosphotyrosine is up-regulated on CIB1a overexpression (WB: pY). CIB1a mutations did not further affect FAK activation. CIB1a protein expression was verified in WCL by immunoblotting with anti-CIB. Supplementary Figure S6. CIB1a interacts with PAK1, but mutation within CIB1a does not affect significantly its binding capacity to the kinase. GFP-CIB1a-WT (lane 1), GFPCIB1a-S118A (lane 2), GFP-CIB1a-S118E (lane 3) or GFP (line 4) were co-expressed with Myc-PAK1 (lane 1, 2 and 3) or Myc (lane 4) in HEK293-T cells. The proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP (top left) or anti-Myc (bottom left) followed by anti-Myc or anti-CIB Western blotting, respectively. Protein expression was verified in WCL by immunoblotting with anti-Myc (for PAK1, top right) and anti-GFP, respectively (for CIB1a, 3 bottom right). Graphs represent quantification of integrated density done by ImageJ. Results shown represent the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (* p<0.05; **p<0,001;***p<0, 0001). (B) CIB1a does not regulate PAK1 kinase activity. Immunoprecipitate kinase assay using mock- and HEK293-T cells co-transfected with CIB1a mutants and Myc-PAK1 (upper panel). Myelin basic protein (MPB) was used as a PAK1 substrate. Protein expression was verified in WCL by immunoblotting with anti-CIB (for CIB1a) and anti-Myc (for PAK1). Graphs represent quantification integrated density done by AIDA Image Analyzer. Results shown represent the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (* p<0.05; **p<0.001;***p<0.0001). Supplementary Figure S7. (A) CIB1a stimulates Nur77 transcription, however, there is with no further change in Nur77 promoter activity upon CIB1a phosphorylation by PKD2. HeLa cells were co-transfected with a luciferase reporter plasmid driven by the Nur77 promoter (pNur77-Luc) and CIB1a mutants (WT, S118A or S118E) or PKD2-3SE (positive control). Luciferase activities were determined and normalized based on Renilla luciferase expression and represented as relative light units (RLUs) of firefly luciferase. (B) CIB1a phosphorylation by PKD1 has no effect on hypoxia-induced VEGF-A reporter activity. HeLa cells co-transfected with pGL2-VEGF-luc, pTK-Renilla and wild type (CIB1a-WT), non-phosphorylatable (CIB1a-S118A) or phosphomimetic CIB1a mutants (CIB1a-S118E) were incubated under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 24 h followed by luciferase activity assays. (C) Phosphorylation of CIB1a does not affect FGF2 secretion by epithelial tumour cells. Cancer cells were transfected with wild type (CIB1a-WT), the nonphosphorylatable (CIB1a-S118A), or phosphomimetic CIB1a mutant (CIB1a-S118E), respectively. Cells were subsequently incubated under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 12h as indicated. FGF2 was determined in supernatant of the tumour cells using a specific ELISA. Results are representative for three independent experiments each performed in 4 triplicates. Protein expression was verified in WCL by immunoblotting with anti-CIB (for CIB1a) and anti-GFP (for PKD2). Bars are the means +/- SEM of the three independent experiments (T-test: *p<0.05; **p<0.001) Supplementary Figure S8. (D) Basal level of CIB1a phosphorylation at Ser118 in various tumour cell lines. CIB1a was immunoprecipitated from equal amount of cell lysate (500µg) from the respective cell lines, and IP was verified by anti-CIB1a. Baseline phosphorylation level was tested by immunoblotting with anti-phospho CIB1a-Ser118 antibody. 5