EasternRomanEmpire
advertisement

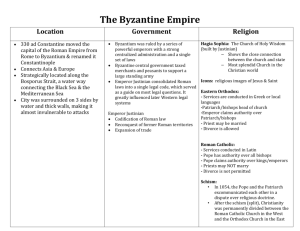
Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine East) Political Organization • • • The capital of the Byzantine empire, Constantinople, was under imperial rule. The imperial court looked over other areas such as the Sansanid and Germanic empires. The Byzantine empire used the theme system, which entitled a military general to the responsibility of military defense and civil affairs of a province. Interaction/Trade Among Other Major Societies • • • • Byzantine was a principal supplier of silk to the Mediterranean basin. Constantinople served as a main clearinghouse for trade in western Eurasia. Merchants of Constantinople maintained direct contact with central Asian merchants. Byzantine also dealt regularly with their muslim counterparts. Technology • • • • Some Romans made maps. They were also fascinated with volcanoes. Public baths were created along with flushing toilets. Sun roofs were built upon theaters and amphitheaters. Education • • • • Constantinople was the educational center of the Byzantine empire. People whom were learning to become government officials learned to read and write Greek. Greek was used for official purposes, a simple form of Greek was commonly spoken by most Byzantines. History and religious poetry were written in Greek too. Culture and Religion • • • • • • • Christianity influenced Byzantine art, music, and architecture. Art – featured pictures of holy people. Music – wrote hymns about Christ and Christianity. Architecture – Built huge cathedrals and churches that were domed. Justinian made Christianity popular in Rome. He was called the sleepless emperor. Chariot races and other events were popular entertainment for people who went to the hippodrome. Social and Gender Structure • • • • • • Free peasants owned small plots of land and served as the backbone of the Byzantine military. They cultivated their land intensively in hopes to improve their family’s fortune. Byzantine also had a wealthy class; they cultivated large amounts of land and watched over peasants. This did not cause the peasants to be slaves but the wealthier land owners bound the peasants to their land and did not allow them to leave without their lord’s permission. Women received apartments and were restricted from male visitors. Women often didn’t participate in banquets when wine was passed around freely because it might compromise a woman’s honor. Justinian • • • • Justinian was the most important early Byzantine emperor. He lavished resources in the imperial capital. But he eventually fell from his want of power and land. Belisarius, a brilliant general, eventually lost the war for the classical Roman Empire. Justinian’s Code • • • Codification of Roman law. Justinian issued the Corpus iuris civilis (Body of the Civil Law). Through Justinian’s code, Roman law influenced civil law codes throughout much of western Europe. Constantinople • • • Built the imperial capital, “Constantinople”. He was the 1st Christian emperor. He also inputted many resources and riches into Constantinople. Monasticism • • Byzantine monasticism grew out of efforts of individuals to lead especially holy lives. Some ascetics abandoned society all together and lived as hermits. External Conflict Islamic conquests • Fights between Christians of eastern and western societies. Strategoi • • They were generals of war. Very highly ranked in society. Icons • • Emperor Leo III put in the policy of iconoclasm, which means the breaking of empires. Iconoclasts eventually quit their efforts after a century of riots. Timeline - Early Byzantine Period Early fourth The Armenians adopt Christianity as their state religion; century they develop their own alphabet in the fifth century. 330 The pro-Christian Roman emperor Constantine I dedicates the city of Constantinople (in Greek "the city of Constantine"), established on the site of the Greek city Byzantium, as the new capital of the Roman Empire. 337 Saint Nina converts the Georgians to Orthodox Christianity. 395 The empire is divided into eastern and western portions under Arkadios and Honorius, the sons of Emperor Theodosius I. 410 Rome is sacked by the Visigoths. 476 Romulus Augustulus, the last Western Roman emperor, is deposed by the German Odoacer. 527 Justinian becomes Eastern Roman emperor. Constantinople covers eight square miles (Manhattan covers twenty-two square miles) with at least 500,000 inhabitants. 53237 Justinian builds the church of Hagia Sophia in Constantinople. 54865 Justinian builds a monastery dedicated to the Virgin on Mount Sinai; in the ninth century it is renamed for Saint Catherine. 639 Muslim armies conquer the southern territories of the Byzantine Empire (Syria, the Holy Land, Egypt, and Jordan). 726 Byzantine Emperor Leo III orders all icons in the Byzantine Empire destroyed. 800 Charlemagne, king of the Franks, is crowned "Emperor of the West" by Pope Leo III in Rome. Ninth century Saint Constantine the Philosopher and Saint Methodios create a writing system for the Slavs; the Cyrillic alphabet will follow.