Kas 6-15E: 1/Patient with diarrhoea
advertisement

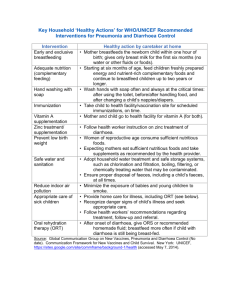
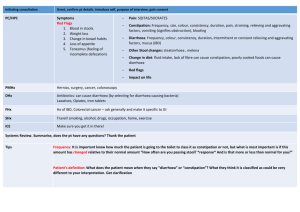
Course 6, case 15 revised 2009 Kas 6-15E: A patient with diarrhoea 50- year-old woman A.B, shopkeeper. She has never been seriously ill. Now she is suffering from watery diarrhoea lasting for 4 days. Family history: mother – hypertension, died at 75 because of stroke father is still alive, 80 years old, he has diabetes since his 62, 1 sister and two children are healthy Personal history: common children´s ailments, she has no chronic disease, she uses only hormonal substitution therapy. No operations, no transfusions, no allergy, social conditions are good. She smokes 5 cigarettes per day. Present illness: She had urethrocystitis with dysuria and fever 2 weeks ago. The practitioner gave her chinolon therapy (norfloxacin).The therapy was finished 5 days ago. The second day after finishing the therapy the diarrhoea started, she has 6-8 watery stools per day, including night, without "belly ache", without vomiting, without fever, there was no mucus or blood in the stool, only the day before today there was small stain of blood on the toilet paper. Epidemiological history: she thinks she made no diet mistake, she eats rational diet, she had no fast food, no eggs, no chicken. No other members of family suffer from such problems. Physical examination: She is conscious, completely oriented, without fever, normosthenic, lowered cutaneous turgor, dry tongue, blood pressure 110/60, pulse 90 beats/min, no arrhythmias, no murmurs, soft abdomen, painless, without resistance, without hepato- and splenomegaly, legs without oedemas. Laboratory findings: blood count – normal, ESR 15/20, osmolarity 305 mosmol/l, K 3.2 mmol/l, Na 130 mmol/l, Cl 95 mmol/l, AST, ALT, GMT, ALP and bilirubin – normal, proteinaemia and albuminaemia – normal, urine – normal. Questions and tasks: 1. What type of diarrhoea is it? 2. What etiology of the diarrhoea do you suppose? 3. Why has she hypokalemia? 4. Evaluate serum osmolality 5. What diagnostic procedures do you suggest? 6. How will you treat the patient? 7. What is the prognosis of this illness? 8. Infectious enteritis and colitis